C#: Creating a Custom VR Game Controller using Arduino
Introduction
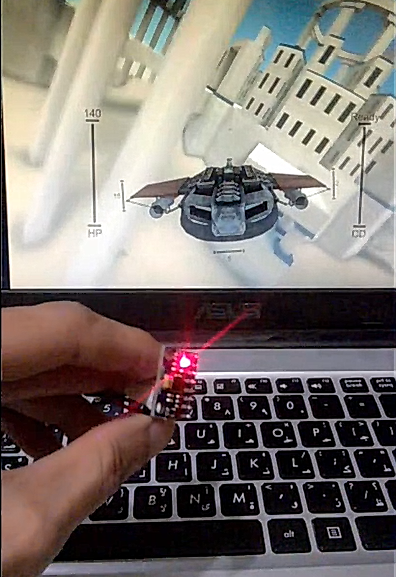
This article explains step by step how to create a custom game controller using Arduino Uno and MPU6050 motion sensor. This is the game controller we will be making,
Step 1: Programming Arduino
If you are not interested in details of how the program works then simply upload the code given in resources section in Arduino Uno and jump to Step 2.
Initializing Sensor
To initialize the sensor, we first initialize the I2C communication using standard Wire library then configure the MPU. If configuration fails, then the Arduino goes in forever while loop as it's useless to continue.
void InitializeMpu()
{
Wire.begin();
Wire.setClock(400000UL);
i2cData[0] = 7; // Set the sample rate to 1000Hz - 8kHz/(7+1) = 1000Hz
i2cData[1] = 0x00; // Disable FSYNC and set 260 Hz Acc filtering, 256 Hz Gyro filtering, 8 KHz sampling
i2cData[2] = 0x00; // Set Gyro Full Scale Range to ?250deg/s
i2cData[3] = 0x00; // Set Accelerometer Full Scale Range to ?2g
while (i2cWrite(0x19, i2cData, 4, false)); // Write to all four registers at once
while (i2cWrite(0x6B, 0x01, true)); // PLL with X axis gyroscope reference and disable sleep mode
while (i2cRead(0x75, i2cData, 1));
if (i2cData[0] != 0x68)
{ // Read "WHO_AM_I" register
Serial.print(F("Error reading sensor"));
while (1);
}
}
Reading the Motion Data
Motion data is read from IMU sensor (MPU6050) in every loop and the respective gyro and accelerometer values are updated. The following function does this job.
void UpdateReadings()
{
while (i2cRead(0x3B, i2cData, 14));
accX = ((i2cData[0] << 8) | i2cData[1]);
accY = ((i2cData[2] << 8) | i2cData[3]);
accZ = ((i2cData[4] << 8) | i2cData[5]);
tempRaw = (i2cData[6] << 8) | i2cData[7];
gyroX = (i2cData[8] << 8) | i2cData[9];
gyroY = (i2cData[10] << 8) | i2cData[11];
gyroZ = (i2cData[12] << 8) | i2cData[13];
}
Computing Angles Using Complementary Filter
Angles can be computed using complementary filter with a good accuracy. We will use complementary filter since it's fine for most of the application. But if you need even better accuracy, you can use Kalman Filter.
void ComputeAngles()
{
double roll = atan2(accY, accZ) * RAD_TO_DEG;
double pitch = atan(-accX / sqrt(accY * accY + accZ * accZ)) * RAD_TO_DEG;
double gyroXrate = gyroX / 131.0; // Convert to deg/s
double gyroYrate = gyroY / 131.0; // Convert to deg/s
compAngleX = 0.98 * (compAngleX + gyroXrate * dt) + 0.02 * roll; // Calculate the angle using a Complimentary filter
compAngleY = 0.98 * (compAngleY + gyroYrate * dt) + 0.02 * pitch;
}
Set Controller Data Object
We need a dataForController_t object to send data to the computer/host as a joystick. We use the following code to create and fill dataForController_t object.
dataForController_t getControllerData(double _roll, double _pitch)
{
//Restrict roll and pitch to +-90
if (_roll > 90 || _roll < -90)
_roll = 90 * _roll / abs(_roll);
if (_pitch > 90 || _pitch < -90)
_pitch = 90 * _pitch / abs(_pitch);
//Get new instance with default values of buttons and sticks
dataForController_t controllerData = getBlankDataForController();
controllerData.rightStickX = (int)(_roll * 1.42 + 128);
controllerData.rightStickY = (int)(_pitch * 1.42 + 128);
//You can use these and many other buttons also
// controllerData.triangleOn = !digitalRead(2);
// controllerData.circleOn = !digitalRead(3);
// controllerData.squareOn = !digitalRead(4);
// controllerData.crossOn = !digitalRead(5);
return controllerData;
}
In loop() we will call this function as,
dataForController_t controllerData = getControllerData(compAngleX, compAngleY);
Send Controller Data to Computer
To send this data to joystick simple call the setControllerData() function as follows,
setControllerData(controllerData);
Step 2: Connect the MPU Sensor
Connect the MPU sensor with Arduino Uno as,
Arduino MPU6050
3.3V ------------- Vcc
Gnd ------------- Gnd
A5 --------------- SCL
A4 --------------- SDA
After you have programmed your Arduino Uno with the given code, connect the MPU. You can uncomment the following line to check on serial monitor/plotter if everything is working fine, moving the sensor will change the values accordingly. Be sure to comment it again after testing.
//#define DEBUG
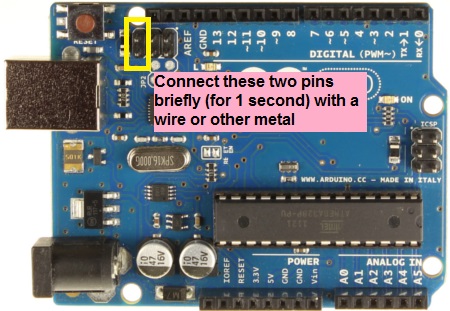
Step 3: Turn Arduino into Joystick
To turn Arduino into joystick first you need to turn start Arduino into DFU mode. To do this, just connect the following Arduino pins,
On Windows the Arduino (usb device) will disconnect with a sound (be-dun). And connect again (buh-din!)
Now Arduino is on DFU mode, just open the TurnIntoAJoystick.bat file in UnoJoy.zip (see resources section) and it will turn your Arduino into a joystick. Atmel FLIP must be installed for this to work. In windows 10 go to Settings > Devices > Connected Devices and it will show up as a Joystick.
Step 4: Testing the Joystick
You can test the joystick using TestJoystick.exe (see resources section). Just connect the Arduino Joystick into your computer and run TestJoystick.exe. It will show a floating plane that rotates as you move the joysytick.
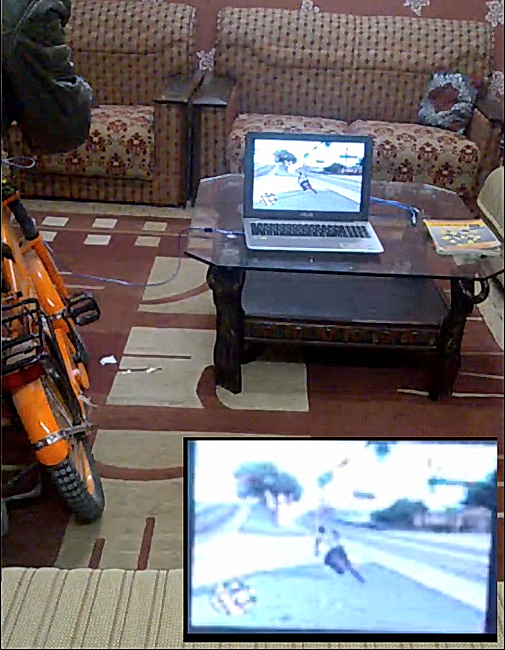
If it works fine then go ahead and try it with your favorite games!