Stubs and Shims
Stubs and Shims
Stubs: Stubs replace the functionality with the different implementation. One should have interface based programming i.e. we cannot directly instantiate a class, instead you should be using the interface (which helps in replacing the original functionality with the stub, based on the same interface).
Shims: Replace the functionality provided by .NET framework. It modifies the complied code at runtime to replace the method call.
Stubs Example: The functionality in class EmployeeRepositrywill search for an employee in the list. This class implement the interface IEmployeeRepositry
public class Employee
{
public string FirstName { get; set; }
public string LastName { get; set; }
}
public interface IEmployeeRepositry
{
Employee FindEmployee(Employee emp);
}
public class EmployeeRepositry : IEmployeeRepositry
{
List<Employee> list;
public EmployeeRepositry()
{
list = new List<Employee>{new Employee{FirstName = "Girish",LastName = "Goudar" },
new Employee{FirstName = "Deepak",LastName = "H" }};
}
public Employee FindEmployee(Employee emp)
{
return list.Find(item =>item.FirstName.Equals(emp.FirstName));
}
}
**Unit testing without stubs:**Unit test calls the Employee repository FindEmployeemethod to search for an employee
** **
** ** publicvoid TestMethod1()
{
Employeeemp = newEmployee();
emp.FirstName = "Girish";
emp.LastName = "Singh";
IEmployeeRepositryrepositry = newEmployeeRepositry();
Employeeemployee = repositry.FindEmployee(emp);
Assert.AreEqual(emp.FirstName,employee.FirstName);
}
}
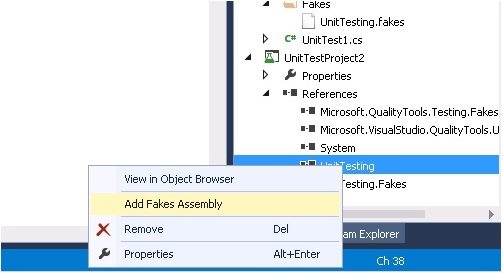
Unit testing with stubs: Generate the fakes assembly using the Microsoft fakes framework and the stub methods will be generated as shown.
** **
** **
The stub method is created as “FindEmployeeEmployee”.The name convention used will be first the name of the method and then the type of parameter name
** **
The Interface IEmployeeRepositry this time will use the stub employee repository and provide its own implementation of the FindEmployee method.
** **
** **
** ** publicvoid TestMethod1()
{
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.FirstName = "Girish";
emp.LastName = "Singh";
** IEmployeeRepositry repositry = new StubIEmployeeRepositry()**
** {**
** FindEmployeeEmployee = emp1 =>**
** {**
** return new Employee { FirstName ="Mohan",LastName ="v"};**
** }**
** };**
Employee employee = repositry.FindEmployee(emp);
Assert.AreEqual(emp.FirstName,employee.FirstName);
}
**Shims Example:**The functionality in class EmployeeRepositrywill search for an employee in the list.Shims can be used to replace calls to assemblies that you cannot modify, such .NET assemblies.
public class EmployeeRepositry
{
List<Employee> list;
public EmployeeRepositry()
{
list = newList<Employee>{newEmployee{FirstName = "Girish",LastName = "Goudar" },
newEmployee{FirstName = "Deepak",LastName = "H" }};
}
public Employee FindEmployee(Employee emp)
{
returnlist.Find(item =>item.FirstName.Equals(emp.FirstName));
}
**Unit testing with shims:**Consider the EmployeeRepositryClass to be part of3rd party solution or legacy code which cannot be refactored by us. Use the shims created by Microsoft fakes framework as shown.
publicvoid TestMethod1()
{
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.FirstName = "Girish";
emp.LastName = "Singh";
using (ShimsContext.Create())
{
EmployeeRepositryrepositry = new ShimEmployeeRepositry()
{
FindEmployeeEmployee = emp1 =>
{
return new Employee { FirstName = "Girish", LastName = "v" };
}
};
Employee employee = repositry.FindEmployee(emp);
Assert.AreEqual(emp.FirstName, employee.FirstName);
}
}
Difference between stubs and shims
** **
|
Stubs |
Shims |
Static methods, sealed types |
You can only use stubs to implement interfaces. Therefore, stub types cannot be used for static methods, non-virtual methods, sealed virtual methods, methods in sealed types |
Shims can be used for Static methods and sealed types |
Internal types |
Stubs can be used with internal types that are made accessible by using the assembly attribute InternalsVisibleToAttribute. |
Shims can be used with internal types that are made accessible by using the assembly attribute InternalsVisibleToAttribute. |
Private methods |
Stubs can only replace visible methods. |
Shims can replace calls to private methods if all the types on the method signature are visible. |
Interfaces and abstract methods |
Stubs provide implementations of interfaces and abstract methods that can be used in testing |
Shims can’t instrument interfaces and abstract methods, because they don’t have method bodies. |
Performance |
Stubs do not have this performance overhead and are as fast as virtual methods can go |
Shims run slower because they rewrite your code at run time |