Hosting the SharePoint Server 2013 Three-Tier Test Lab with Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V
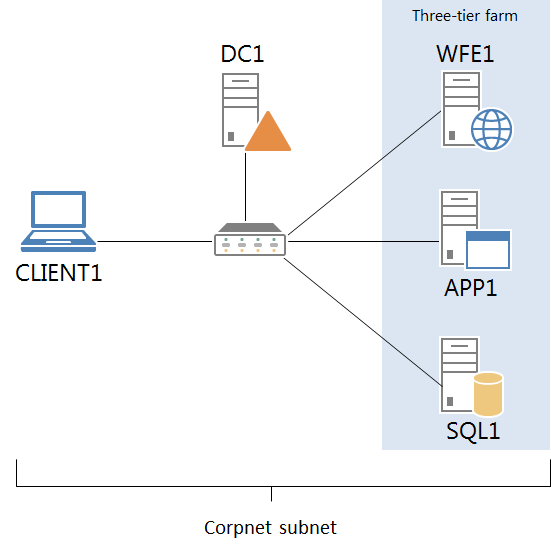
The SharePoint Server 2013 three-tier test lab consists of five separate computers on the Corpnet subnet:
- DC1: The domain controller, DNS server, certification authority, and DHCP server
- WFE1: The front-end web server of the SharePoint Server 2013 three-tier farm
- APP1: The application server of the three-tier farm
- SQL1: The SQL database server of the three-tier farm
- CLIENT1: The web client computer
All computers are members of the corp.contoso.com Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) domain.
The following figure shows the SharePoint Server 2013 three-tier test lab.
This figure shows the computers and their connections using a hub or switch. You can implement this configuration using physical computers and a switch, virtual computers and a switch, or a combination of physical and virtual components.
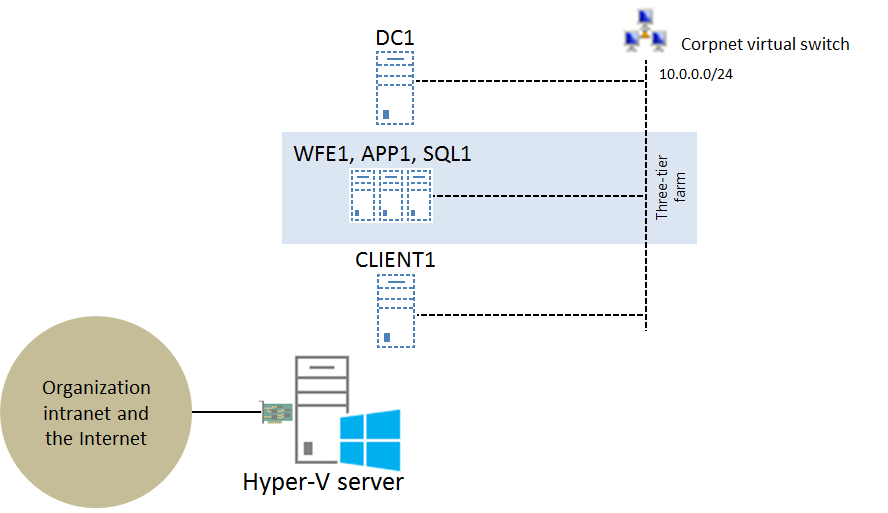
If you are using Windows Server 2012 and the Hyper-V server role for your virtualization solution, you can configure the SharePoint three-tier farm test lab in Hyper-V on a single server as shown in the following figure (click on it for a larger version):
The key elements of this configuration are the following:
- All five computers (DC1, WFE1, APP1, SQL1, and CLIENT1) are virtual machines running on the Hyper-V server.
- The Corpnet subnet is implemented as the Corpnet virtual switch and all five computers are connected to it.
- The Hyper-V server has at least one physical network adapter that connects to your organization intranet and the Internet. You can use this connection to connect a computer to the real Internet to install software or updates. For more information, see How do I get my base configuration computers on the Internet?
See the following for a short overview of the configuration process.
To build out the SharePoint Server 2013 three-tier farm in Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V, do the following:
- Create a private virtual switch named Corpnet. For the steps to do this, see Creating a new virtual switch.
- Create a new virtual machine named DC1 that is connected to the Corpnet virtual switch. For the steps to do this, see Creating a new virtual machine.
- Create a new virtual machines named WFE1, APP1, SQL1, and CLIENT1 and connect them to the Corpnet virtual switch.
- Follow the instructions in the Test Lab Guide: Configure SharePoint Server 2013 in a Three-Tier Farm.
-
- Step 1 installs and configures DC1, APP1, and CLIENT1. To install Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows 8, or Windows 7 on a virtual machine, see Installing an operating system on a new virtual machine.
- Steps 2 and 3 configure SQL1 and install SQL Server on it.
- Step 4 installs SharePoint Server 2013 on APP1, creating a new farm that uses SQL1 as its database server.
- Steps 5 and 6 configure WFE1 and install SharePoint Server 2013, joining the farm created on APP1.
| Windows PowerShell commands |
| The following Windows PowerShell cmdlet or cmdlets perform the same function as steps 1-3 of the preceding procedure. You must supply values for the –MemoryStartupBytes and -NewVHDSizeBytes parameters for each virtual machine. Enter each cmdlet on a single line, even though they may appear word-wrapped across several lines here because of formatting constraints. New-VmSwitch -Name Corpnet -SwitchType Private New-VM –Name DC1 –MemoryStartupBytes <MemorySize> -NewVHDSizeBytes <DiskSize> –SwitchName Corpnet New-VM –Name WFE1 –MemoryStartupBytes <MemorySize> -NewVHDSizeBytes <DiskSize> –SwitchName Corpnet New-VM –Name APP1 –MemoryStartupBytes <MemorySize> -NewVHDSizeBytes <DiskSize> –SwitchName Corpnet New-VM –Name SQL1 –MemoryStartupBytes <MemorySize> -NewVHDSizeBytes <DiskSize> –SwitchName Corpnet New-VM –Name CLIENT1 –MemoryStartupBytes <MemorySize> -NewVHDSizeBytes <DiskSize> –SwitchName Corpnet |
For additional information about configuring test labs with Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V, see Hosting Test Lab Guide environments in Windows Server 2012 Hyper-V.
- For more information, see Test Lab Guides.
- For information about additional TLGs for SharePoint Server 2013, see SharePoint Server 2013 Test Lab.
- For the latest developments in the Test Lab Guides initiative, see the Microsoft Test Lab Guides blog.