Microsoft Security Compliance Manager (SCM): Release Notes
The [[Microsoft Security Compliance Manager (SCM)]] engineering team is constantly improving the tool and maintains this article to share the latest release information and known issues.
Version History
SCM v3.0.60.0 (January 28, 2013)
**
**In addition to key features from the previous version, SCM 3.0 offers new baselines for Windows Server 2012, Windows 8, and Internet Explorer 10! SCM enables you to quickly configure and manage computers and your private cloud using Group Policy and Microsoft System Center Configuration Manager.
SCM v2.5.40 (April 2, 2012)
**
**The latest version of the SCM tool includes the following new features, tools, and capabilities to help you manage product baselines from Microsoft, and other baselines that you can customize to meet the requirements of your organization:
- New product baselines designed to take full advantage of the security features and options in Microsoft Exchange Server 2010 SP2 and Exchange Server 2007 SP3. The product baselines are designed to harden the following server roles for Exchange Server: Client Access, Mailbox, Hub Transport, Edge Transport, and Unified Messaging. New Windows PowerShell-based script kits are included to assist you in applying the Exchange Server baseline settings to the servers in your environment. For more information, see the Exchange Server 2010 SP2 PowerShell Script Kit User Guide and the Exchange Server 2007 SP3 PowerShell Script Kit User Guide in the Attachments \ Guides node of these Microsoft product baselines in SCM.
- IT Governance, Risk, and Compliance (IT GRC) baseline information for many Microsoft product baselines is now available in SCM. These Microsoft baselines include new compliance-based setting groups that allow quicker and easier compliance reporting and audit preparation. SCM is designed to work closely with IT GRC solutions from Microsoft.
SCM v2.0.20.0 (September 27, 2011)
This version of the SCM tool included the following new features, tools, and capabilities:
- IT Governance, Risk, and Compliance (IT GRC) baseline information on Windows Server operating system baselines.Improved GPO Backup (folder) feature that provides a more robust import process.
- Simplified setting management to help you manage your product baselines in setting groups, and the Advance View feature that you can use in multiple ways to filter baseline setting information.
- The LocalGPO command-line tool that you can use to back up a domain-based Group Policy Object (GPO) and then apply it to non-domain joined computers in your environment. The new version of this tool also makes it easier to automate this process.
- Improved Compare / Merge feature that provides the ability to export comparison results to Excel format.
SCM v1.1.3.0 (December 6th, 2010)
- SCM Import: fixed ability to import baselines which contain .ZIP file attachments (SQL / Exchange baselines)
SCM v1.1.2.0 (November 19th, 2010)
- SCM Download: fixed ability to obtain baselines and application updates behind some proxy servers
SCM v1.1.1.0 (September 8th, 2010)
- SCM UI: fixed various display problems when using a very low screen resolution
- SCM Export: optimized the .CAB file size when users export in the SCM baseline format
- Local GPO tool: fixed local import of settings so that this tool now applies them incrementally (instead of full reset)
SCM v1.0.0.0 (April 6th, 2010)
- Initial Release
Update Existing Installation
The following procedure is the only way to install the latest version of the SCM tool and not re-install the database for the tool to avoid losing your data. Use the Upgrade option in the SCM setup wizard to complete this procedure.
Important Before using the following procedure, do not manually uninstall or delete the SCM tool or database schema on your computer.
To use the Upgrade option in the SCM setup wizard:
**
**1. Check for updates in your currently installed version of SCM. To do so, on the main menu of the tool, click File, and then click Check for Updates Ctrl+U.
2. When prompted, download SCM 3.0 to a desired location on your computer.
3. Double-click the Security_Compliance_Manager_Setup.exe to start the Microsoft Security Compliance Manager Setup Wizard, click the SCM install link, and then follow the steps in the wizard until you reach the Configuration Options page.
4. On the Configuration Options page, click the Upgrade the Microsoft Security Compliance Manager option, and then click Next.
5. Complete the remaining installation steps of the setup wizard.
Known Issues
The following are known issues for the SCM 3.0 tool:
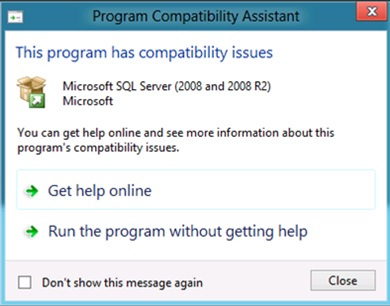
- If you perform a clean installation of SCM 3.0 on a computer running either Windows 8 or Windows Server 2012 that does not also have Microsoft SQL Server software installed on it, you may receive the following compatibility warning message.
This is a known issue that causes this message to display after installing Microsoft SQL Server 2008 R2 on a computer running either Windows 8 or Windows Server 2012. The workaround to resolve this issue is to click the Run the program without getting help option on the warning message and then proceed with the SCM 3.0 installation. SCM 3.0 will install on the computer without any impact from the warning message.
- For known issues related to a baseline, double click release note URL in the related product attachment folder in SCM UI
- The GPO import feature in SCM may introduce settings that are not in your original GPO. This is because a GPO is product agnostic. We found some settings in different products have exactly the same GPO data. Examples:
- The setting "Windows Firewall: Prohibit notifications" in Windows Vista shares the same registry data as the setting "Windows Firewall: Domain: Display a notification" in Windows 7 SP1.
- The setting "Windows Firewall: Prohibit unicast response to multicast or broadcast requests" in Windows Vista has the same registry data as the setting "Windows Firewall: Domain: Allow unicast response" in Windows 7 SP1.
- For this reason, if a GPO for Windows 7 SP1 with the configured setting "Windows Firewall: Domain: Display a notification" is imported into SCM, an unexpected setting called "Windows Firewall: Prohibit notifications" appears. The workaround to fix this issue is to manually remove the unexpected settings from the GPO.
- The value of the setting "Allow users to connect remotely using Remote Desktop Services" is imported incorrectly when a GPO contains this setting. The workaround for this issue is to manually configure the setting value in the SCM UI.
- The domain part of the account in the format of domain\user is missing after importing the setting "Profile System Performance" from a GPO. The workaround for this issue is to manually define the domain part of the account in the SCM UI after importing this setting from a GPO.
- The value of the setting "Audit: Audit the use of Backup and Restore privilege" is not configured correctly when a GPO is imported. The workaround for this issue is to manually configure this setting in SCM UI.
- The SCM UI refreshes incorrectly and loses focus on the setting that a user is configuring when the setting has a string data type. In such cases, the value of the setting is defined as any text that the user typed when this setting is prescribed in more than one setting group. This makes customizing setting values a slow and unreliable process. The workaround for this issue is to first type the customizing setting value in full in a text editor, such as Microsoft Notepad, and then perform a cut-and-paste operation of the setting value into the SCM UI.
- When a regular user uninstalls SCM, residual baseline files remain on the computer. Also, when a regular user re-installs SCM on the same computer, the residual baselines files are retained with those of the new installation baseline files. For these reasons, it is a best practice to always ensure that only users with administrator rights install and uninstall SCM on the computer. The location of the residual baseline files depends on the type of user who is logged on the computer:
- If the user is a regular user, the location is at %AppData%\Microsoft.
- If the user is an administrator, the location is %SystemDrive%\Users\Public\Microsoft\SecurityCompliance Manager.
- Administrative template settings, which are also called ADMX settings, that allow you to configure values with a list element and a Show... button in the UI of SCM 2.5 cannot be associated correctly to the product settings in the Baseline Library during the GPO import process. SCM organizes these settings into a setting group called "Additional Settings."
- If a computer has either SCM 2.0 or SCM 2.5 installed, and you then install SCM 1.1.3 on the same computer, neither SCM 2.0 nor SCM 2.5 will function normally. For this reason, you should not install SCM 1.1.3 on a computer that has either SCM 2.0 or SCM 2.5 installed on it.
- SCM 2.5 baselines can be imported into SCM 2.0 but not into SCM 1.1.3. This is by design for backward compatibility.
- The Export to Excel feature of the tool requires you to enable macros in Excel. The export process will not complete if macros are not enabled. Excel will open and you will see a security warning above the workbook. Click the Options button in the security warning, select Enable this content, and then click OK to complete the export process.
- When using the Group Policy Management Console (GPMC) to import a GPO backup created with the tool, clicking the View Settings... button may cause the following error message to appear: "Could not find file '$GPO-Backup-Path$\gpreport.xml." The GPO backup can be successfully imported by not clicking this button.
- If the SCM tool is installed using an account with normal user privileges that has been elevated with User Account Control, the user will not be able to import or duplicate baselines.
- If you recently installed Windows Internet Explorer 8 you may not be able to install SQL Express, which is required by the SCM tool. If you encounter this problem, close Internet Explorer, launch Internet Explorer again, complete the Internet Explorer Welcome Wizard, and then restart the SCM installation process.
- The SCM installation process will fail if it attempts to install SQL Express, and the account that was used to start the installation does not have all of the required user privileges. The account used to install SCM must be a member of the Administrators group. In addition, the account must have the following user rights in order to install SQL Express:
- Backup files and directories (SeBackupPrivilege)
- Debug Programs (SeDebugPrivilege)
- Manage auditing and security log (SeSecurityPrivilege)
- The following settings are not currently supported when generating SCAP content or DCM configuration packs:
- Accounts: Rename administrator account
- Accounts: Rename guest account
- Accounts: Administrator account status
- Accounts: Guest account status
- Network security: Force logoff when logon hours expire
- The following settings are not supported when generating SCAP content or DCM configuration packs for either Windows Vista or later versions of Windows:
- Audit account logon events
- Audit account management
- Audit directory service access
- Audit logon events
- Audit object access
- Audit policy change
- Audit privilege use
- Audit process tracking
- Audit system events