PCNS: Troubleshooting Event ID 6025
Overview
You just recently installed and configured the Password Change Notification Service (PCNS) onto your Source Domain Controller(s). You have configured the Synchronization Service Manager and Management Agents to work with Password Management. You execute a test and receive an Event ID 6025 in the Application Event Log.
The Event ID 6025 can have a few different messages, which can control how you troubleshoot the Event ID 6025 error message. Essentially, the Event ID 6025 indicates that the source domain controller is not able to communicate with the Synchronization Service Manager machine.
One of the very first things to understand about your Password Management Solution is where the Synchronization Service Machine is setup.
- Is the Synchronization Service Machine a member of the Source Forest or the Target Forest?
The password change notification target could not be authenticated
The password change notification target could not be authenticated. |
The following iteration of the Event ID 6025 is an indication that there is a problem with the ServicePrincipalName that was configured on the Synchronization Service Account, and configured in the PCNS Configuration Data.
Here is a check list of items to check to isolate and resolve the issue:
- Validate that the SPN set on the Synchronization Service Account matches exactly to the SPN specified in the PCNS Configuration File. ( Validation Steps )
- Validate that there are no duplicate SPNs. ( Validation Steps )
- This would include the Source and Target Forest, if you are setting PCNS up where the Synchronization Service Engine is in the Target Forest.
- The name of the PCNS Configuration Target is note the same as the machine name for the Synchronization Service machine.
- If the PCNS Configuration Target name is the same as the name of the machine that the Synchronization Service Engine is installed, an Event ID 6025 can occur. Utilize PCNSCFG –list to validate that the Target Name is unique and not the machine name for the Synchronization Service Engine.
Status 1753: There are no more endpoints available from the endpoint mapper
Password Change Notification Service received an RPC exception attempting to deliver a notification. |
The following iteration of the Event ID 6025 is an indication of the inability to make a successful RPC connection to the Synchronization Server from the Source Domain Controller. The Source Domain Controller is where the Password Change Notification Service (PCNS) is installed.
Here are some focus points for troubleshooting and resolving the 6025 Event ID with a status of 1753. The focus should be around network connectivity, and some PCNS-Password Synchronization configurations.
- Validate that you have enabled Password Synchronization in Tools > Options. ( Validation Steps )
[TROUBLESHOOTING] . Password Change Notification Service received an RPC exception attempting to deliver
- PCNS utilizes Kerberos to be able to reset the password so there must be SRV record access between the Synchronization Service machine and the Source Domain Controller.
- Validate that all the correct ports are open between the Source Domain Controller and the Synchronization Service machine. ( Management Agent Communication Ports, Rights and Permissions ) ( Validation Information )
- Validate Local Security Settings - User Rights Assignment contain the default information ( (Local) Administrators, Everyone, Users ) ( Validation Steps )
- Support-Tip: (PCNS): Passwords stopped synchronizing, Passwords stopped working (Support Team Blog Post)
Status 1747: The authentication service is unknown
Log Name: Application Thread ID: 1584 ProcessID is 4632 ProcessID is 4632 |
This iteration of the Event ID 6025 is an indication that something is invalid with the configuration of the PCNS-Password Synchronization Solution.
Here are some focus areas to help troubleshooting and resolving the 6025 Event ID.
- Validate that the SPN set on the Synchronization Service Account matches exactly to the SPN specified in the PCNS Configuration File. ( Validation Steps )
- Validate that there are no duplicate SPNs. ( Validation Steps )
- This would include the Source and Target Forest, if you are setting PCNS up where the Synchronization Service Engine is in the Target Forest.
- Validate that the Synchronization Service is a Domain Account and not a Local Account
- Validate that the Synchronization Service Account running the Synchronization Service Engine is a Domain Account.
FIM-TROUBLESHOOTING-PCNS: Event ID: 6025 – Status: 1747
Status 10060: A connection attempt failed because the connected party did not properly respond after a period of time or established connection failed because connected host has failed to respond.
This status is an indication that the Password Change Notification Service (PCNS) is not able to succeed with the RPC connection because the Synchronization Service Manager Console cannot be opened. The reason for this is there is no user in the FIMSyncAdmins Group.
Add correct user to the FIMSyncAdmins group.
Additional Troubleshooting Tool Suggestions
If the above information has not assisted in resolving the issue, you can utilize some of the following tools to assist in troubleshooting/isolating the Event ID 6025.
- Network Monitor 3.4 ( Download )
- Utilize Network Monitor 3.4 to monitor network traffic. A simultaneous network trace is very beneficial in troubleshooting network related issues. In a PCNS Troubleshooting perspective, executing a network capture on the source domain controller, and the Synchronization Service Engine machine would be a good recommendation. Here are some protocols that will be of interest when reviewing the network capture information:
- LDAP
- KERBEROSV5
- DNS
- MSRPC
- Utilize Network Monitor 3.4 to monitor network traffic. A simultaneous network trace is very beneficial in troubleshooting network related issues. In a PCNS Troubleshooting perspective, executing a network capture on the source domain controller, and the Synchronization Service Engine machine would be a good recommendation. Here are some protocols that will be of interest when reviewing the network capture information:
- NSLookup
- Utilize NSLookup to test/validate DNS Connectivity.
Appendix
Validate ServicePrincipalName between Synchronization Service Account and PCNS Configuration Data
The ServicePrincipalName (SPN) that is set on the Domain Synchronization Service Account needs to match exactly to that specified in the PCNS Configuration Data. The following steps should assist in validating this information. I have found that the easiest way to validate this information, is to dump the information to a text file, and then review the information.
On the Source Domain Controller, Open an Administrative Command-Prompt by right clicking on the command prompt and selecting Run as Administrator.
Change directory to %programfiles%\Microsoft Password Change Notification
In the command-prompt, type the following and then press the ENTER key
pcnscfg list > pcnscfg.txt
In the command-prompt, type the following and press the ENTER key
setspn –L <DOMAIN NAME>\SYNCHRONIZATION SERVICE ACCOUNT> > spn.txt
Review both text files to ensure that the ServicePrincipalName (SPN) set on the Domain Synchronization Service Account matches exactly to the Service Principal Name line in the PCNS Configuration information.
If they do not match, you may need to rebuild the information, or modify the information to ensure that the SPNs match.
Validate that Password Synchronization is enabled
This is extremely easy to validate and a common miss when setting up Password Management. Validation can be done through the following steps.
On the Synchronization Service Manager machine, Open the Synchronization Service Manager Console
From the Tools menu, select Options
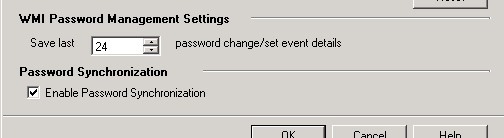
In the Options dialog, validate the check mark is beside the Enable Password Synchronization.
Click Ok to close the Options Dialog
Firewall
In most cases a firewall between two machines in the same forest/domain normally does not occur. If there is, in most cases it will be that the Windows Firewall is enabled either on the Source Domain Controller and/or the Synchronization Service machine. The necessary ports need to be open in the Windows Firewall, if the intent is to keep the Windows Firewall enabled.
Firewalls are seen to be more of an issue in a Password Management Solution (PCNS-Password Synchronization Solution) between the Synchronization Service machine and the Target forest. Either way, ensure that the correct ports are open to allow communication between the servers.
PCNS does require DNS connectivity, Kerberos Connectivity and RPC Connectivity. RPC connectivity will require an open range of ports for RPC communication. Here is some more information about RPC.
- How RPC Works: Remote Procedure Call (RPC)
- How to configure RPC dynamic port allocation to work with firewalls
- PCNS: RPC exception attempting to deliver a notification
Service
Protocol
Port
Kerberos
TCP/UDP
88
DNS
TCP/UDP
53
Kerberos Change Password
UDP
464
RPC Endpoint mapper
TCP
135
Dynamic RPC ports (PCNS)
TCP
5000-5100
Validate duplicate SPNs
Duplicate Service Principal Names (SPN) can cause communication problems with the Synchronization Service Machine. Searching for duplicate SPNs will depend on which Windows Server that you are currently running.
Duplicate SPNs can be:
- The same SPN existing on multiple accounts in the same forest, or
- The same SPN existing on an account in the source forest, and in the target forest.
We have seen #2 when the Synchronization Service Engine is installed in the Target Forest, and PCNS is setup and configured in the Source Forest and the Synchronization Service Account exists in both environments. In this situation, you will want to use the –Q switch to help see if the SPN exists on both accounts. It can only exist on one, the account that is being used for the Synchronization Service.
Windows Server 2008: http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc731241(WS.10).aspx
Query Mode Parameters
Description
Usage
-Q <spn>
Query for existence of SPN
setspn –Q SPN
-X
Query for duplicate SPNs
setspn –X
NOTE: Searching for duplicates, especially forest-wide can take a long period of time and a large amount of memory
Windows Server 2003 |
Recommend to download the SETSPN.EXE update from Microsoft Knowledge Base Article 970536. If the update is installed then the two commands above can be utilized for SPN searches. |
Validate Local Security Settings
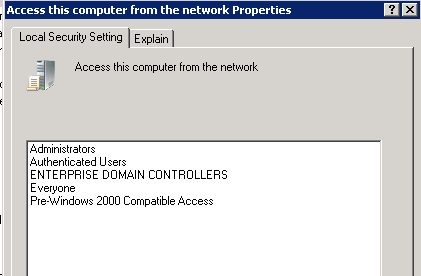
At a minimum, all Domain Controllers that will be sending password changes must be given Access this computer from the network permissions. It is recommended not to change the default settings of this User Assignment.
The Default settings of the Access this computer from the network are:
- Administrators ( The Local Administrators Group )
- Everyone
- Authenticated Users
You can validate this setting through the following steps:
Navigate to Administrative Tools > Local Security Policy
Expand Local Policies then select User Rights Assignment
Select Access this computer from the network
View the Properties for Access this computer from the network properties
For more information on the Access this computer from the network, review this Microsoft TechNet Document.
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc740196(v=WS.10).aspx