ASP.NET Core 2.0 - How to use Dependency Injection
Introduction
In this article, we'll show you the new feature introduced in ASP .NET Core that allows you to inject dependencies directly into a View using the dependency injection container.
ASP .NET Core has introduced a feature called view injection that allows you to inject dependencies into a view using the inject keyword.
Previously, to retrieve data from a View, we needed to pass it from the Controller using the Controller properties, such as ViewBag, ViewData, or Model properties.
In ASP.NET Core MVC, this task became very simple using the Inject directive that allows you to inject the dependencies directly into the View and retrieve the data.
Let's see this working in practice!
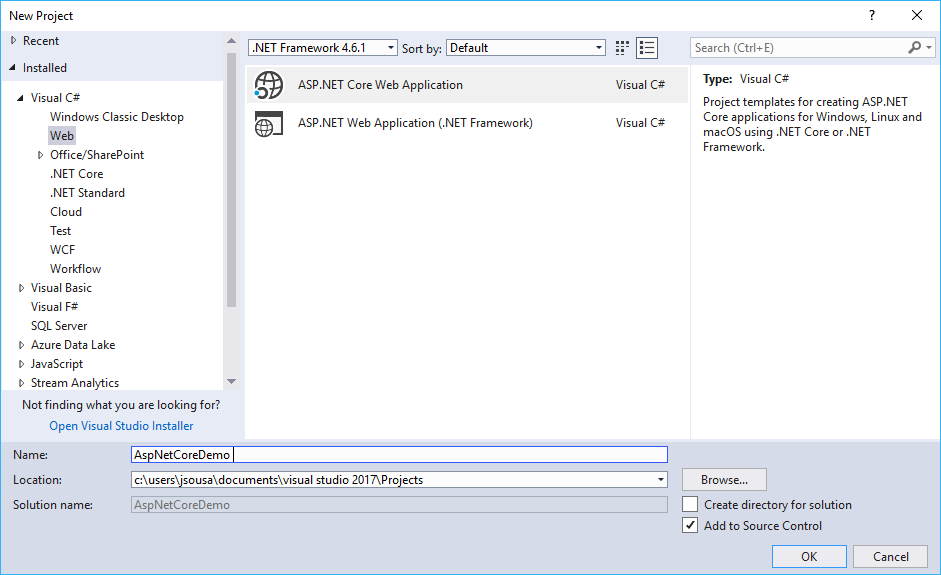
STEP 1 - Creating the ASP .NET Core Project in VS 2017
Open VS 2017 and on the File menu click New Project. Then select the Visual C # -> Web template and check ASP .NET Core Web Application (.NET Core).
Then enter the name AspNetCoreDemo and click OK.
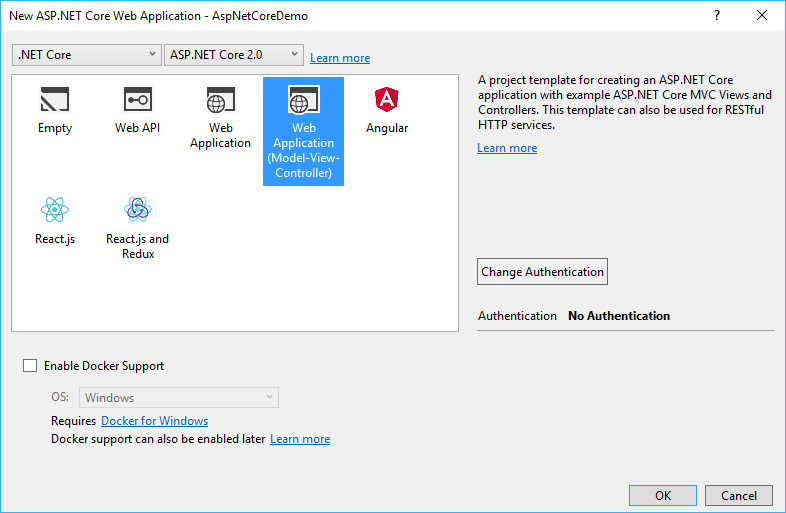
In the next window, choose the ASP .NET Core 2.0 version and mark the Web Application (Model-View-Controller) template without authentication and click the OK button:
STEP 2 - Creating a new service in the application
**
**
Let's define a very simple service just for testing in our application.
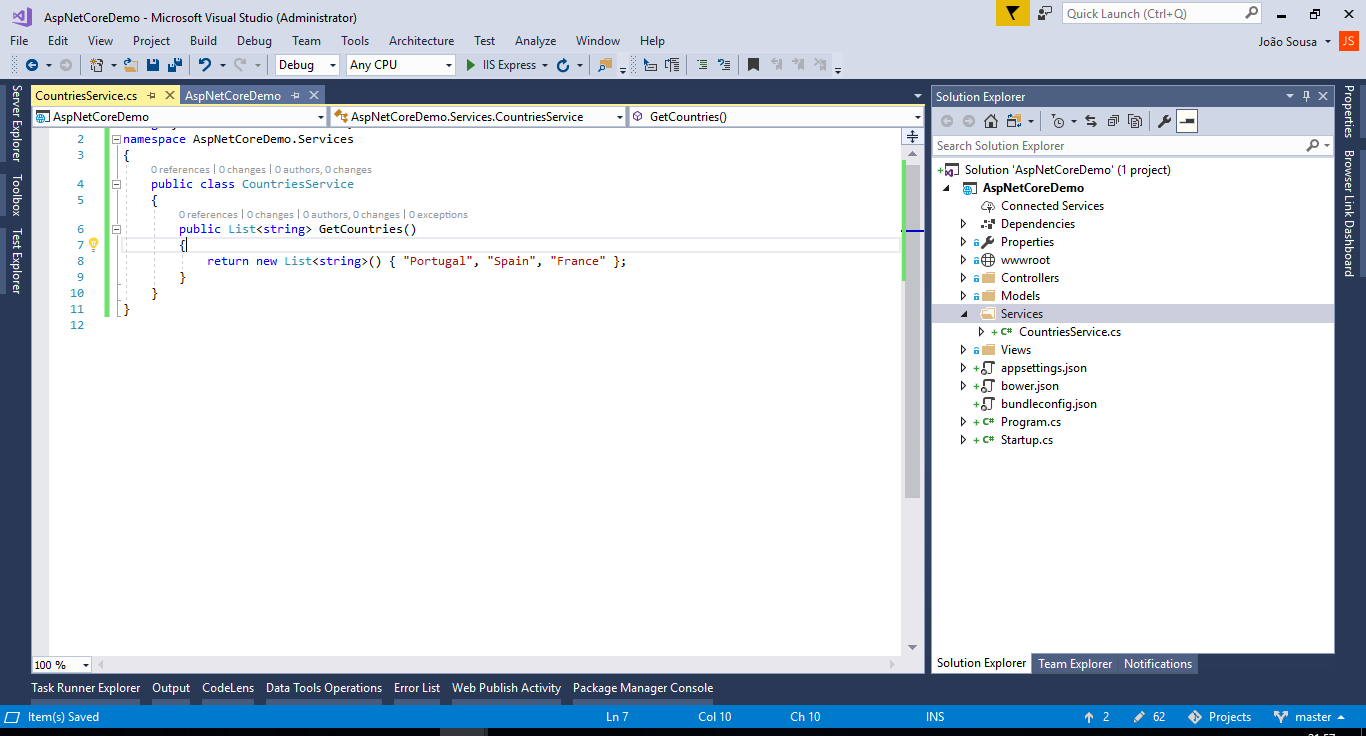
Create the Services folder in the project (Project -> New Folder), and then add the CountriesService.cs file to this folder containing the following code:
using System.Collections.Generic;
namespace AspNetCoreDemo.Services
{
public class CountriesService
{
public List<string> GetCountries()
{
return new List<string>() { "Portugal", "Spain", "France" };
}
}
}
STEP 3 - Injecting the service into View
We will now see how we can inject the service created in the project view using the @inject directive.
Think of the @Inject directive as a property being added in your View and populating the property using dependency injection.
The basic syntax used is: @inject <service> <name>
At where :
- @ inject - is the directive used to inject dependencies;
- <service> - is the class of service.
- <name> - is the service injection name through which we can access the service's methods.
Let's open the Index.cshtml file from the /Views/Home folder and include the code below in this file
@inject AspNetCoreDemo.Services.CountriesService Countries
@foreach (var countryName in Countries.GetCountries())
{
<ul>
<li>@countryName</li>
</ul>
}
STEP 4 - Registering the service in the Startup.cs file
Open the Startup.cs file and add the code below to this file that registers the service created for dependency injection in the ConfigureServices method.
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddMvc();
services.AddTransient<CountriesService>();
}
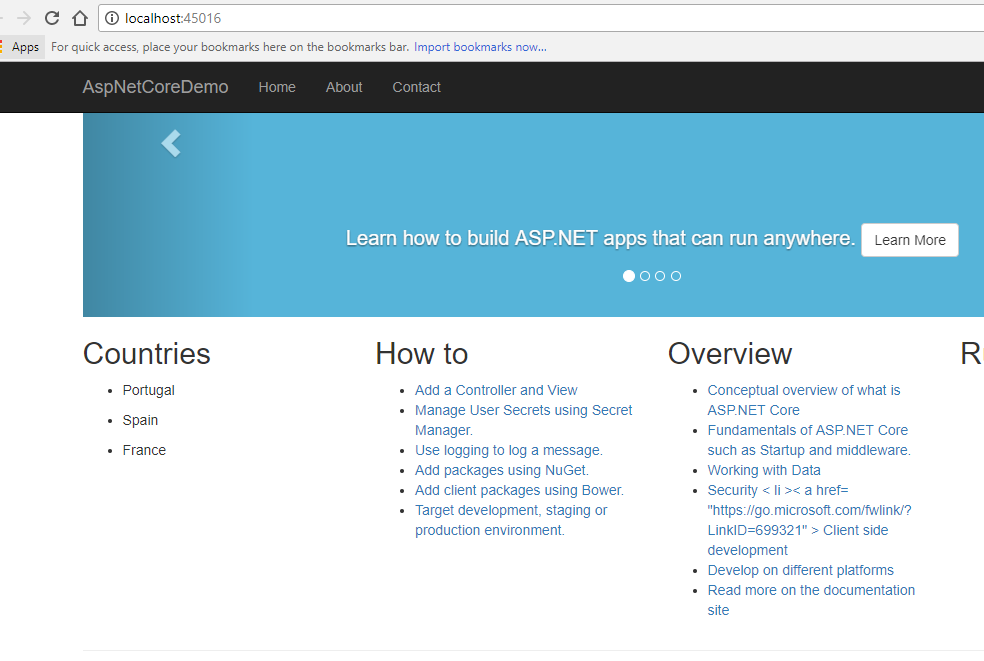
STEP 5 - Result
Executing the project, we will obtain the following result:
Resources
- My Blog - joaoeduardosousa.wordpress.com
- Download Code: https://code.msdn.microsoft.com/ASPNET-Core-20-Dependency-66c68ff0