Microsoft Dynamics CRM 2011 – Auditing
Enabling Auditing
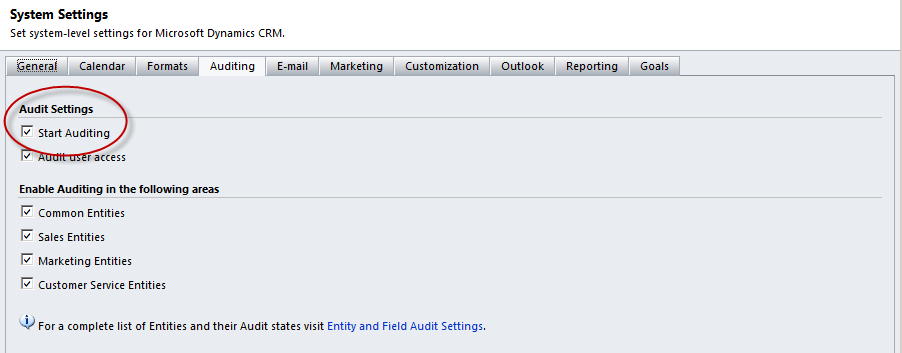
Before auditing can be used in CRM 2011 you will need to enable it at the system level. You can enable auditing from Settings -> Auditing -> Global Audit Settings or Settings -> Administration -> System Settings. On the Auditing tab you will be able to check the box next to Start Auditing to enable audit functionality.
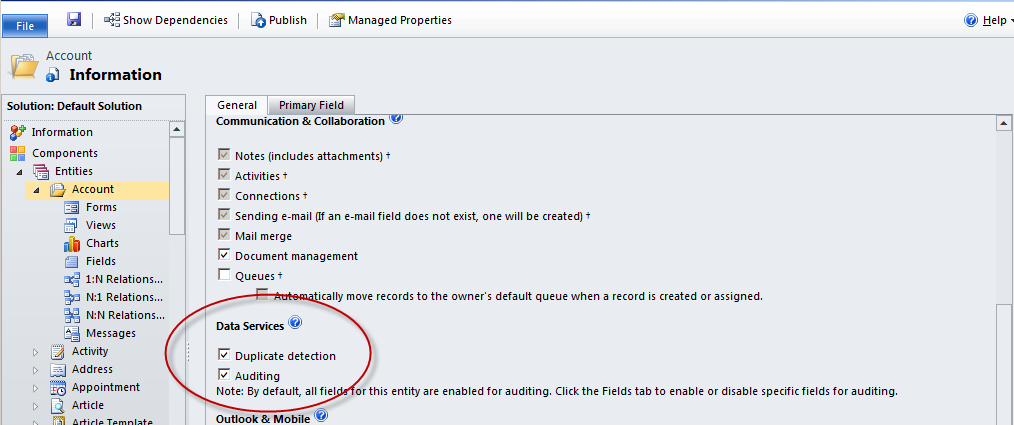
If auditing is enabled at the system level, options to enable auditing user access and by area become available. Enabling auditing initially will enable auditing on all the entities in that area by default. Individual entities can be enabled or disabled through the entity’s own settings. This can be accomplished by navigating to Settings -> Customizations -> Entities -> Specific Entity or Settings -> Auditing -> Entity and Field Settings -> Specific Entity. Under the Data Services section there is an option to enable or disable auditing.
An area will only be available to enable or disable as a group if all of the entities within it have auditing set to the same level.
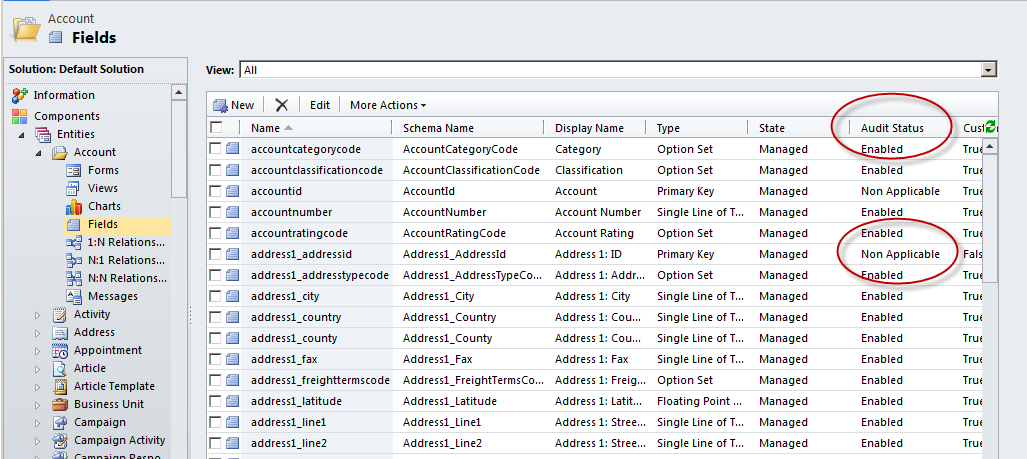
Auditing can be enabled or disabled on a field level basis by navigating to the specific field on a given entity and updating the auditing value. This feature is limited to fields which do not have an Audit Status of Non Applicable. Once changed, the entity is required to be published before the changes in auditing will take effect.
Audit Summary View
Existing audit logs can be viewed by navigating to Settings -> Auditing -> Audit Summary View. The resulting view is fixed by the system with predetermined columns that display the date and time of the event, the type of event, who made the change, the record effected by the event, the corresponding entity type and the operation performed. This data cannot be exported to Excel like the standard grids. To assist in finding relevant data, filters can be enabled for all the columns except the effected record column; this works similarly to the corresponding functionality in Excel. Selecting an individual audit record will provide additional details for the given transaction.
Audit Log Management
In order to delete audit logs, navigate to Settings -> Auditing -> Audit Log Management. Groups of audit logs are available for deletion by quarter. These groups are also known as partitions*. For each, the starting and ending dates logged and numbers of audit log entries are displayed. In CRM 2011 Online the size of the audit log partition is also displayed. Only the oldest audit log partition can be deleted at any given time and the current audit log partition cannot be deleted regardless of auditing being enabled or disabled at the system level.
CRM 2011 Online users should be aware that audit log data counts against data storage quotas.
*For additional information on table partitions see the article “Auditing and Table Partitions in Dynamics CRM 2011”.
Audit History
Audit history related to a specific record can be viewed by navigating to Audit History under the Related section of the left navigation. In addition this view will also display audit log records that have an effect on the entity’s auditing such as global auditing starts and stops as well as changes to individual field auditing levels.
Audited Information
If user access is being audited, login times and means through which they access CRM (web or Outlook) are recorded. A caveat to this is that logins may only be recorded every four hours to prevent the audit logs from recording enormous amounts of user activity.
If auditing is enabled on an entity, an audit log entry is made when a new record is created. The detail contains the initial values of the new record. When a record is updated, the field name, the old value, and the new value are provided in the detail. Record deletions are logged along with the values at the time of deletion. Status changes to a record, including activations and deactivations are logged along with the current and previous Status and Status Reason field values.
Non-Audited Information
- Excel exports
- Records that were viewed
- Log off times of users
- Reports that were generated
- Workflows that were executed
- Workflow and Dialog Step Changes
Audit Security
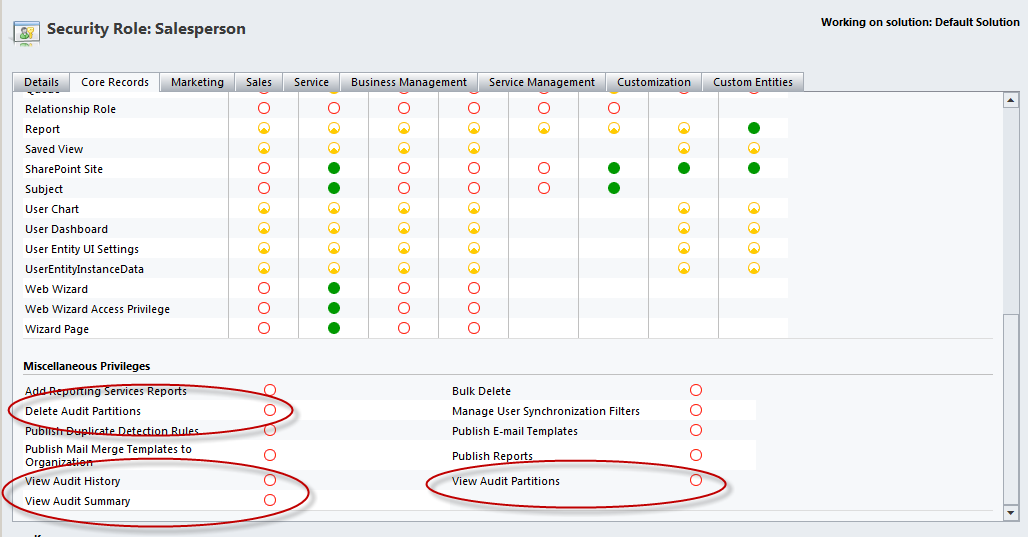
There are four primary security role privileges associated with auditing which can be found under the Miscellaneous Privileges section on the Core Records tab of a role.
- View Audit History – allows Audit History to be viewed within the context of a record
- View Audit Summary – allows the Audit Summary View of all audit records to be viewed from Settings -> Auditing
- View Audit Partitions – allows the Audit Log Management area to be viewed from Settings -> Auditing
- Delete Audit Partitions – allows audit log partitions to be deleted from the Audit Log Management area
Individual audit log entries cannot be deleted either through the user interface or programmatically using the SDK.
Auditing Best Practices
- Disable auditing during your initial data import
- Only audit what is important
- Periodically delete old audit log partitions