ASP.NET Core 2.0: CRUD Operation With Razor Pages
Introduction
In this article, we are going to create a web application in ASP.NET Core using Razor pages and ADO.NET. We will create a sample Employees Record Management System with the help of Visual Studio 2017 and SQL Server 2008 or above.
Prerequisites
Install .NET Core 2.0.0 or above SDK from here.
Install Visual Studio 2017 Community Edition (Version 15.3.5 or above) from here.
Now, we are ready to proceed with the creation of our web application.
Creating Table and Stored Procedures
We will be using a DB table to store all the records of employees. Open SQL Server and use the following script to create *tblEmployee *table.
Create table tblEmployee(
EmployeeId int IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
Name varchar(20) NULL,
City varchar(20) NULL,
Department varchar(20) NULL,
Gender varchar(6) NULL
)
Now, we will create stored procedures to add, delete, update, and get employee data.
To insert an Employee Record
Create procedure spAddEmployee
(
@Name VARCHAR(20),
@City VARCHAR(20),
@Department VARCHAR(20),
@Gender VARCHAR(6)
)
as
Begin
Insert into tblEmployee (Name,City,Department, Gender)
Values (@Name,@City,@Department, @Gender)
End
To update an Employee Record
Create procedure spUpdateEmployee
(
@EmpId INTEGER ,
@Name VARCHAR(20),
@City VARCHAR(20),
@Department VARCHAR(20),
@Gender VARCHAR(6)
)
as
begin
Update tblEmployee
set Name=@Name,
City=@City,
Department=@Department,
Gender=@Gender
where EmployeeId=@EmpId
End
To delete an Employee Record
Create procedure spDeleteEmployee
(
@EmpId int
)
as
begin
Delete from tblEmployee where EmployeeId=@EmpId
End
To view all Employee Records
Create procedure spGetAllEmployees
as
Begin
Select *
from tblEmployee
End
Now, our Database part is completed. So, we will move on to create the web application with Visual Studio 2017.
Create Razor Page Web Application
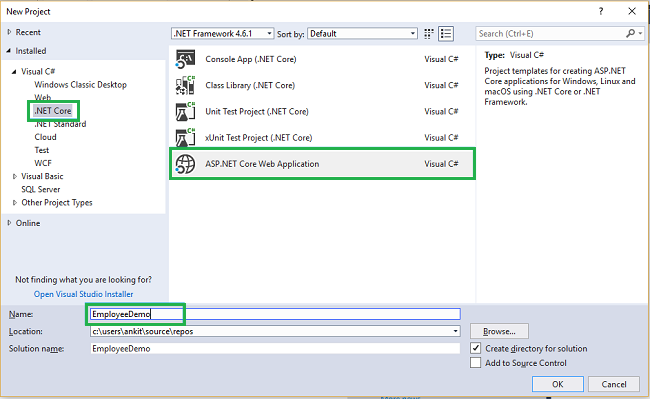
Open Visual Studio and select File >> New >> Project.
After selecting the project, a new dialog will open. Select .NET Core inside Visual C# menu from the left panel.
Then, select “ASP.NET Core Web Application” from available project types. Put the name of the project as EmployeeDemo and press OK. Refer to this image.
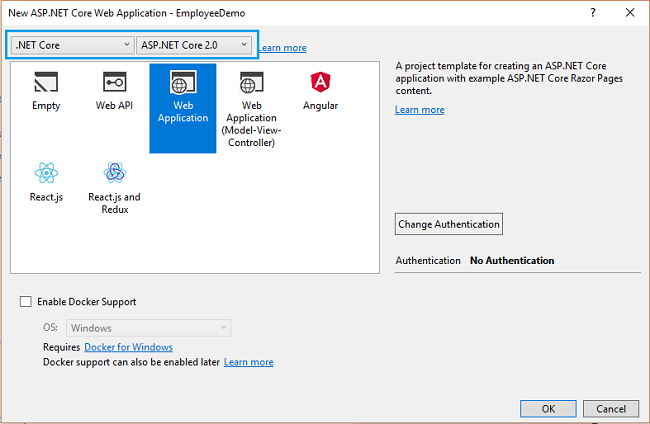
After clicking OK, a new dialog will open asking to select the project template. You can observe two drop-down menus at the top left of the template window. Select “.NET Core” and “ASP.NET Core 2.0” from these dropdowns. Then, select “Web application” template.
Now, our project will open. You can see the project files in Solution Explorer. Note that there are no Model, View, and Controller folders by default but we do have a Pages folder which contains all the default Razor pages. We will be creating our own Razor pages inside this folder.
Adding A Model to the Application
We will add a folder with name Models inside our project. Right-click Project and select Add >> New Folder. A new folder will be created inside the project. Rename it as Models.
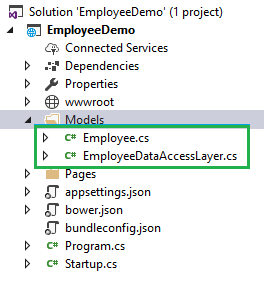
Now, we will be adding our class files to Models folder. Right click on Models folder and select Add >> Class. Name your class Employee.cs. This class will contain our Employee model properties. Add one more class file to Models folder. Name it as EmployeeDataAccessLayer.cs . This class will contain our Database related operations.
Now, the Models folders have the following structure.
Open Employee.cs and put the following code in it. Since we are adding the required validators to the fields of Employee class, so we need to use System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations at the top.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
namespace EmployeeDemo.Models
{
public class Employee
{
public int ID { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Gender { get; set; }
[Required]
public string Department { get; set; }
[Required]
public string City { get; set; }
}
}
Open EmployeeDataAccessLayer.cs and put the following code to handle database operations. Make sure to put your connection string.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Data;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
namespace EmployeeDemo.Models
{
public class EmployeeDataAccessLayer
{
string connectionString = "Your Connection string here";
//To View all employees details
public IEnumerable<Employee> GetAllEmployees()
{
List<Employee> lstemployee = new List<Employee>();
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("spGetAllEmployees", con);
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
con.Open();
SqlDataReader rdr = cmd.ExecuteReader();
while (rdr.Read())
{
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.ID = Convert.ToInt32(rdr["EmployeeID"]);
employee.Name = rdr["Name"].ToString();
employee.Gender = rdr["Gender"].ToString();
employee.Department = rdr["Department"].ToString();
employee.City = rdr["City"].ToString();
lstemployee.Add(employee);
}
con.Close();
}
return lstemployee;
}
//To Add new employee record
public void AddEmployee(Employee employee)
{
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("spAddEmployee", con);
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name", employee.Name);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Gender", employee.Gender);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Department", employee.Department);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@City", employee.City);
con.Open();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
con.Close();
}
}
//To Update the records of a particluar employee
public void UpdateEmployee(Employee employee)
{
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("spUpdateEmployee", con);
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@EmpId", employee.ID);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Name", employee.Name);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Gender", employee.Gender);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Department", employee.Department);
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@City", employee.City);
con.Open();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
con.Close();
}
}
//Get the details of a particular employee
public Employee GetEmployeeData(int? id)
{
Employee employee = new Employee();
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
string sqlQuery = "SELECT * FROM tblEmployee WHERE EmployeeID= " + id;
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand(sqlQuery, con);
con.Open();
SqlDataReader rdr = cmd.ExecuteReader();
while (rdr.Read())
{
employee.ID = Convert.ToInt32(rdr["EmployeeID"]);
employee.Name = rdr["Name"].ToString();
employee.Gender = rdr["Gender"].ToString();
employee.Department = rdr["Department"].ToString();
employee.City = rdr["City"].ToString();
}
}
return employee;
}
//To Delete the record on a particular employee
public void DeleteEmployee(int? id)
{
using (SqlConnection con = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
SqlCommand cmd = new SqlCommand("spDeleteEmployee", con);
cmd.CommandType = CommandType.StoredProcedure;
cmd.Parameters.AddWithValue("@EmpId", id);
con.Open();
cmd.ExecuteNonQuery();
con.Close();
}
}
}
}
Now, we will proceed to create our Razor pages.
Adding Razor Pages
First of all, we will be creating a page to create Employee records. Right-click on Pages folder and select Add >> New item. Refer to the image below.
A new dialog box will open. Select ASP.NET Core from the left panel, then select “Razor Pages” from templates panel, and put the name as CreateEmployee.cshtml. Press OK.
Now, you can observe that our Razor page has been added to Pages folder. You can also observe that the Razor page has code behind file with extension .cshtml.cs also, just the same as web forms (aspx.cs). The code behind page will be used to handle business logic.
Similarly, we will add four more Razor pages to Pages folder, DeleteEmployee.cshtml, EditEmployee.cshtml, EmployeeDetails.cshtml and EmployeeIndex.cshtml to perform the CRUD operations.
Now, our Pages folder will look like this showing all the five newly created Razor pages.

Now, the pages have been created, so we will put codes in them.
Create Employee
In this Razor page, we will be creating a new employee record.
Open CreateEmployee.cshtml and put the following code in it.
@page
@model CreateEmployeeModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Create";
}
<h2>Create Employee Record</h2>
<hr />
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">
<form method="post">
<div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="employee.Name" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="employee.Name" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="employee.Name" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="employee.Gender" class="control-label"></label>
<select asp-for="employee.Gender" class="form-control">
<option value="">-- Select Gender --</option>
<option value="Male">Male</option>
<option value="Female">Female</option>
</select>
<span asp-validation-for="employee.Gender" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="employee.Department" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="employee.Department" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="employee.Department" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="employee.City" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="employee.City" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="employee.City" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="submit" value="Create" class="btn btn-default" />
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<a asp-page="EmployeeIndex">Back to List</a>
</div>
@section Scripts {
@{await Html.RenderPartialAsync("_ValidationScriptsPartial");}
}
Open CreateEmployee.cshtml.cs and put the following code in it.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using EmployeeDemo.Models;
namespace EmployeeDemo.Pages
{
public class CreateEmployeeModel : PageModel
{
EmployeeDataAccessLayer objemployee = new EmployeeDataAccessLayer();
[BindProperty]
public Employee employee { get; set; }
public ActionResult OnPost()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return Page();
}
objemployee.AddEmployee(employee);
return RedirectToPage("./EmployeeIndex");
}
}
}
You can observe that we are using [BindProperty] attribute on employee object we have created in CreateEmployee.cshtml.cs file. This will help to capture the data posted by the form in our object. If we remove [BindProperty] attribute, then the employee object will be null as it won’t capture any data from post request.
Employee index
In this Razor page, we will be displaying all the employee records available in the database. Additionally, we will be providing action methods Edit, Delete, and View on each record.
Open EmployeeIndex.cshtml and put the following code in it
@page
@model EmployeeIndexModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Index";
}
<h2>Index</h2>
<p>
<a asp-page="CreateEmployee">Create New</a>
</p>
<table class="table">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.employee[0].ID)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.employee[0].Name)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.employee[0].Gender)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.employee[0].Department)
</th>
<th>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.employee[0].City)
</th>
<th></th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var item in Model.employee)
{
<tr>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.ID)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Name)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Gender)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.Department)
</td>
<td>
@Html.DisplayFor(modelItem => item.City)
</td>
<td>
<a asp-page="./EditEmployee" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Edit</a> |
<a asp-page="./EmployeeDetails" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Details</a> |
<a asp-page="./DeleteEmployee" asp-route-id="@item.ID">Delete</a>
</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
Open EmployeeIndex.cshtml.cs and put the following code in it.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using EmployeeDemo.Models;
namespace EmployeeDemo.Pages
{
public class EmployeeIndexModel : PageModel
{
EmployeeDataAccessLayer objemployee = new EmployeeDataAccessLayer();
public List<Employee> employee { get; set; }
public void OnGet()
{
employee = objemployee.GetAllEmployees().ToList();
}
}
}
Employee Details
In this Razor page, we will be displaying the details of a particular employee. This page can be invoked by clicking Details action method on EmployeeIndex page.
Open EmployeeDetails.cshtml and put the following code in it.
@page
@model EmployeeDetailsModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Details";
}
<div>
<h4>Employee</h4>
<hr />
<dl class="dl-horizontal">
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.employee.Name)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.employee.Name)
</dd>
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.employee.Gender)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.employee.Gender)
</dd>
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.employee.Department)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.employee.Department)
</dd>
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.employee.City)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.employee.City)
</dd>
</dl>
</div>
<div>
<a asp-page="./EditEmployee" asp-route-id="@Model.employee.ID">Edit</a> |
<a asp-page="./EmployeeIndex">Back to List</a>
</div>
Open EmployeeDetails.cshtml.cs and put the following code in it.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using EmployeeDemo.Models;
namespace EmployeeDemo.Pages
{
public class EmployeeDetailsModel : PageModel
{
EmployeeDataAccessLayer objemployee = new EmployeeDataAccessLayer();
public Employee employee { get; set; }
public ActionResult OnGet(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
employee = objemployee.GetEmployeeData(id);
if (employee == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Page();
}
}
}
Edit Employee
This Razor page will enable us to edit the record of an existing employee. This page can be invoked by clicking Edit action method on EmployeeIndex page.
Open EditEmployee.cshtml and put the following code in it.
@page
@model EditEmployeeModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Edit";
}
<h2>Edit</h2>
<h4>Employee</h4>
<hr />
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-4">
<form method="post">
<div asp-validation-summary="ModelOnly" class="text-danger"></div>
<input type="hidden" asp-for="employee.ID" />
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="employee.Name" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="employee.Name" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="employee.Name" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="employee.Gender" class="control-label"></label>
<select asp-for="employee.Gender" class="form-control">
<option value="">-- Select Gender --</option>
<option value="Male">Male</option>
<option value="Female">Female</option>
</select>
<span asp-validation-for="employee.Gender" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="employee.Department" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="employee.Department" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="employee.Department" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="employee.City" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="employee.City" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="employee.City" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<input type="submit" value="Save" class="btn btn-default" />
</div>
</form>
</div>
</div>
<div>
<a asp-page="./EmployeeIndex">Back to List</a>
</div>
@section Scripts {
@{await Html.RenderPartialAsync("_ValidationScriptsPartial");}
}
Open EditEmployee.cshtml.cs and put the following code in it.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using EmployeeDemo.Models;
namespace EmployeeDemo.Pages
{
public class EditEmployeeModel : PageModel
{
EmployeeDataAccessLayer objemployee = new EmployeeDataAccessLayer();
[BindProperty]
public Employee employee { get; set; }
public ActionResult OnGet(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
employee = objemployee.GetEmployeeData(id);
if (employee == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Page();
}
public ActionResult OnPost()
{
if (!ModelState.IsValid)
{
return Page();
}
objemployee.UpdateEmployee(employee);
return RedirectToPage("./EmployeeIndex");
}
}
}
Delete Employee
This Razor page will enable us to delete the record of an existing employee. This page can be invoked by clicking Delete action method on EmployeeIndex page
Open DeleteEmployee.cshtml and put the following code in it
@page
@model DeleteEmployeeModel
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Delete";
}
<h2>Delete</h2>
<h3>Are you sure you want to delete this?</h3>
<div>
<h4>Employee</h4>
<hr />
<dl class="dl-horizontal">
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.employee.Name)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.employee.Name)
</dd>
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.employee.Gender)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.employee.Gender)
</dd>
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.employee.Department)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.employee.Department)
</dd>
<dt>
@Html.DisplayNameFor(model => model.employee.City)
</dt>
<dd>
@Html.DisplayFor(model => model.employee.City)
</dd>
</dl>
<form method="post">
<input type="hidden" asp-for="employee.ID" />
<input type="submit" value="Delete" class="btn btn-default" /> |
<a asp-page="./EmployeeIndex">Back to List</a>
</form>
</div>
Open DeleteEmployee.cshtml.cs and put the following code in it.
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
using EmployeeDemo.Models;
namespace EmployeeDemo.Pages
{
public class DeleteEmployeeModel : PageModel
{
EmployeeDataAccessLayer objemployee = new EmployeeDataAccessLayer();
public Employee employee { get; set; }
public ActionResult OnGet(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
employee = objemployee.GetEmployeeData(id);
if (employee == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
return Page();
}
public ActionResult OnPost(int? id)
{
if (id == null)
{
return NotFound();
}
objemployee.DeleteEmployee(id);
return RedirectToPage("./EmployeeIndex");
}
}
}
Note that we have two methods, OnGet and OnPost in DeleteEmployee.cshtml.cs. When we click Delete on the EmployeeIndex page, it will send a Get request and return a View of the employee using OnGet method. When we click Delete on this page, it will send a Post request to delete the record which is handled by the OnPost method. Performing a delete operation in response to a Get request (or for that matter, performing an edit operation, create operation, or any other operation that changes data) opens up a security hole. Hence we have two separate methods.
And that’s it. We have created our first ASP.NET Core application using Razor pages. Now, we will proceed to perform CRUD operations.
Execution Demo
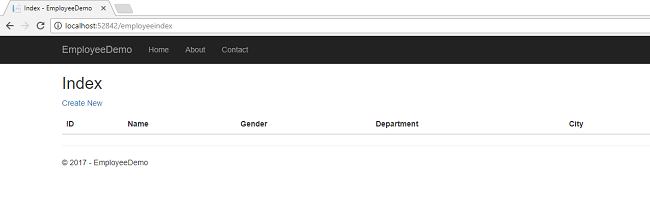
Launch the application and to access any page, put the Razor page name in the URL. Open EmployeeIndex page as http://localhost:xxxx/EmployeeIndex
You can see the page as shown below.
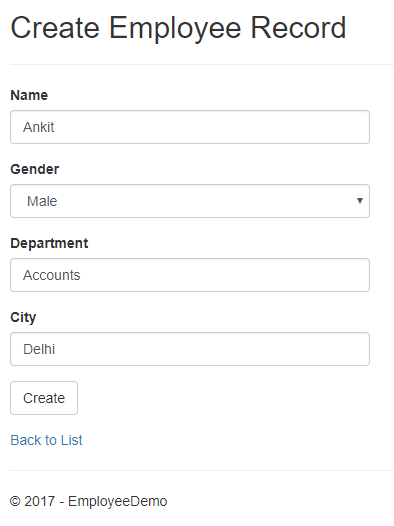
Click on CreateNew to create a new Employee record. Add a new Employee record as shown in the image below.
If we miss the data in any field while creating employee record, we will get a required field validation error message.
After inserting the data in all the fields, click "Create" button. The new employee record will be created and you will be redirected to the EmployeeIndex page, having records of all the employees. Here, we can also see action methods Edit, Details and Delete.
If we want to edit an existing employee record, then click Edit action link. It will open EditEmployee page as below where we can change the employee data.
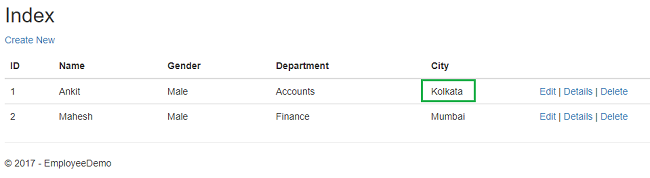
Here, we have changed the city of an employee named Ankit from Delhi to Kolkata. Click "Save" to return to the EmployeeIndex page to see the updated changes as highlighted in the image below.
If we miss any fields while editing employee records, then the Edit page will also throw required field validation error message.
If you want to see the details of any Employee, then click Details action link, which will open the EmployeeDetails page as shown in the image below.
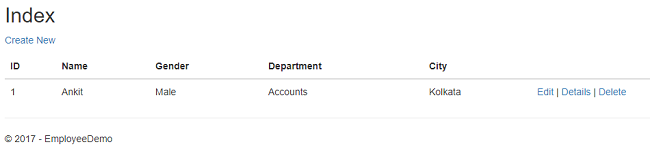
Click "Back to List" to go back to the EmployeeIndex page. Now, we will perform Delete operation on an employee named Mahesh. Click Delete action link which will open DeleteEmployee page asking for a confirmation to delete.
Once we click on Delete button, the employee record gets deleted and we will be redirected to the Employee Index page. Here, we can see that the employee with name Mahesh has been removed from our record.
Conclusion
We have learned how to create a Razor page web application with ASP.NET Core using ADO.NET. We have also performed CRUD operations on it.
Source Code
Download the source code files from here