Hyper-V: How to Merge a Differencing Disk
The term "a differencing disk" (sometimes called a "diffdisk") is a virtual hard disk that stores the changes or "differences" to an associated parent virtual hard disk for the purpose of keeping the parent intact. The differencing disk is a separate .vhd file (that may be stored in a separate location) that is associated with the .vhd file of the parent disk. These disks are often referred to as "children" or "child" disks to distinguish them from the "parent" disk. There can be only one parent disk in a chain of differencing disks. There can be one or more child disks in a differencing disk chain of disks that are "related" to each other. Changes continue to accumulate in the differencing disk until it is merged to the parent disk.
A common use for differencing disks is to manage storage space on a virtualization server. For example, you can create a base parent disk- such as a Windows 2008 R2 Standard base image- and use it as the foundation for all other guest virtual machines and disks that will be based on Windows Server 2008 R2.
NOTE: Any changes you make to the parent disk (such as software patches or compact/convert/degrament operations) may invalidate the chain and cause your child disks to stop functioning correctly.
For more information on differencing disks see:
To merge a differencing disk:
- Under Server Manager, in the Hyper-V Manager, click Edit Disk, and locate the disk that you want to merge into a new differencing disk:

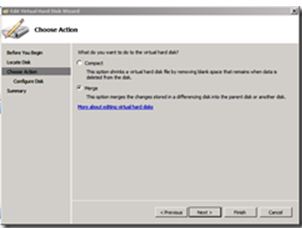
- On the next screen, under Action, select Merge.
- Select To a new virtual disk, and choose a name and path for the new disk that you created in the initial copy.

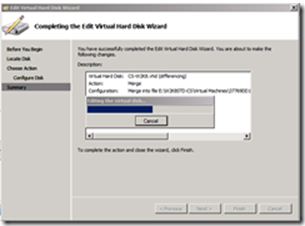
- The "old" differenced disk, which is based on the original parent disk plus state from the "old" differenced disk is merged into the new disk on the drive you specified.