Microsoft Azure and Availability Sets for VMs
Introduction
Behind the scenes, Microsoft Azure is actually racks of servers, network equipment and storage that have virtualization capabilities. As any physical equipment in the world might face failures and downtimes, it might happen that VMs hosted in Microsoft Azure become temporary not available. This Wiki article describes how to minimize the impacts of similar events on your services running on Microsoft Azure VMs by using the Availability Sets.
What are Availability Sets and how can they improve the availability of services running on VMs?
By running multiple VMs to provide the same service on Microsoft Azure, you are certainly trying to introduce a high availability and minimize the downtime of the service. However, Microsoft will have no idea about what your VM is used for and this may end up in having your VMs running on the same physical hardware or using a common power source and network switch. In case of a planned or unplanned maintenance, this may end with your service fully down while it was possible to avoid it.
By using Availability Sets for VMs, you are telling Microsoft that a group of VMs are used to provide the same service for high availability reasons and should not be down in the same time. That is very important to have as you cannot choose where your VM resides but Microsoft can and will provide you with a better pinning when you provide the required information about your environment.
Availability Sets for VMs is then a feature provided by Microsoft Azure that is used to regroup VMs providing the same service to minimize the risk of full interruption when a planned or an unplanned maintenance is done.
How are Availability Sets working?
Availability Sets are using the following domains:
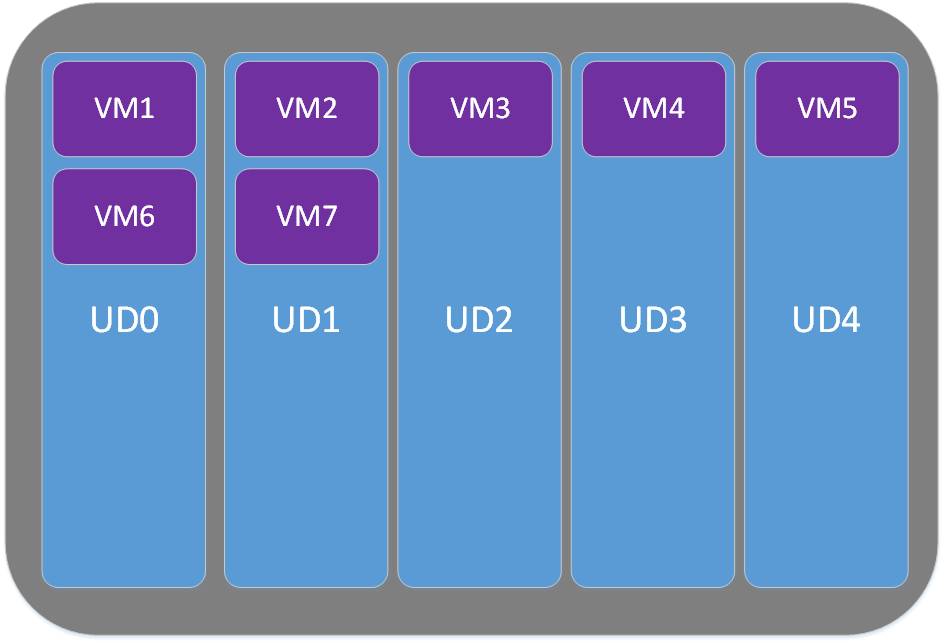
- Update Domain (UD): They define physical hardware that can be rebooted at the same time. Each Availability Set has five (5) UDs. When you assign a VM to an Availability Set, it will be part of the next available UD. If you have more than five (5) VMs then the VM number 6 will take the same UD as the VM number 1, the VM number 7 will take the same UD as the VM number 2 and so on. Below is a screen capture about how VMs are assigned to UDs in case you have seven (7) VMs part of the Availability Set
Let’s suppose that UD1 will be rebooted. You will then have VM1 and VM6 not available while the other VMs are still up and running. Your service will continue running with no interruption.
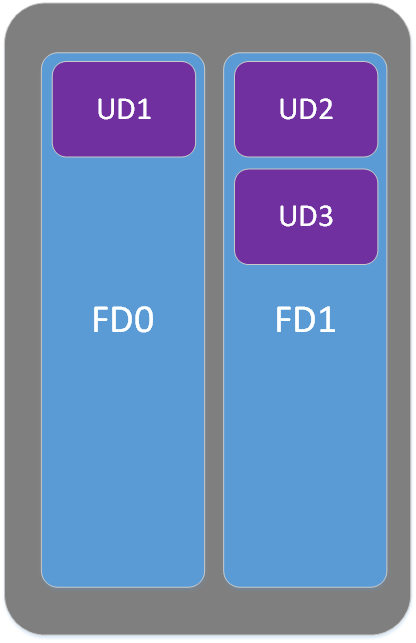
- Fault Domain (FD): They define the group of VMs that share a common power source and network switch. Each Availability Set has two (2) FDs and VMs will be assigned to both of them.
How can we know the VMs assignment to UDs and FDs?
It is true UDs and FDs assignments are not user-configurable. However, Microsoft Azure allows its administrators to get the details about the current assignments.
This could be done by using the following method:
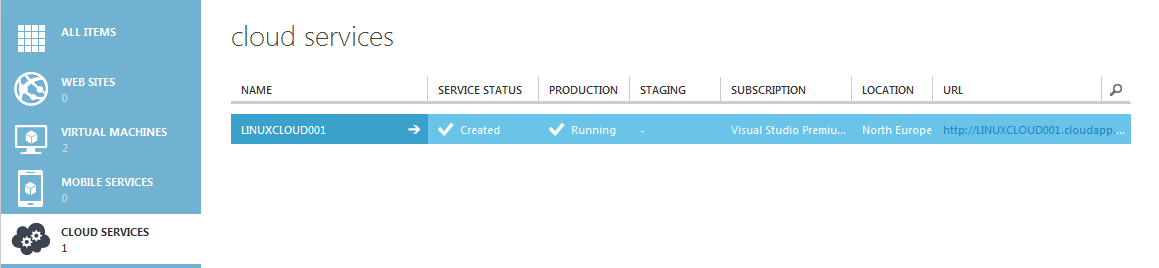
- Go to CLOUD SERVICES and then click on your cloud service
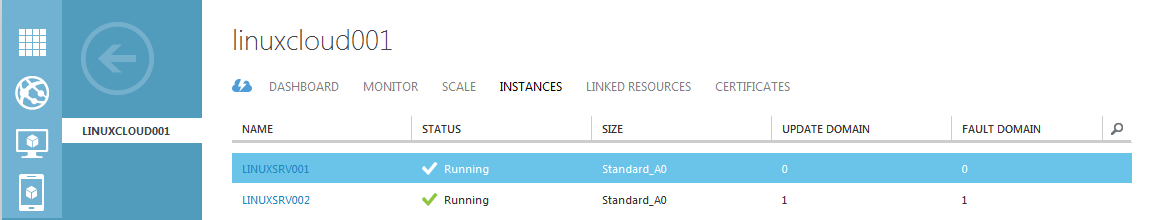
- Go to INSTANCES tab and you will get the details
Conclusion
Availability Sets is a Microsoft Azure feature that provides details to Microsoft about VMs that are providing the same service and should not be down at the same time. This makes Microsoft do a better assignment of these VMs to physical hardware, power source sources and network switches using Update Domains (UDs) and Fault Domains (FDs). The expected output is that, when a planned or an unplanned maintenance is done, your service will not be fully down.