ASP.NET MVC 5: Code First Migration With Entity Framework Core
Introduction
In this article, we are going to explain Code First Migration in ASP.NET Core MVC 6 with EntityFrameWork Core, using Command Line Interface ( CLI ).
Before reading this article, you must read the articles given below for ASP.NET Core knowledge.
- ASP.NET CORE 1.0: Getting Started
- ASP.NET Core 1.0: Project Layout
- ASP.NET Core 1.0: Middleware And Static files (Part 1)
- Middleware And Staticfiles In ASP.NET Core 1.0 - Part Two
Model Class
We are going to create a sample Code First Migration project in ASP.NET Core 1.0. Model class given below contains the properties of the user details in our Applications.
using System;
namespace CodeFirstMigration.Models
{
public class UserDetails
{
public Guid Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string EmailId { get; set; }
public string Company { get; set; }
}
}
LocalDB Configuration in ASP.NET Core 1.0
In the previous versions, everything is handled by Web.Config but in ASP.NET Core, the connection string is written in appsettings.json file. By default, it will show as a LocalDB path and as per our requirement, we can change the connection string path.
In the way given below, we can create connection string in ASP.NET Core 1.0.
The appsetting JSON file contains the LocalDB connection string details in our Application and we have given the database name as "UserDb". If you want to know more about JSON file configuration in ASP.NET Core, please check our previous article ASP.NET Core 1.0: Adding A Configuration Source File.
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"DefaultConnection": "Server=(localdb)\\MSSQLLocalDB;Database=UserDb;Trusted_Connection=True;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
}
}
DbContext in ASP.NET Core 1.0
The code given below contains the information about EntityFrameWork Core DbContext. We can add the LocalDB connection string details with the help of "UseSqlServer" Method.
using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
namespace CodeFirstMigration.Models
{
public class CodeDbContext : DbContext
{
private IConfigurationRoot _config;
public CodeDbContext(IConfigurationRoot config, DbContextOptions options) : base(options)
{
_config = config;
}
public DbSet<UserDetails> userDetails { get; set; }
protected override void OnConfiguring(DbContextOptionsBuilder optionsBuilder)
{
base.OnConfiguring(optionsBuilder);
optionsBuilder.UseSqlServer(_config["ConnectionStrings:DefaultConnection"]);
}
}
}
Seed Data in EntityFrameWork Core
We are going to implement Code First Migrations in Entity Framework Core to seed the database with test data and manually we are entering the seed data information in the "CodeDbSeedData" class. The code given below contains the default values of User Details Table in our Application.
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace CodeFirstMigration.Models
{
public class CodeDbSeedData
{
private CodeDbContext _context;
public CodeDbSeedData(CodeDbContext context)
{
_context = context;
}
public async Task SeedData()
{
if (!_context.userDetails.Any())
{
var user = new UserDetails()
{
Id = Guid.NewGuid(),
Name = "RajeeshMenoth",
EmailId = "rajeeshmenoth@gmail.com",
Company = "HappiestMinds Technologies Pvt Ltd"
};
_context.userDetails.Add(user);
await _context.SaveChangesAsync();
}
}
}
}
project.json
project.json contain the complete picture of dependency in our Applications.
{
"dependencies": {
"Microsoft.NETCore.App": {
"version": "1.0.1",
"type": "platform"
},
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Diagnostics": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.IISIntegration": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.Kestrel": "1.0.1",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Logging.Console": "1.0.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.Core": "1.1.1",
"Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.FileExtensions": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration.Json": "1.1.0",
"Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Design": "1.0.0-preview2-final"
},
"tools": {
"Microsoft.AspNetCore.Server.IISIntegration.Tools": "1.0.0-preview2-final",
"Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.Tools": {
"version": "1.0.0-preview2-final",
"imports": [
"portable-net45+win8+dnxcore50",
"portable-net45+win8"
]
}
},
"frameworks": {
"netcoreapp1.0": {
"imports": [
"dotnet5.6",
"portable-net45+win8"
]
}
},
"buildOptions": {
"emitEntryPoint": true,
"preserveCompilationContext": true
},
"runtimeOptions": {
"configProperties": {
"System.GC.Server": true
}
},
"publishOptions": {
"include": [
"wwwroot",
"web.config"
]
},
"scripts": {
"postpublish": [ "dotnet publish-iis --publish-folder %publish:OutputPath% --framework %publish:FullTargetFramework%" ]
}
}
Startup.cs
The class given below contains the complete middleware details in our Applications.
using CodeFirstMigration.Models;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Hosting;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Http;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Logging;
using System;
namespace CodeFirstMigration
{
public class Startup
{
private IConfigurationRoot _config;
public Startup(IHostingEnvironment env)
{
var ConfigBuilder = new ConfigurationBuilder().SetBasePath(env.ContentRootPath)
.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json");
_config = ConfigBuilder.Build();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to add services to the container.
// For more information on how to configure your application, visit http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkID=398940 ;
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services)
{
services.AddSingleton(_config);
services.AddDbContext<CodeDbContext>();
services.AddTransient<CodeDbSeedData>();
services.AddMvc();
}
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory,
CodeDbSeedData seeder)
{
loggerFactory.AddConsole();
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.UseMvc();
app.Run(async (context) =>
{
await context.Response.WriteAsync(" Welcome to Dotnet Core !!");
});
try
{
seeder.SeedData().Wait();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ex;
}
}
}
}
Code First Migration
The steps given below will explain the step by step Code First Migration in EntityFrameWork Core.
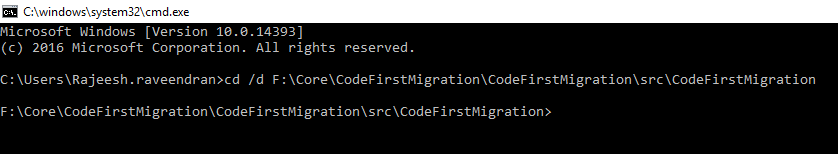
Setting Project Location
The command given below will help to change our current "C Drive" to "F Drive" because currently our Code First Migration project is saved into "F Drive".
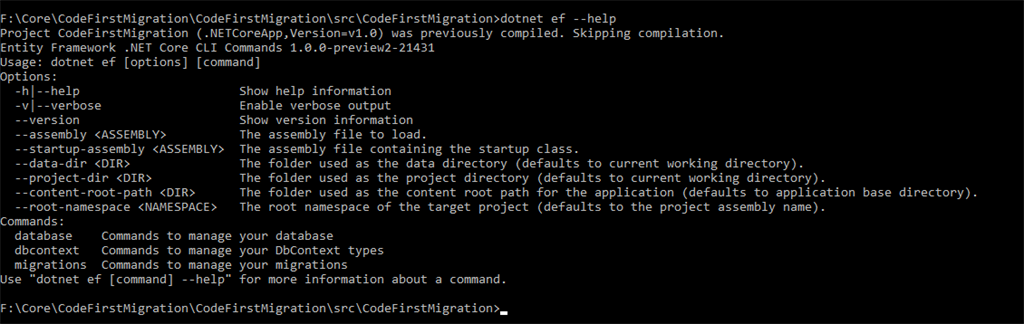
Dotnet ef-help command
The command given below will display for more information about dotnet ef command.
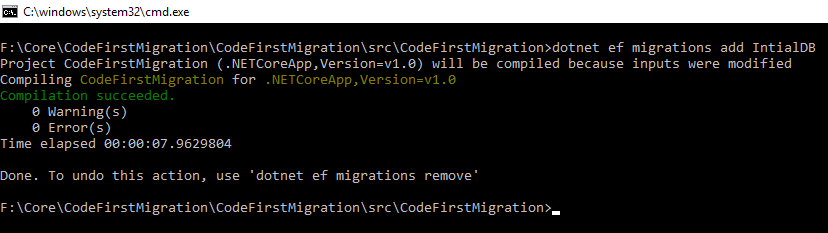
Starting With new migration
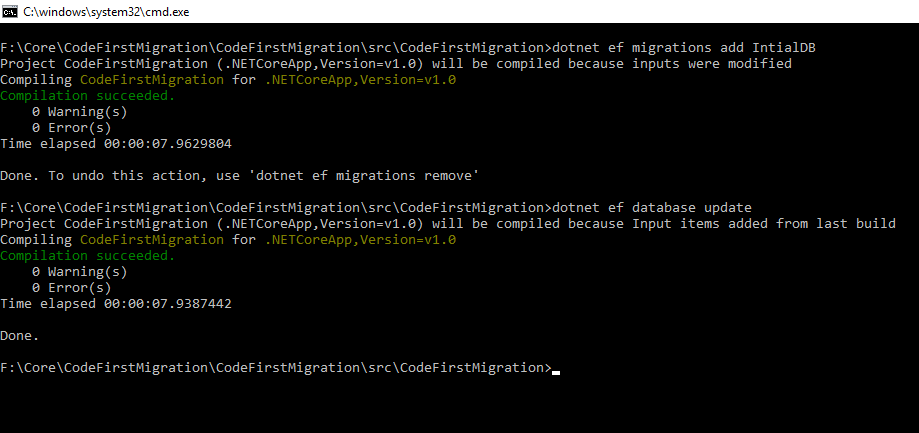
We are going to start with new EntityFrameWork migration, using the command given below.
"dotnet ef migrations add IntialDB"
Update the database
The command given below will update the EntityFrameWork Core database in ASP.NET Core Application.
"dotnet ef database update"
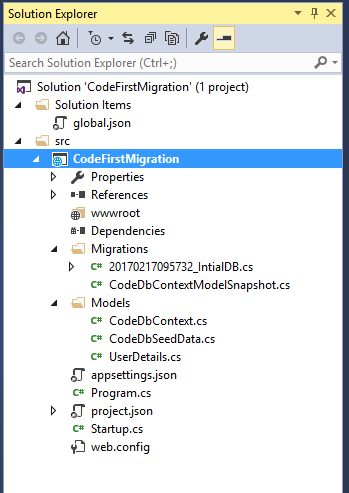
Project Structure After Migration
The structure given below will be created after the ef migration in .NET Core.
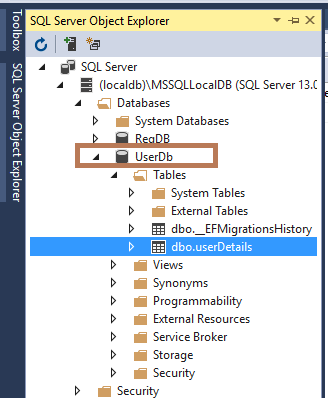
Local Db Created
The Dotnet EntityFrameWork CLI ( Command Line Interface ) creates the Local DB as "UserDB". Go to "View" and select "SQL Server Object Explorer" in Visual Studio. Now, expand "SQL Server -> (localdb) -> Databases -> UserDB".
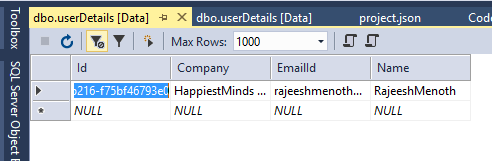
Output
Conclusion
We learned about Code First Migration in ASP.NET Core MVC 6 with EntityFrameWork Core, using Command Line Interface ( CLI ) and I hope you liked this article. Please share your valuable suggestions and feedback.
Reference
Downloads
You can download other ASP.NET Core 1.0 source code from the MSDN Code, using the links, mentioned below.
- Middleware And Staticfiles In ASP.NET Core 1.0 - Part One
- Middleware And Staticfiles In ASP.NET Core 1.0 - Part Two
- Create An Aurelia Single Page Application In ASP.NET Core 1.0
- Create Rest API Or Web API With ASP.NET Core 1.0
- Adding A Configuration Source File In ASP.NET Core 1.0
See Also
It's recommended to read more articles related to ASP.NET Core.
- ASP.NET CORE 1.0: Getting Started
- ASP.NET Core 1.0: Project Layout
- ASP.NET Core 1.0: Middleware And Static files (Part 1)
- Middleware And Staticfiles In ASP.NET Core 1.0 - Part Two
- ASP.NET Core 1.0 Configuration: Aurelia Single Page Applications
- ASP.NET Core 1.0: Create An Aurelia Single Page Application
- Create Rest API Or Web API With ASP.NET Core 1.0
- ASP.NET Core 1.0: Adding A Configuration Source File