VB.Net: OOP Calculator - calc2
The purposes of this project was to create an OOP Calculator. More precisely, the Requirements Specification is:
The user should be able to implement a calculation consisting of performing a mathematical operation on two numbers and retrieve a result*.*
The Core Application
The words underlined were:
- **Calculation - **The Core classes of the application should include a Calculation class used for communicating between the core classes and the GUI.
- **Operation - **The Operator would consist of a one character variable in the Calculation class and there is no reason to make it a class.
- **Two numbers - **The two numbers involved in the calculation would both be represented by an instance of a Number class as it is appropriate to represent each number by a Decimal value and a String value, mainly due to the method of inputting numbers. It would also be useful to have methods to append and remove digits in this class.
- **Result - **As with the Operator there is no reason to make this a class, but also in this case it is not necessary even as a variable either.
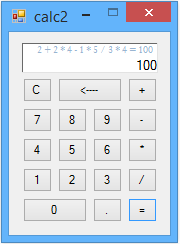 ** Figure 1. **The method used for saving
** Figure 1. **The method used for saving
the result allows long strings of multiple calculations.
So after analyzing the project requirements the core application consists of just two classes.

Figure 1.1. The distinct core classes
A Calculation class with several properties used in differentiating between various input values, with one Public function the push method which is used for passing and retrieving values to and from the GUI. The Calculation class has three notable properties, two to represent Number class instances and an [Operator] property. I haven't posted the Calculation class in this article, but it's available in the download.
This shows the instances of the classes and the Relationship between them:

Figure 1.2. Instances and Relationship
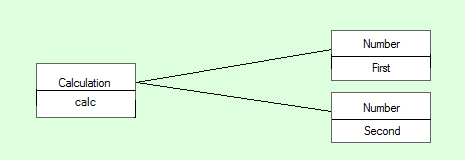
Figure 1.3. Core classes diagram
The Number class has a Decimal property and a String property, both of which are used to keep track of numbers and two functions for adding and removing digits.
By some juggling of the two Number classes property values it's possible to perform long strings of multiple calculations (see Figure 1).
The Number class:
Public Class Number
#Region " properties"
Private _value As Decimal
Public Property value() As Decimal
Get
Return _value
End Get
Set ( ByVal value As Decimal)
_value = value
End Set
End Property
Private _valueString As String = ""
Public Property valueString() As String
Get
If _valueString.StartsWith(".") Then
Return "0" & _valueString
End If
Return _valueString
End Get
Set ( ByVal value As String)
_valueString = value
If _valueString <> "." AndAlso _valueString <> "" AndAlso _valueString <> "-" Then
Me .value = CDec (_valueString)
Else
Me .value = 0D
End If
End Set
End Property
#End Region
#Region " functions"
''' <summary>
''' handles parsing button input to decimal
''' </summary>
''' <param name="aValue">the button text</param>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Function appendDigit(aValue As String) As String
If aValue = "." Then
If Not Me.valueString.Contains(".") Then
Me .valueString &= aValue
End If
Else
Me .valueString &= aValue
End If
If Not valueString = "." AndAlso _valueString <> "-" Then
Me .value = CDec (valueString)
Else
Me .value = 0
End If
Return Me.valueString
End Function
''' <summary>
''' handles removing digits with the backspace button,
''' then parsing the remaining digits as decimal
''' </summary>
''' <returns></returns>
Public Function backSpace() As String
If Me.valueString.Length > 0 Then
Me .valueString = Me .valueString.Substring(0, valueString.Length - 1)
End If
If Not Me.valueString = "." AndAlso Not Me.valueString = "" AndAlso Not Me.valueString = "-" Then
Me .value = CDec ( Me .valueString)
Else
Me .value = 0
End If
Return Me.valueString
End Function
#End Region
End Class
The GUI
Figure 2. The GUI.
In terms of component controls the GUI consists of a Panel, 18 Buttons, an extended TextBox, and a Label. At runtime the TextBox and the Label appear as one control (see Figure 1.). The TextBox is restricted to allow no other input except the programmatic input from the Core classes.
The Form code is limited to handling the Panel_Paint event where it draws a border around the Label and TextBox, handling all of the Button click events in one handler, and capturing keyboard input. The 18 Buttons are the only Controls that respond to user input, either through mouseclicks or by typing the number, operator, or controlchar keys.
This is the Form code:
Public Class calcForm
''' <summary>
''' this is the calculator object
''' </summary>
Private calc As New Calculation
''' <summary>
''' the textbox is actually a textbox with a label above it.
''' this draws a border around both controls to give the appearance of one control
''' </summary>
''' <param name="sender"></param>
''' <param name="e"></param>
Private Sub Panel1_Paint(sender As Object, e As PaintEventArgs) Handles Panel1.Paint
Dim r As New Rectangle(TextBox1.Left - 1, Label1.Top - 1, Label1.Width + 2, Label1.Height + TextBox1.Height + 2)
ControlPaint.DrawBorder3D(e.Graphics, r, Border3DStyle.SunkenInner)
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' this sets up the buttons for keyboard or mouseclick input
''' </summary>
''' <param name="sender"></param>
''' <param name="e"></param>
Private Sub Form1_Load(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles MyBase.Load
Me.KeyPreview = True
For Each b As Button In Panel1.Controls.OfType(Of Button)
AddHandler b.Click, AddressOf button_clicked
Next
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' onclick the button's text is sent to the calculator object's push method
''' which handles all input, and returns the textual output for the textbox and the label
''' </summary>
''' <param name="sender"></param>
''' <param name="e"></param>
Private Sub button_clicked(sender As Object, e As EventArgs)
Dim output() As String = calc.push(DirectCast(sender, Button).Text)
TextBox1.Text = output(0)
Label1.Text = output(1)
End Sub
''' <summary>
''' this converts keyboard input into button clicks
''' </summary>
''' <param name="sender"></param>
''' <param name="e"></param>
Private Sub Form1_KeyPress(sender As Object, e As KeyPressEventArgs) Handles Me.KeyPress
If e.KeyChar = Chr(Keys.Back) Then
Button1.PerformClick()
Else
Dim btn As Button = Panel1.Controls.OfType(Of Button).FirstOrDefault(Function(b) b.Text.ToLower = e.KeyChar)
If Not btn Is Nothing Then
btn.PerformClick()
End If
End If
End Sub
End Class
The extended TextBox assigns a new empty ContextMenuStrip to the TextBox, which has the effect of removing the right click menu. The Cut, Copy, Paste, Clear, and Undo keyboard shortcuts are also detected and nullified.
This is the restrictedTextBox code:
''' <summary>
''' removes the textbox contextmenustrip and disables keyboard shortcuts
''' </summary>
Public Class restrictedTextBox
Inherits TextBox
Const WM_CUT As Integer = &H300
Const WM_COPY As Integer = &H301
Const WM_PASTE As Integer = &H302
Const WM_CLEAR As Integer = &H303
Const WM_UNDO As Integer = &H304
Public Sub New()
Me.ContextMenuStrip = New ContextMenuStrip
End Sub
Protected Overrides Sub WndProc(ByRef m As Message)
Dim disabledOperations() As Integer = {WM_CUT, WM_COPY, WM_PASTE, WM_CLEAR, WM_UNDO}
If disabledOperations.Contains(m.Msg) Then Return
MyBase.WndProc(m)
End Sub
End Class
Other Resources
Full article and download here...
