Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Abstract
This article talks about various SQL methods to fetch the disk usage details and use of T-SQL in conjunction with invoking OLE automation procedures and WMI class libraries using SQL Windows Shell interface.
The step by step details about "OLE automation and WMI Query" approach to capture disk space and the use of sqlcmd with looping construct, data storage for querying and reporting are discussed below
Method 1 - Using OLE automation and Extended SP
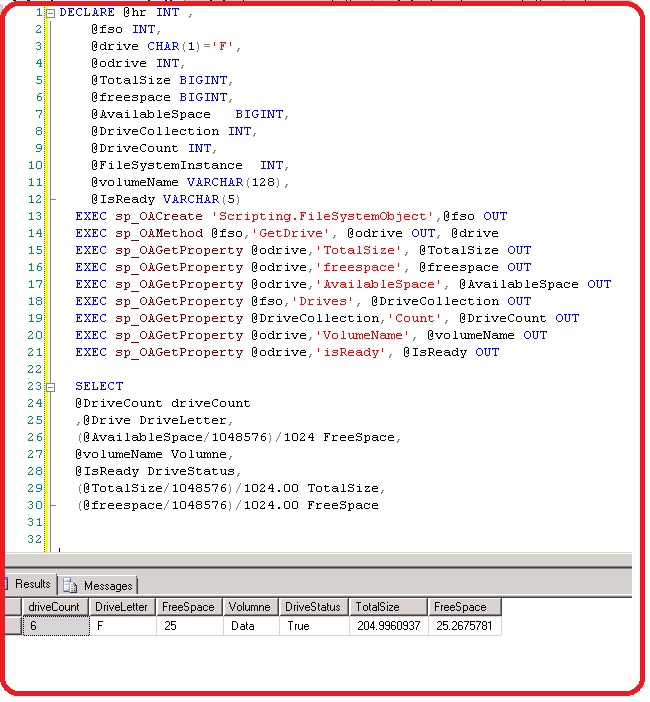
In this method OLE automation and xp_cmdshell configuration components are enabled on the sql server. The sp_OACreate creates an instance of a Scripting.FileSystemObject OLE class. The sp_OAMethod gets a unique id for each volume attached to filesystem object and sp_OAGetProperty retrieves properties of each drive and filesystem.
The reason for enabling xp_cmdshell is to execute xp_fixeddrives an extended stored procedure. The output is stored in a temporary table. The records are traversed with a while loop construct for %free space calculation. The sp_OAMethod requires a drive letter as its input . The below SQL has hard coded value for F drive. You can change the sql as per your requirement
DECLARE @hr INT ,
@fso INT,
@drive CHAR(1)='F', /* To demonstrate have hard coded the drive letter to F */
@odrive INT,
@TotalSize BIGINT,
@freespace BIGINT,
@AvailableSpace BIGINT,
@DriveCollection INT,
@DriveCount INT,
@FileSystemInstance INT,
@volumeName varchar(128),
@IsReady VARCHAR(5)
EXEC sp_OACreate 'Scripting.FileSystemObject',@fso OUT
EXEC sp_OAMethod @fso,'GetDrive', @odrive OUT, @drive
EXEC sp_OAGetProperty @odrive,'TotalSize', @TotalSize OUT
EXEC sp_OAGetProperty @odrive,'freespace', @freespace OUT
EXEC sp_OAGetProperty @odrive,'AvailableSpace', @AvailableSpace OUT
EXEC sp_OAGetProperty @fso,'Drives', @DriveCollection OUT
EXEC sp_OAGetProperty @DriveCollection,'Count', @DriveCount OUT
EXEC sp_OAGetProperty @odrive,'VolumeName', @volumeName OUT
EXEC sp_OAGetProperty @odrive,'isReady', @IsReady OUT
SELECT
@DriveCount driveCount
,@Drive DriveLetter,
(@AvailableSpace/1048576)/1024 FreeSpace,
@volumeName Volumne,
@IsReady DriveStatus,
(@TotalSize/1048576)/1024.00 TotalSize,
(@freespace/1048576)/1024.00 FreeSpace
Data flow diagram
This process requires enabling OLE automation procedures and xp_cmdshell SQL windows shell components on all the servers. The servers are traversed one by one via batch scripting along with sqlcmd and the result is stored in a shared file. This file has a collection of insert SQL statements. later the insert statement is executed on the centralized server. The repository can be queried, used for forecasting and capacity planning and reporting.
OLE - Capturing Disk Space of multiple servers
The section describes the requirement and briefs about every configuration required for successful execution of the code. The major issue is enabling OLE automation procedures and xp_cmdshell on all the servers. There is a risk of exposing SQL server to a threat. The workaround is to add the little piece of configuring and de-configure sql statement in the sql file. Enable the configuration value in the beginning of the code and disable it at the end.
Pre-requisites
We can check the disk space by executing a T-SQL script using xp_cmdshell from SSMS. In order to do this, you need to make sure that xp_cmdshell is enabled on the SQL instance. You can execute the below script to check and enable xp_cmdshell . To enable xp_cmdshell you must have at least the ALTER SETTINGS server-level permission.
- Enable xp_cmdshell on Centralized Server
- Enable Ole automation on all the listed servers
- Shared path for sql file
- Share path for output file to prepare insert statement
- Requires membership in the sysadmin fixed server role.
Step By Step Details
The below are the steps to store the data into a central repository
- Enable xp_cmdshell
- List all Servers in c:\Server.txt
- Enable ole automation
- Table Creation [TLOG_SpaceUsageDetails]
- save T-SQL script in SpaceCheck.sql
- Execute dynamic sqlcmd from SSMS
- select the output by querying TLOG_SpaceUsageDetails
Enable xp_cmdshell
The xp_cmdshell option is a SQL Server server configuration option that enables system administrators to control whether the extended stored procedure can be executed on a system also this procedure allows you to issue operating system commands directly to the Windows command shell via T-SQL code
sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1;
GO
RECONFIGURE;
GO
sp_configure 'xp_cmdShell', 1;
GO
RECONFIGURE;
GO
Enable OLE automation
Use the Ole Automation Procedures option to specify whether OLE Automation objects can be instantiated within Transact-SQL batches
sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1;
GO
RECONFIGURE;
GO
sp_configure 'Ole Automation Procedures', 1;
GO
RECONFIGURE;
GO
List servers in text file
Lists all the servers in a text file c:\server.txt and enable the OLE automation across all the servers. The other way to get around this problem is to include the sp_configure commands in the sql file and take it out after it is been executed across all the servers
ABC
DEF
EFG
Create SQL Table
Create TLOG_SpaceUsageDetails on the centralized server
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[TLOG_SpaceUsageDetails](
[ID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[ServerName] [VARCHAR](100) NULL,
[LogDate] [VARCHAR](10) DEFAULT (CONVERT([varchar](10),getdate(),(112))),
[Drive] [CHAR](3) NULL,
[FreeSpaceGB] [INT] NULL,
[TotalSizeGB] [INT] NULL,
[percentageOfFreeSpace] DECIMAL(5,2) NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
Create SQL File
Save the below content to sql file and place it on the shared path so that sqlcmd can read the file while traversing across listed servers. for example, the content is saved under Spacecheck.sql on \abcd\hq\ The full path of the file is going to be \abcd\hq\spacecheck.sql
DECLARE @hr INT ,
@fso INT,
@drive CHAR(1),
@odrive INT,
@TotalSize VARCHAR(20),
@MB NUMERIC ,
@FreeSpace INT,
@free INT,
@RowId_1 INT,
@LoopStatus_1 SMALLINT,
@TotalSpace VARCHAR(10),
@Percentage VARCHAR(3),
@drive1 varchar(2),
@TotalSizeMB varchar(10),
@FreeSpaceMB varchar(10),
@percentageOfFreeSpace varchar(10),
@RowId_2 INT,
@LoopStatus_2 SMALLINT,
@DML nvarchar(4000)
SET NOCOUNT ON
------------------------------------------------------
--Table to Store Drive related information
------------------------------------------------------
CREATE TABLE #drives
(
id INT IDENTITY(1,1) PRIMARY KEY,
drive CHAR(1),
FreeSpaceMB INT ,
TotalSizeMB INT NULL,
percentageOfFreeSpace INT
)
------------------------------------------------------
--Inserting the output of xp_fixeddrives to #SpaceSize Table
------------------------------------------------------
INSERT #drives(drive,FreeSpaceMB) EXEC master.dbo.xp_fixeddrives
------------------------------------------------------
--Using the sp_OACreate, sp_OAMethod and sp_OAGetProperty system stored procedures to create Ole Automation (ActiveX) applications that can do everything an ASP script can do*/
--Creates an instance of the OLE object
------------------------------------------------------
EXEC @hr=sp_OACreate 'Scripting.FileSystemObject',@fso OUT
SET @MB = 1048576
SET @RowId_1 = 1
SET @LoopStatus_1 = 1
------------------------------------------------------
--To Get Drive total space
------------------------------------------------------
WHILE (@LoopStatus_1 <> 0) BEGIN
SELECT
@drive=drive,
@FreeSpace=FreeSpaceMB
FROM
#drives
WHERE
( ID = @RowId_1 )
IF ( @@ROWCOUNT = 0 )
BEGIN
SET @LoopStatus_1 = 0
END
ELSE
BEGIN
EXEC @hr = sp_OAMethod @fso,'GetDrive', @odrive OUT, @drive
EXEC @hr =sp_OAGetProperty @odrive,'TotalSize', @TotalSize OUT
UPDATE #drives SET TotalSizeMB=@TotalSize/@MB
WHERE
drive=@drive
UPDATE #drives SET percentageOfFreeSpace=(@FreeSpace/(TotalSizeMB*1.0))*100.0
WHERE drive=@drive
END
SET @RowId_1 = @RowId_1 + 1
END
SELECT @RowId_2=1,@LoopStatus_2=1
------------------------------------------------------
--To prepare insert statement
------------------------------------------------------
WHILE (@LoopStatus_2 <> 0) BEGIN
SET @DML=''
SELECT
@drive1=drive,
@FreeSpace=FreeSpaceMB,
@TotalSizeMB=TotalSizeMB,
@FreeSpaceMB=FreeSpaceMB,
@percentageOfFreeSpace=percentageOfFreeSpace
FROM
#drives
WHERE
( ID = @RowId_2 )
IF ( @@ROWCOUNT = 0 )
BEGIN
SET @LoopStatus_2 = 0
END
ELSE
BEGIN
SET @DML=@DML+ 'insert into TLOG_SpaceUsageDetails(servername,drive,TotalSizeMB,FreeSpaceMB,percentageOfFreeSpace)values('+''''+@@servername+''''+','+''''+@drive1+''''+','+''''+@TotalSizeMB+''''+','+''''+@FreeSpaceMB+''''+','+''''+@percentageOfFreeSpace+'''' +')'
END
PRINT @DML
SET @RowId_2 = @RowId_2 + 1
END
drop table #drives
Execute SQL
Make sure sql file and output path is a shared path. We are going to write a concatenated output to spaceDetails.sql
The below three parameters are important to loop through all the listed servers
- Input server list
- Shared path where you can place query file
- Shared output path, the prepared insert statement are written into the file
MASTER..XP_CMDSHELL 'for /f %j in ( f:\servers.txt) do sqlcmd -S %j -i "\\share\hq\SpaceCheck.sql" -E >> "\\share\hq\SpaceDetails.sql"'
GO
MASTER..XP_CMDSHELL 'sqlcmd -S ABCD -i "\\share\hq\SpaceDetails.sql"'
Output
The output is selected by querying the TLOG table
select * from TLOG_SpaceUsageDetails
Method 2 - Querying WMI object
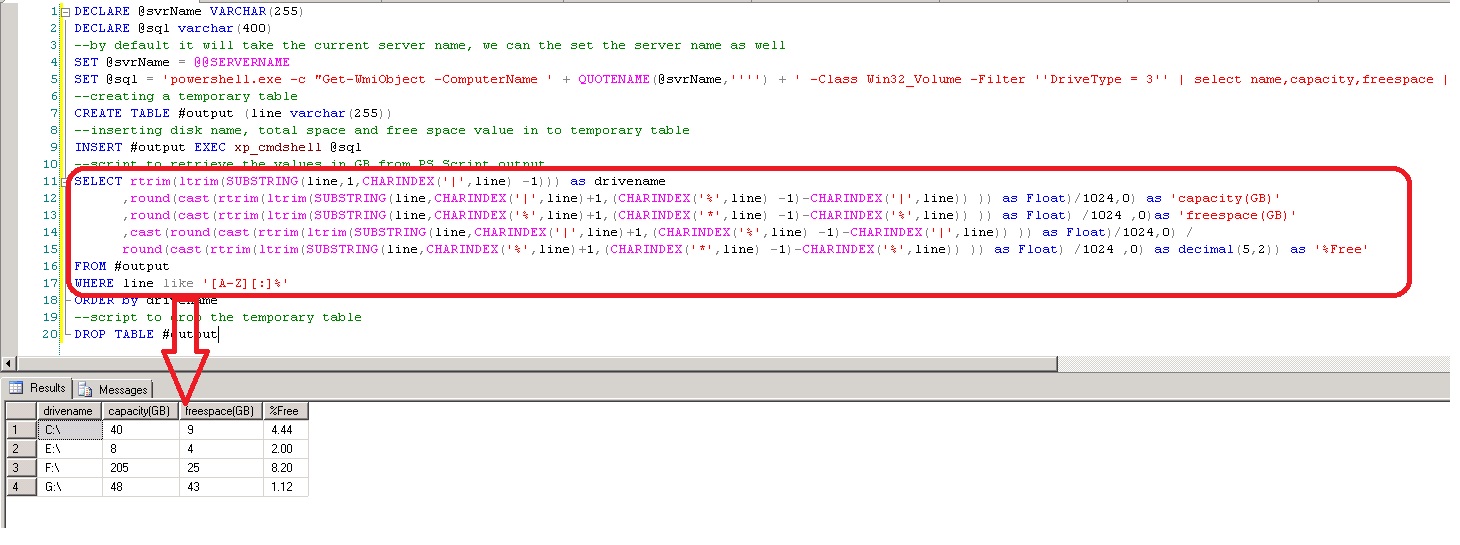
On Querying WMI Win32_volume class to gather volume names, free space, total size (capacity) into a temporary table using xp_cmdshell windows shell.
Using xp_cmdshell, the PowerShell.exe is being invoked to gather to required details and further stored in the temp table for manipulation.
You can pass the server name, By default it will take the current server name.
DECLARE @svrName VARCHAR(255)
DECLARE @sql varchar(400)
--by default it will take the current server name, we can the set the server name as well
SET @svrName = @@SERVERNAME
SET @sql = 'powershell.exe -c "Get-WmiObject -ComputerName ' + QUOTENAME(@svrName,'''') + ' -Class Win32_Volume -Filter ''DriveType = 3'' | select name,capacity,freespace | foreach{$_.name+''|''+$_.capacity/1048576+''%''+$_.freespace/1048576+''*''}"'
--creating a temporary table
CREATE TABLE #output (line varchar(255))
--inserting disk name, total space and free space value in to temporary table
INSERT #output EXEC xp_cmdshell @sql
--script to retrieve the values in GB from PS Script output
SELECT rtrim(ltrim(SUBSTRING(line,1,CHARINDEX('|',line) -1))) as drivename
,round(cast(rtrim(ltrim(SUBSTRING(line,CHARINDEX('|',line)+1,(CHARINDEX('%',line) -1)-CHARINDEX('|',line)) )) as Float)/1024,0) as 'capacity(GB)'
,round(cast(rtrim(ltrim(SUBSTRING(line,CHARINDEX('%',line)+1,(CHARINDEX('*',line) -1)-CHARINDEX('%',line)) )) as Float) /1024 ,0)as 'freespace(GB)'
,cast(round(cast(rtrim(ltrim(SUBSTRING(line,CHARINDEX('|',line)+1,(CHARINDEX('%',line) -1)-CHARINDEX('|',line)) )) as Float)/1024,0) /
round(cast(rtrim(ltrim(SUBSTRING(line,CHARINDEX('%',line)+1,(CHARINDEX('*',line) -1)-CHARINDEX('%',line)) )) as Float) /1024 ,0) as decimal(5,2)) as '%Free'
FROM #output
WHERE line like '[A-Z][:]%'
ORDER by drivename
--script to drop the temporary table
DROP TABLE #output
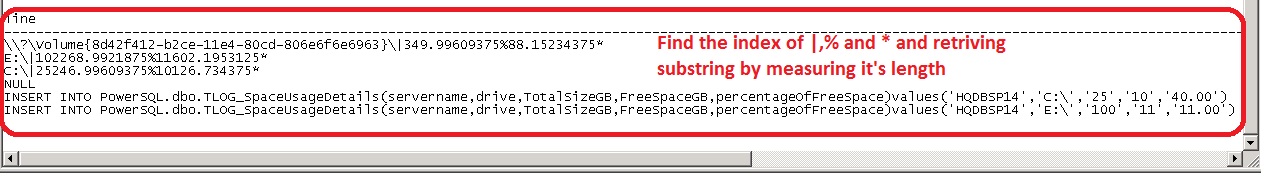
The output of the temp table is then parsed to get the required values using string functions. Using charindex string function, the index is found for the characters |,* and %. Based on the index the respective portion of the string fetched from the main string.
The advantage of this method is that xp_cmdshell enabled only the centralized machine. You don't have to enable it across all the servers also non-sql database servers space metrics can be gathered as we are querying WMI class.
Pre-requisites
We can check the disk space by executing a T-SQL script using xp_cmdshell from SSMS. In order to do this, you need to make sure that xp_cmdshell is enabled on the SQL instance. You can execute the below script to check and enable XP_Cmdshell. To enable XP_Cmdshell you must have at least the ALTER SETTINGS server-level permission.
- Enable xp_cmdshell Only on the centralized Server.
Data Flow Diagram
This process requires enabling xp_cmdshell windows shell components only on the centralized servers. The servers are traversed one by one via batch scripting along with sqlcmd and the result is stored in a file. This file has a collection of insert SQL statements. later the insert statement is executed on the centralized server. The repository can be queried, used for forecasting and capacity planning and reporting.
WMI - Capturing Disk Space of multiple servers
The section describes the requirements and briefs about every configuration required for successful execution of the code.
Step by Step details:
- Enable XP_CMDShell
- List all Servers in c:\Server.txt
- Table Creation [TLOG_SpaceUsageDetails]
- save T-SQL script in SpaceCheck.sql
- Execute dynamic sqlcmd from SSMS
- select the output by querying TLOG_SpaceUsageDetails
Enable xp_cmdshell
The xp_cmdshell option is a SQL Server server configuration option that enables system administrators to control whether the xp_cmdshell extended stored procedure can be executed on a system
sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1;
GO
RECONFIGURE;
GO
sp_configure 'xp_cmdShell', 1;
GO
RECONFIGURE;
GO
List servers in text file
Lists all the servers in a text file c:\server.txt and enable the OLE automation across all the servers. The other way to get around this problem is to include the sp_configure commands in the sql file and take it out after it's been executed across all the servers
ABC
DEF
EFG
Create SQL Table
Create TLOG_SpaceUsageDetails on the centralized server
CREATE TABLE [dbo].[TLOG_SpaceUsageDetails](
[ID] [int] IDENTITY(1,1) NOT NULL,
[ServerName] [VARCHAR](100) NULL,
[LogDate] [VARCHAR](10) DEFAULT (CONVERT([varchar](10),getdate(),(112))),
[Drive] [CHAR](3) NULL,
[FreeSpaceGB] [INT] NULL,
[TotalSizeGB] [INT] NULL,
[percentageOfFreeSpace] DECIMAL(5,2) NULL
) ON [PRIMARY]
GO
Create SQL File
Save the below content to sql file. for example, the content is saved under Spacecheck_v1.sql
The SQL file has two input parameters that are fed through sqlcmd.
- ServerName - The server name is used to query the respective server using WMI win32_volume computer name parameter also the Server name is used to prepare insert statement. The output of the insert statement is written to an sql file.
- dbname - The dbname used in conjunction with preparing a fully qualified name for the insert statement.
------------------------------------------------------
--variable declaration
------------------------------------------------------
DECLARE @svrName varchar(255),
@sql varchar(400),
@drive varchar(3),
@TotalSizeGB varchar(10),
@FreeSpaceGB varchar(10),
@percentageOfFreeSpace varchar(10),
@RowId_1 INT,
@LoopStatus_1 SMALLINT,
@DML nvarchar(4000)
------------------------------------------------------
--To stop the message that shows the count of number of rows affected.
------------------------------------------------------
SET NOCOUNT ON
------------------------------------------------------
--The servername parameter are fed through sqlcmd
------------------------------------------------------
SET @svrName = '$(servername)'
------------------------------------------------------
--Querying WMI class win32_volume and store the result into temporary table
------------------------------------------------------
SET @sql = 'powershell.exe -c "Get-WmiObject -ComputerName ' + QUOTENAME(@svrName,'''') + ' -Class Win32_Volume -Filter ''DriveType = 3'' | select name,capacity,freespace | foreach{$_.name+''|''+$_.capacity/1048576+''%''+$_.freespace/1048576+''*''}"'
------------------------------------------------------
--creating a temporary table
------------------------------------------------------
CREATE TABLE #output
(line varchar(255))
------------------------------------------------------
--inserting disk name, total space and free space value in to temporary table
------------------------------------------------------
INSERT #output
EXEC xp_cmdshell @sql
------------------------------------------------------
--Table to Store Drive related information
------------------------------------------------------
CREATE TABLE #drives
(
ID INT IDENTITY(1,1),
drive CHAR(5),
FreeSpaceGB INT ,
TotalSizeGB INT NULL,
percentageOfFreeSpace decimal(5,2)
)
------------------------------------------------------
--To Get Drive capacity and percentage of free space
------------------------------------------------------
select * from #output
INSERT INTO #drives(drive,TotalSizeGB,FreeSpaceGB,percentageOfFreeSpace)
------------------------------------------------------
--script to retrieve the values in GB from PS Script output
--Find the string for |,% and * using string function - CHARINDEX
------------------------------------------------------
SELECT rtrim(ltrim(SUBSTRING(line,1,CHARINDEX('|',line) -1))) as drivename
,round(cast(rtrim(ltrim(SUBSTRING(line,CHARINDEX('|',line)+1,(CHARINDEX('%',line) -1)-CHARINDEX('|',line)) )) as Float)/1024,0) as 'capacity(GB)'
,round(cast(rtrim(ltrim(SUBSTRING(line,CHARINDEX('%',line)+1,(CHARINDEX('*',line) -1)-CHARINDEX('%',line)) )) as Float) /1024 ,0)as 'freespace(GB)'
,cast(round(cast(rtrim(ltrim(SUBSTRING(line,CHARINDEX('%',line)+1,(CHARINDEX('*',line) -1)-CHARINDEX('%',line)) )) as Float) /1024 ,0)/round(cast(rtrim(ltrim(SUBSTRING(line,CHARINDEX('|',line)+1,(CHARINDEX('%',line) -1)-CHARINDEX('|',line)) )) as Float)/1024,0)*100 as decimal(5,2)) '%Free'
FROM #output
WHERE line like '[A-Z][:]%'
ORDER BY drivename
------------------------------------------------------
---select the output
------------------------------------------------------
--select * from #drives
------------------------------------------------------
-- Initialize the counters
------------------------------------------------------
SELECT @RowId_1=1,@LoopStatus_1=1
------------------------------------------------------
--To prepare insert statement, Have used a logic to concatenate the string into a @DML variable
------------------------------------------------------
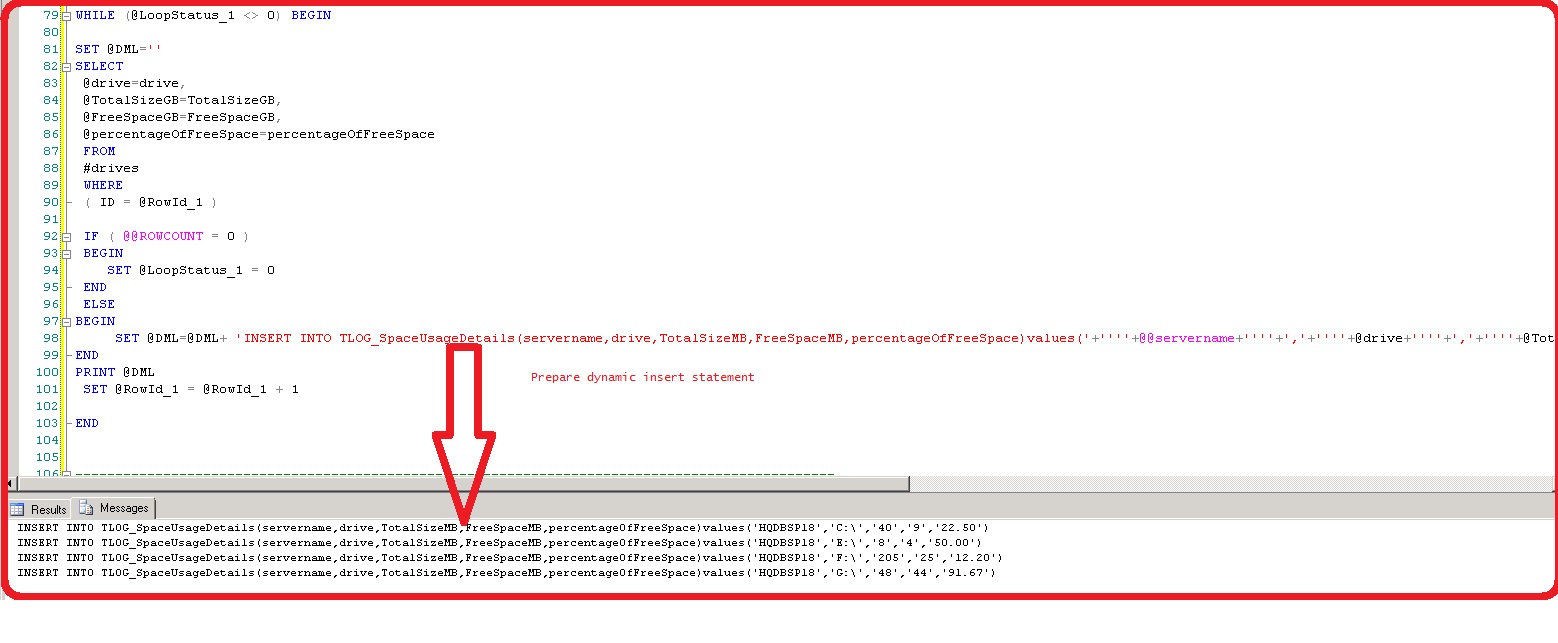
WHILE (@LoopStatus_1 <> 0) BEGIN
SET @DML=''
SELECT
@drive=drive,
@TotalSizeGB=TotalSizeGB,
@FreeSpaceGB=FreeSpaceGB,
@percentageOfFreeSpace=percentageOfFreeSpace
FROM
#drives
WHERE
( ID = @RowId_1 )
IF ( @@ROWCOUNT = 0 )
BEGIN
SET @LoopStatus_1 = 0
END
ELSE
BEGIN
SET @DML=@DML+ 'INSERT INTO $(dbname).dbo.TLOG_SpaceUsageDetails(servername,drive,TotalSizeGB,FreeSpaceGB,percentageOfFreeSpace)values('+''''+@svrName+''''+','+''''+@drive+''''+','+''''+@TotalSizeGB+''''+','+''''+@FreeSpaceGB+''''+','+''''+@percentageOfFreeSpace+'''' +')'
END
PRINT @DML
SET @RowId_1 = @RowId_1 + 1
END
------------------------------------------------------
--script to drop the temporary table
------------------------------------------------------
DROP TABLE #output
DROP TABLE #drives
The below SQL generates insert statement and written to file. The @DML concatenates the values into a string. The looping construct uses the pointer to traverse through record one by one.
SET @DML=@DML+ 'INSERT INTO $(dbname).dbo.TLOG_SpaceUsageDetails(servername,drive,TotalSizeGB,FreeSpaceGB,percentageOfFreeSpace)values('+''''+@svrName+''''+','+''''+@drive+''''+','+''''+@TotalSizeGB+''''+','+''''+@FreeSpaceGB+''''+','+''''+@percentageOfFreeSpace+'''' +')'
Execute SQL
The below sql requires
- Input file - it has the list of the servers
- SQL file - contains the sql code to executed across listed servers - need not to be in shared path
- Output file - the output of the sql file written into this file
- ServerName parameter for sqlcmd which is an input to WMI query
- DB name- Have used a static value. This depends on where are intended to create the sql table. This parameter used to prepare SQLInsert statement
MASTER..XP_CMDSHELL 'for /f %j in ( f:\PowerSQL\servers.txt) do sqlcmd -i "\\share\hq\SQL Server\SpaceCheck_v1.sql" -E -v servername=%j dbname="tempdb">> "\\share\hq\SQL Server\SpaceDetails_v1.sql"'
GO
MASTER..XP_CMDSHELL 'sqlcmd -S <CentralServerName>-i "\\share\hq\SQL Server\SpaceDetails_v1.sql"'
GO
SELECT * FROM TLOG_SpaceusedDetails
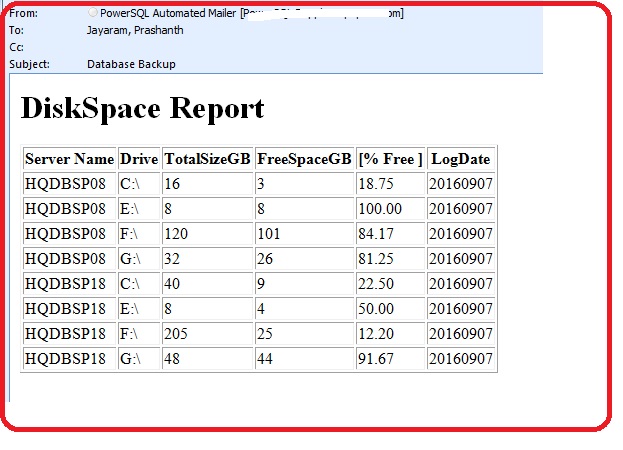
HTML Reporting
It requires database mail profile configured on the central server.
DECLARE @tableHTML NVARCHAR(MAX) ;
SET @tableHTML =
N'<H1>DiskSpace Report</H1>' +
N'<table border="1">' +
N'<tr><th>Server Name</th>
<th>Drive</th>
<th>TotalSizeGB</th>
<th>FreeSpaceGB</th>
<th>[% Free ]</th>
<th>LogDate</th>
</tr>' +
CAST ( (
Select
td=ServerName,' ',
td=Drive,' ',
td =TotalSizeGB,' ',
td=FreeSpaceGB,' ',
td=percentageOfFreeSpace,' ',
td=LogDate,' '
FROM [TLOG_SpaceUsageDetails]
where LogDate=CONVERT(varchar(10),getdate()-2,112)
FOR XML PATH('tr'), TYPE
) AS NVARCHAR(MAX) ) +
N'</table>' ;
EXEC msdb.dbo.sp_send_dbmail @recipients='pjayaram@appvion.com',
@subject = 'Database Backup',
@body = @tableHTML,
@profile_name= '<ProfileName>',
@body_format = 'HTML' ;
Highlights
- The working of sp_OA* OLE automation and xp_* extended stored procedures
- The use of xp_cmdhell - Windows SQL shell to execute WMI query and invoke Extended stored procedure
- Invoke PowerShell.exe using windows shell in SQL
- Batch programming with sqlcmd in SQL - The use of for loop construct to traverse each server
- Dynamic SQL to prepare the insert sql file
- Parameter passing for sqlcmd - Server and central database repository for data storage and manipulation
- Database mail configuration and HTML Reporting
Download
- SQL Server Operations: Monitoring Disk Space with WMI Class
- SQL Server Operations: Monitoring Disk Space with OLE Automation Objects
Conclusion
| Method1 v/s Method 2 | ||
| 1 | OLE automation procedure and xp_cmdshell components should be enabled on all the servers |
Enable xp_cmdshell configuration only on the central server |
| 2 | Non-SQL servers can't be monitored | Non-SQL servers can be monitored |
| 3 | Risk prone | Less risk-prone |
| 4 | Common share is required | Share is not mandatory, sql is executed on central server |
The OLE automation stored procedures provide access to the Component Object Model (COM), which grants Visual Basic or ASP scripting functionality to T-SQL scripts. It could be used to manipulate documents, utilize other COM-compatible code, or send e-mails etc:-
Warning: By default access to the OLE Automation stored procedures is disabled. If enabled it allows any SQL script to invoke any OLE Automation object on the computer (such as the Windows Shell). It is a significant security risk and should not be done lightly. For example you need to be extra careful to protect against SQL-injection attacks. It is basically the same as allowing xp_cmdshell.
The xp_cmdshell option is a server configuration option that enables system administrators to control whether the xp_cmdshell extended stored procedure can be executed on a system. Nowadays there is not much need of this particular command. I prefer doing this kind of administration tasks using PoSH. The PoSH provides to flexibility in many ways to handle such operations. However, there was a time when PoSH did not exist and we had to do lots of tasks with the help of the command shell.
Note:- The intention behind this article is not to expose the server to security risk. Its up to an individual to know an implication of using and enabling OLE automation
References
OLE Automation Objects
sqlcmd references
SQL Tips
Database Mail Profile