C#: Asynchronous Programming Using Delegates
Introduction
Delegated allows us to call any synchronous method asynchronously. In this post we will discuss way of doing this.
BeginInvoke() :
When a delegate is called using BeginInvoke it has same parameters as the method that we want to execute and two other parameters.
- AsyncCallback :delegate that references a method to be called when the asynchronous call completes
- Sender Object: a user-defined object that passes information into the callback method
Step by Step
Lets see how this could be done step by step:
Step 1: Define delegate & call it asynchronously
As the first step we can do the following.
- Define a delegate with same signature as the method to be called asynchronously
- Assign the method to be called asynchronously to the delegate
- Invoke the delegate asynchronously
See the sample code here:
//Define a delegate with same signature as the method to be called asynchronously
private delegate void UpdateWorkLogHandler(int hours, string workType);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
DoWork(10, "Development");
}
public static void DoWork(int hours, string workType)
{
//Assign the method to be called asynchronously to the delegate
UpdateWorkLogHandler updateWorkLogHandler = UpdateWorkLog;
//Invoke the delegate asynchronously
updateWorkLogHandler.BeginInvoke(hours, workType, null, null);
Console.WriteLine("Work Completed!. Log updating in progress");
Console.ReadLine();
}
public static void UpdateWorkLog(int hours, string workType)
{
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("Work log updated!");
Console.ReadLine();
}
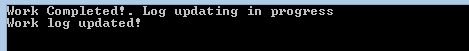
*Output Window :
**
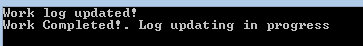
***We can see here before completion of UpdateWorkLog method, programs has printed the “Work Completed!. Log updating in progress”. It is because as UpdateWorkLog is called asynchronously rest of the code in DoWork method is been executed. If we have invoked the delegate without BeginInvoke output will be the following.
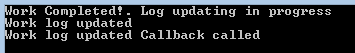
Step 2: With Callback
In case we want to know whether that method is executed and call back to a method which we define & then execute some other logic we can assign a callback method on BeginInvoke as below.
//Define a delegate with same signature as the method to be called asynchronously
private delegate void UpdateWorkLogHandler(int hours, string workType);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
DoWork(10, "Development");
}
public static void DoWork(int hours, string workType)
{
//Assign the method to be called asynchronously to the delegate
UpdateWorkLogHandler updateWorkLogHandler = UpdateWorkLog;
//Invoke the delegate asynchronously
updateWorkLogHandler.BeginInvoke(hours, workType, UpdateWorkLogCompleted, null);
Console.WriteLine("Work Completed!. Log updating in progress");
Console.ReadLine();
}
//Callback Method
public static void UpdateWorkLogCompleted(IAsyncResult ar)
{
Console.WriteLine("Work log updated Callback called");
Console.ReadLine();
}
public static void UpdateWorkLog(int hours, string workType)
{
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("Work log updated");
}
Step 3: With EndInvoke
In case we need a return value from the asynchronously called method we can use EndInvoke.
The EndInvoke method retrieves the results of the asynchronous call. It can be called any time after BeginInvoke. If the asynchronous call has not completed, EndInvoke blocks the calling thread until it completes.
See the sample code below. It take the return value and then do the rest of the execution.
//Define a delegate with same signature as the method to be called asynchronously
private delegate bool UpdateWorkLogHandler(int hours, string workType);
static void Main(string[] args)
{
DoWork(10, "Development");
}
public static void DoWork(int hours, string workType)
{
//Assign the method to be called asynchronously to the delegate
UpdateWorkLogHandler updateWorkLogHandler = UpdateWorkLog;
//Invoke the delegate asynchronously
IAsyncResult result= updateWorkLogHandler.BeginInvoke(hours, workType,null,null);
Console.WriteLine("Work Completed!. Log updating in progress");
// Call EndInvoke and get the returned value
bool returnedValue = updateWorkLogHandler.EndInvoke(result);
UpdateWorkLogCompleted(returnedValue);
Console.WriteLine("Do Work Completed");
Console.ReadLine();
}
//Callback Method
public static void UpdateWorkLogCompleted(bool result)
{
Console.WriteLine("Work log updated Callback called Result:"+ result);
}
public static bool UpdateWorkLog(int hours, string workType)
{
System.Threading.Thread.Sleep(1000);
Console.WriteLine("Work log updated");
return true;
}
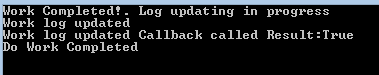
*Output Window :
**
So can see here it has received the return value. Also the it did not execute the rest of the code until after EndInvoke until it received the returned value.