Hosting the Integrated Exchange, Lync, and SharePoint Test Lab with Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V
The integrated Exchange, Lync, and SharePoint test lab consists of seven separate computers on the Corpnet subnet:
- DC1: The domain controller, DNS server, and DHCP server
- SQL1: The SQL database server
- EX1: An Exchange Server 2013 server
- LYNC1: A Lync Server 2013 server
- SP1: A SharePoint Server 2013 server and certification authority
- CLIENT1 and CLIENT2: Client computers
All computers are members of the corp.contoso.com AD DS domain.
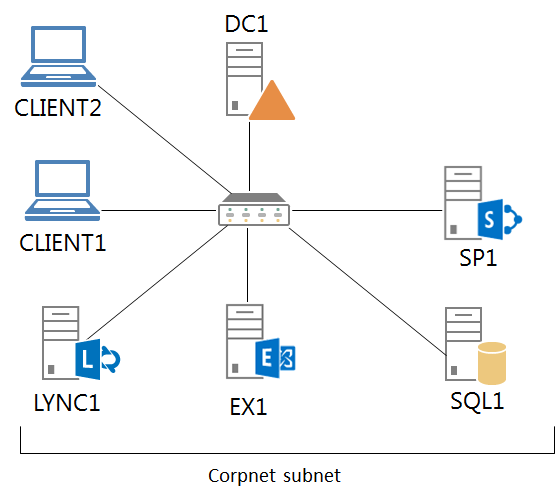
The following figure shows the integrated Exchange, Lync, and SharePoint test lab.
This figure shows the computers and their connections using a hub or switch. You can implement this configuration using physical computers and a switch, virtual computers and a switch, or a combination of physical and virtual components.
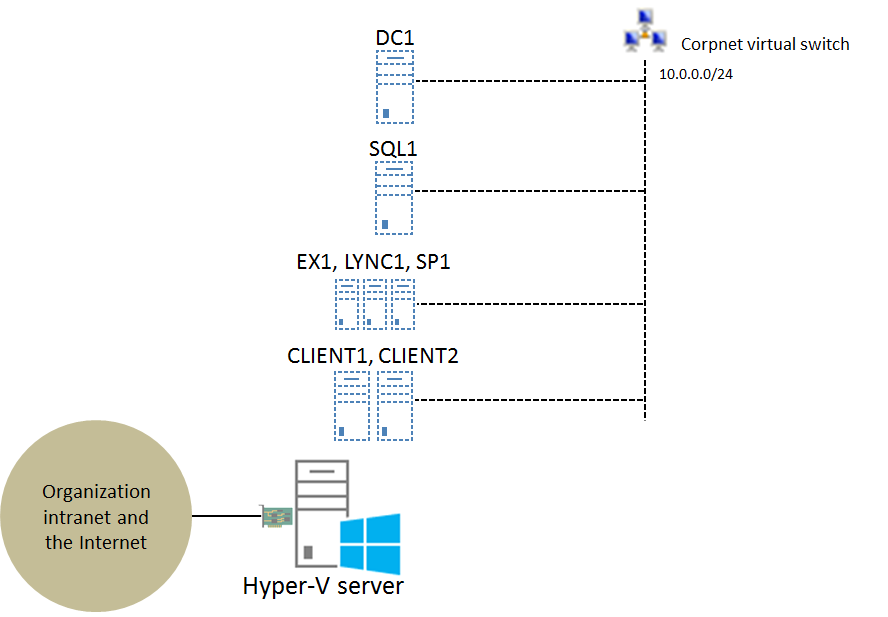
If you are using Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V for your virtualization solution, you can configure the integrated test lab on a single Hyper-V server as shown in the following figure (click on it for a larger version):
The key elements of this configuration are the following:
- All seven computers (DC1, SQL1, EX1, LYNC1, SP1, CLIENT1, and CLIENT2) are virtual machines running on the Hyper-V server.
- The Corpnet subnet is implemented as the Corpnet private virtual switch, to which all seven computers are connected.
- The Hyper-V server has at least one physical network adapter that connects to your organization intranet and the Internet. You can use this connection to connect a computer to the real Internet to install software or updates. For more information, see How do I get my base configuration computers on the Internet?
To build out the integrated Exchange, Lync, and SharePoint test lab in Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V, do the following:
- Create a private virtual switch named Corpnet. For the steps to do this, see Creating a new virtual switch.
- Create a new virtual machine named DC1 that is connected to the Corpnet virtual switch. For the steps to do this, see Creating a new virtual machine.
- Create new virtual machines named SQL1, EX1, LYNC1, SP1, CLIENT1, and CLIENT2, all of which connect to the Corpnet virtual switch.
- Follow the instructions in the Test Lab Guide: Configure an Integrated Exchange, Lync, and SharePoint Test Lab.
-
- Step 1 installs and configures DC1, APP1 (which is renamed to SP1), and CLIENT1. To install Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, or Windows 7 on a virtual machine, see Installing an operating system on a new virtual machine.
- Steps 2 and 3 install and configure SQL1.
- Step 4 installs and configures CLIENT2.
- Step 5 installs and configures EX1.
- Steps 6 and 7 install and configure LYNC1.
- Step 8 installs and configures SP1.
- Step 9 configures server-to-server trust relationships between EX1, LYNC1, and SP1.
| Windows PowerShell commands |
| The following Windows PowerShell cmdlet or cmdlets perform the same function as steps 1-3 of the preceding procedure. You must supply values for the –MemoryStartupBytes and -NewVHDSizeBytes parameters for each virtual machine. Enter each cmdlet on a single line, even though they may appear word-wrapped across several lines here because of formatting constraints. New-VmSwitch -Name Corpnet -SwitchType Private New-VM –Name DC1 –MemoryStartupBytes <MemorySize> -NewVHDSizeBytes <DiskSize> –SwitchName Corpnet New-VM –Name SP1 –MemoryStartupBytes <MemorySize> -NewVHDSizeBytes <DiskSize> –SwitchName Corpnet New-VM –Name SQL1 –MemoryStartupBytes <MemorySize> -NewVHDSizeBytes < DiskSize> –SwitchName Corpnet New-VM –Name EX1 –MemoryStartupBytes <MemorySize> -NewVHDSizeBytes < DiskSize> –SwitchName Corpnet New-VM –Name LYNC1 –MemoryStartupBytes <MemorySize> -NewVHDSizeBytes < DiskSize> –SwitchName Corpnet New-VM –Name CLIENT1 –MemoryStartupBytes <MemorySize> -NewVHDSizeBytes < DiskSize> –SwitchName Corpnet New-VM –Name CLIENT2 –MemoryStartupBytes <MemorySize> -NewVHDSizeBytes < DiskSize> –SwitchName Corpnet |
For additional Hyper-V test lab configuration articles, see Hosting Test Lab Guide Environments in Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V.
For more information, see Test Lab Guides.
For the latest developments in the Test Lab Guides initiative, see the Microsoft Test Lab Guides blog.