Calculate Fractions in VB.NET
Scope
In this brief article, we'll see a simple method to convert the decimal part of a number into its fractional representation, developing a reusable class apt to that mean. To that end, we'll use Visual Basic .NET.
Calculate and simplify a fraction
To calculate a fraction, we must separate a number's integral part from the decimal one, to work on the latter to express it in terms of numerator and denominator. Let's take for example the number 12.65. We will first express it as 12 + 0.65, proceeding then in writing our decimal part as the largest non-simplified fraction. Since we have two decimals after the dot, the larger denominator we need is 100. So, we can express our 0.65 as 65/100. Then, using the common rules based on finding the GDC (Greatest Common Divisor), we can simplify our fraction, down to 13/20.
Finding the Greatest Common Divisor
Here follows an easy snippet of code to help to find the GDC between two numbers:
Private Function gcd(ByVal n1 As Integer, ByVal n2 As Integer) As Long
Dim minimum As Long
If n1 < n2 Then
minimum = n1
Else
minimum = n2
End If
For i As Long = minimum To 1 Step -1
If n1 Mod i = 0 And n2 Mod i = 0 Then
Return i
End If
Next
End Function
Calculate a fraction
Here follows the routine that will calculate our fraction: it needs a decimal-type input parameter (as the 12.65 used above)
Public Function Calculate(value As Decimal) As String
Dim intPart As Long = Math.Truncate(value)
Dim numerator As Long = CType((value - intPart).ToString.Substring(2), Long)
Dim denominator As Long = CType("1" & StrDup(numerator.ToString.Length, "0"), Long)
Dim _gcd As Long = gcd(numerator, denominator)
Dim nDiv As Long = _gcd
While nDiv > 1
If numerator Mod nDiv = 0 And denominator Mod nDiv = 0 Then
numerator /= nDiv
denominator /= nDiv
nDiv = _gcd
Else
nDiv -= 1
End If
End While
Dim retVal As String = ""
If intPart > 0 Then retVal = intPart.ToString & " + ("
retVal &= numerator.ToString + " / " + denominator.ToString
If intPart > 0 Then retVal &= ")"
Return retVal
End Function
The function will save an integral part of the number for later use, then proceeds in calculating the maximum denominator, by adding a number of zeros to equal the number of decimal places. A call to our previously written GCD routine will compute the Greatest Common Divisor between our numerator and denominator, entering a loop through which we proceed in dividing numerator and denominator for their common divisors until no common divisor is available.
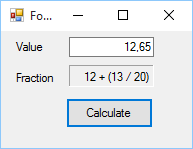
At last, having determined the simplified numerator and denominator, the routine will produce their string representation, joining an integral part. So, for our previous example of value = 12.65, the output will be: 12 + (13/20).
As the reader can note, in case no integral part is present, the fraction will be expressed without parenthesis.
Fraction class
The complete source for a reusable class can be the following:
Public Class Fraction
Dim _value As Decimal
Dim _fraction As String
Public ReadOnly Property Value As String
Get
Return _fraction
End Get
End Property
Public Property Number As Decimal
Get
Return _value
End Get
Set(value As Decimal)
_value = value
_fraction = Calculate(_value)
End Set
End Property
Public Sub New(value As Decimal)
_value = value
_fraction = Calculate(_value)
End Sub
Public Sub New()
_value = 0
_fraction = 0
End Sub
Private Function gcd(ByVal n1 As Integer, ByVal n2 As Integer) As Long
Dim minimum As Long
If n1 < n2 Then
minimum = n1
Else
minimum = n2
End If
For i As Long = minimum To 1 Step -1
If n1 Mod i = 0 And n2 Mod i = 0 Then
Return i
End If
Next
End Function
Public Function Calculate(value As Decimal) As String
Dim intPart As Long = Math.Truncate(value)
Dim numerator As Long = CType((value - intPart).ToString.Substring(2), Long)
Dim denominator As Long = CType("1" & StrDup(numerator.ToString.Length, "0"), Long)
Dim _gcd As Long = gcd(numerator, denominator)
Dim nDiv As Long = _gcd
While nDiv > 1
If numerator Mod nDiv = 0 And denominator Mod nDiv = 0 Then
numerator /= nDiv
denominator /= nDiv
nDiv = _gcd
Else
nDiv -= 1
End If
End While
Dim retVal As String = ""
If intPart > 0 Then retVal = intPart.ToString & " + ("
retVal &= numerator.ToString + " / " + denominator.ToString
If intPart > 0 Then retVal &= ")"
Return retVal
End Function
End Class
In the source code that comes with that article, we've implemented a simple WinForm, with a TextBox and some Labels, to show how the previous code works.
The code behind will be simple as this:
Public Class Form1
Dim f As New Fraction
Private Sub Button1_Click(sender As Object, e As EventArgs) Handles Button1.Click
f.Number = CType(TextBox1.Text, Decimal)
Label3.Text = f.Value
End Sub
End Class
When the Button is clicked, the Number property of our Fraction class will be initialized with a cast towards a Decimal type of what is contained in TextBox1.
Next, the property Value (which will contain our fraction string) will be shown in Label3.
Source Code
The sample code for this article can be downloaded from this link: https://code.msdn.microsoft.com/Calculate-Fractions-in-75d539e7
Other Languages
The present article is available in the following localizations: