.NET Core Application: Unit Testing Using MStest
Introduction
In this article, we are going to learn how to perform unit tests in a .NET Core application using MStest as test library and C# as the programming language. We will be creating a sample application to test if a given integer is even or not and then, we will be running our unit tests on that.
Prerequisites
- Install .NET Core 2.0.0 or above SDK from here.
- Download and install Visual Studio Code from here.
- Familiarize yourself with Visual Studio Code from here.
Create source project
We will be creating a source project from the terminal window in Visual Studio Code. Open VS code and navigate to view >> Integrated Terminal.
This will open the terminal window as shown in the image below.
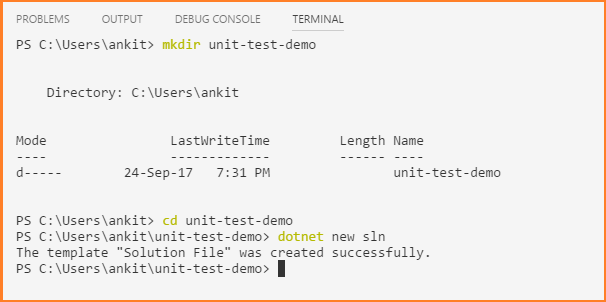
Type the following commands in the terminal window. It will create a directory unit-test-demo and a new solution file for class library and the test project inside that directory.
- mkdir unit-test-demo
- cd unit-test-demo
- dotnet new sln
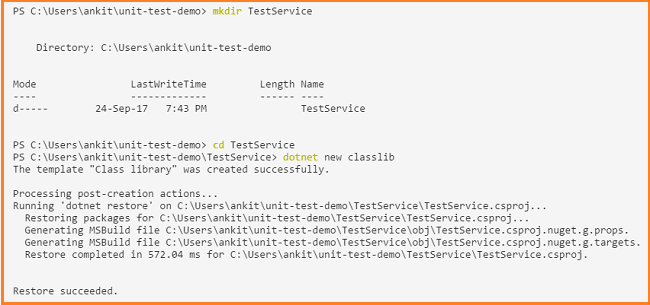
Navigate to *unit-test-demo *directory and run these set of commands. It will create our source project TestService.
- mkdir TestService
- cd TestService
- dotnet new classlib
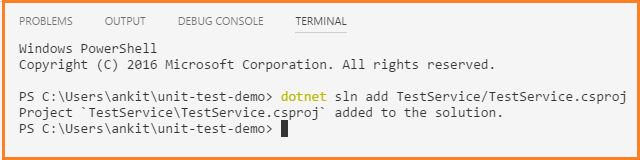
Navigate back to a *unit-test-demo *directory and run the following command. This will add the class library project to the solution.
dotnet sln add TestService/TestService.csproj
We can see the success message on the terminal.
Now, our source project is ready; we will proceed to create our test project.
Create test project
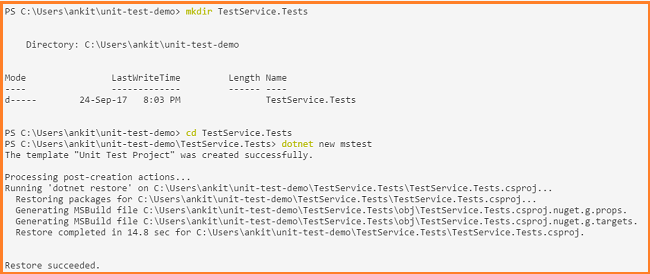
Navigate to a *unit-test-demo *directory and run the following commands.
- mkdir TestService.Tests
- cd TestService.Tests
- dotnet new mstest
This will create a TestService.Tests directory inside a *unit-test-demo *directory and then create a test project that uses MStest as the test library inside TestService.Tests directory. It will also add MSTest SDK, MSTest test framework and MSTest runner in *TestService.Tests.csproj *file. But the test project requires other packages to create and run unit tests. So we will add TestService class library as another dependency to the project.
Navigate to TestService.Tests directory and run the following command,
dotnet add reference ../TestService/TestService.csproj
We can see the following success message in the terminal
Now, open the unit-test-demo directory using VS code and open TestService.Tests.csproj file. Here, we can see all the package references.
< Project Sdk="Microsoft.NET.Sdk">
< PropertyGroup >
< TargetFramework >netcoreapp2.0</ TargetFramework >
< IsPackable >false</ IsPackable >
</ PropertyGroup >
< ItemGroup >
< PackageReference Include="Microsoft.NET.Test.Sdk" Version="15.3.0-preview-20170628-02" />
< PackageReference Include="MSTest.TestAdapter" Version="1.1.18" />
< PackageReference Include="MSTest.TestFramework" Version="1.1.18" /> </ItemGroup>
< ItemGroup >
< ProjectReference Include="..\TestService\TestService.csproj" /> </ItemGroup>
</ Project >
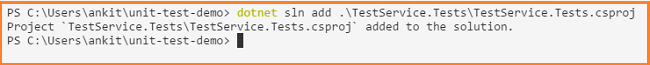
Now, to add a test project to the solution, we will run the following command from the unit-test-demo directory.
dotnet sln add .\TestService.Tests\TestService.Tests.csproj
We can observe that the test project has been added successfully to the solution.
Now, we have successfully created our test project and added it to the solution. Let's proceed to create our first test.
Creating the test
Rename the Class1.cs file in TestService project to *TestService.cs.*Open *TestService.cs *file and put following code into it.
using System;
namespace Test.Services {
public class TestService {
public bool IsEven(int value) {
if (value % 2 == 0) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
}
}
Rename UnitTest1.cs in the TestService.Tests project to IsEvenTest.cs and put the following code in it.
using Microsoft.VisualStudio.TestTools.UnitTesting;
using Test.Services;
namespace Test.UnitTests.Services {
[TestClass]
public class TestService_IsEven {
private readonly TestService _testService;
public TestService_IsEven() {
_testService = new TestService();
}
[TestMethod]
public void ReturnIsEven() {
var result = _testService.IsEven(2);
Assert.IsTrue(result, "2 is even" );
}
}
}
The [TestClass] attribute denotes a class that contains unit tests and the [TestMethod] attribute indicates a method is a test method.
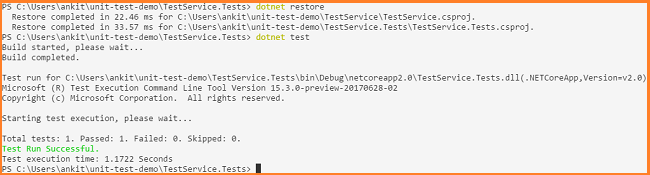
We have created a sample test. To execute it, navigate to TestService.Tests directory and execute the following commands:
- dotnet restore
- dotnet test
"dotnet restore" will restore the packages of both the projects and "dotnet test" will build both projects and run all the configured test. As we can see, our configured test has been passed successfully.
We can observe that we have added only one test case (i.e. 2) inside [TestMethod] attribute.If we need to add multiple test cases, then [TestMethod] attribute is not a viable option as we need to write multiple tests having [TestMethod] attribute. So, we will use [DataTestMethod] attribute of MsTest that will enable us to write a suite of similar tests.A [DataTestMethod] attribute represents a suite of tests that execute the same code but have different input arguments. We can use the [DataRow] attribute to specify values for those inputs.
So, we will now write two separate methods in *IsEvenTest.cs *file, one to test for even numbers and another to test for odd numbers:
[DataTestMethod]
[DataRow(4)]
[DataRow(6)]
[DataRow(8)]
public void ReturnIsEven(int value) {
var result = _testService.IsEven(value);
Assert.IsTrue(result, $ "{value} is Even" );
}
[DataTestMethod]
[DataRow(5)]
[DataRow(7)]
[DataRow(9)]
public void ReturnIsOdd(int value) {
var result = _testService.IsEven(value);
Assert.IsFalse(result, $ "{value} is Odd" );
}
Run dotnet test again and we can see that all the 6 test case (3 for even and 3 for odd) has been passed successfully.
Conclusion
We have learned how to create and execute a sample unit test project using MStest in .NET Core with the help of Visual Studio Code.
Source Code
Download the source code from here
Reference
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-gb/dotnet/core/testing/unit-testing-with-mstest