Troubleshooting Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging whitepaper
There is nicely written whitepaper to help you troubleshoot and understand how Exchange 2007 Unified Messaging works. I pasted in a few whitepaper highlights below:
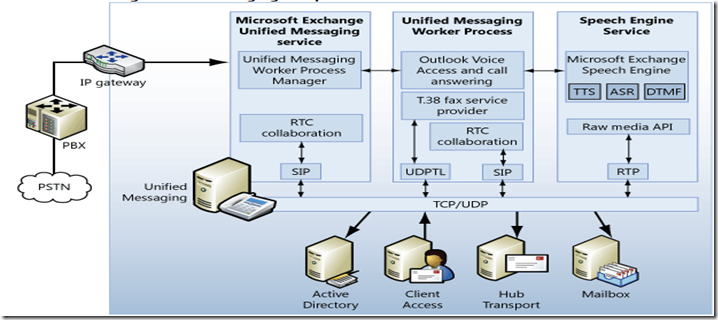
Exchange UM architecture:
Shows a nice breakdown of the UM services and worker processes and what they do and how they talk.
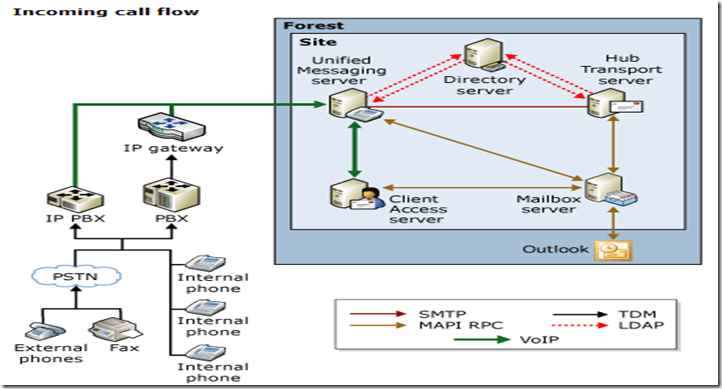
UM Call flows:
Has a nice inbound call flow showing the call from either an IP PBX (direct SIP) or legacy PBX (TDM) which requires a SIP gateway to translate TDM to SIP, etc. UM server than does a directory lookup and hands off to the hub server which then routes the voicemail/fax to the inbox.
Here are the basics of a simple Unified Messaging call flow:
- Caller A places a call to B.
- B doesn't answer the phone.
- Call gets forwarded to voice mail. In this example, it's forwarded to the VoIP gateway first.
- The VoIP gateway sends this call to the Unified Messaging server.
- At this point, caller A should hear the personal greeting of B.
Some nice UM troubleshooting basics for example:
When an incoming call to voice mail fails, the problem usually happens at one of the following stages of the call flow:
- Call isn't routed from the PBX to the IP gateway, so the call doesn't reach the Unified Messaging server.
- Call isn't accepted by the Unified Messaging server.
- Voice mail isn't delivered to the user's mailbox.
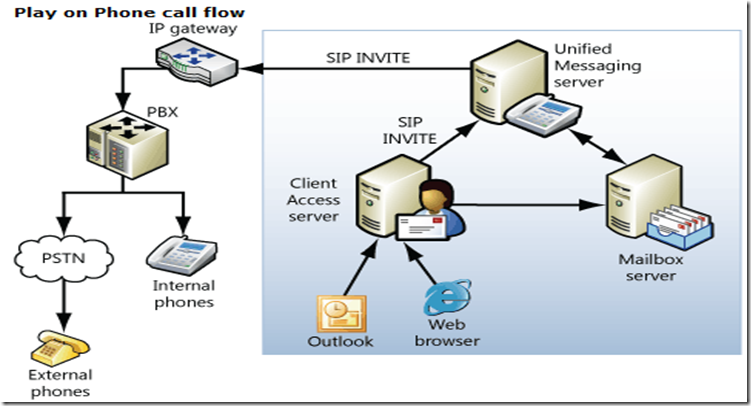
Troubleshooting Play on Phone:
Play on Phone requests first go to the Client Access server. The Client Access server sends a SIP INVITE request to the Unified Messaging server, and Unified Messaging proxies the request to the IP gateway. The best way to troubleshoot these issues is to perform a network trace on the Unified Messaging server. Note the following:
- Which Client Access server is servicing this request?
- Does the Client Access server send a request to the Unified Messaging server?
- Does the Unified Messaging server send a SIP INVITE request to the gateway?
- Does the gateway accept the SIP INVITE request?
.gif) Important:
Important:The Unified Messaging server and Client Access server use mutual TLS to establish the session. For mutual TLS negotiation, both the Unified Messaging server and the Client Access server must have a certificate that has the corresponding FQDN as the Subject Name or the Subject Alternate Name.
For calls from a directory, Unified Messaging sends a REFER request to the IP gateway. The IP gateway should be able to handle REFER requests. Network trace is the best resource to troubleshoot this issue.
Outbound calls are restricted by dialing rules. Enable diagnostics logging and review the application log to see if dialing rules are causing any issues.
Backing Up a Unified Messaging Server
A backup plan for any organization is critical for maintenance and successful recovery. With the introduction of a Unified Messaging server, you need to incorporate new strategies for backing up that server. This section discusses specific files and data that are relevant only to the Unified Messaging environment. In addition, some disaster recovery techniques are described.
To successfully recover a Unified Messaging server, certain files must be backed up. These files aren't Exchange database files, so they aren't automatically selected if you choose an Exchange-aware backup and use the Exchange option only. You need to do a file-level backup of these files. These files don't need to be backed up every day because they are mostly configuration related. The following files need to be backed up from a Unified Messaging server:
- Custom prompt files
- Configuration files
- Grammar files
Useful UM PowerShell commands:
Test-UMConnectivity -ListenPort 5060
Get-UMActiveCalls -Server ServerName | export-csv c:\temp\activecalls.csv
UM Diagnostic event logging:
Logging level
Value
Expert 7
High 5
Medium 3
Low 1
Lowest 0
Set the following categories to a value of 7 to indicate Expert level logging:
- UMWorkerProcess
- UMCore
- UMManagement
- UMService
- UMClientAccess
- UMCallData
Start Registry Editor (regedit). Scroll to the following keys and then set the value of each key to 7:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchange Unified Messaging\Diagnostics
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchange Unified Messaging\UMWorkerProcess
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchange Unified Messaging\UMCore
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchange Unified Messaging\UMManagement
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchange Unified Messaging\UMService
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchange Unified Messaging\UMClientAccess
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\MSExchange Unified Messaging\UMCallData
Value: Lowest – 0x00000000 (0), Expert – 0x00000007 (7)
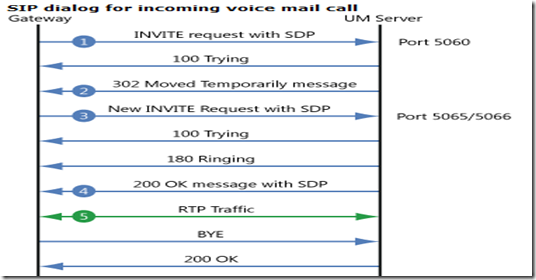
How to analyze a UM sniff trace:
INVITE sip:2501@65.53.2.181;transport=tcp SIP/2.0Via: SIP/2.0/TCP 65.53.0.18;branch=z9hG4bKac791424417;aliasMax-Forwards: 70From: <sip:2510@ACGWMP118.req150587.local>;tag=1c741078876To: <sip:2501@65.53.0.18;user=phone>Call-ID: 74107850232200073840@65.53.0.18CSeq: 3 INVITEDiversion: <tel:2501>;reason=no-answerContact: <sip:2510@65.53.0.18;transport=tcp>Supported: em,100rel,timer,replaces,path,resource-priorityAllow:REGISTER,OPTIONS,INVITE,ACK,CANCEL,BYE,NOTIFY,PRACK,REFER,INFO,SUBSCRIBE,UPDATEUser-Agent: Audiocodes-Sip-Gateway-MP-118 FXS_FXO/v.5.00A.035.003Content-Type: application/sdpContent-Length: 227v=0o=AudiocodesGW 741070197 741070070 IN IP4 65.53.0.18s=Phone-Callc=IN IP4 65.53.0.18t=0 0m=audio 6010 RTP/AVP 0 101a=rtpmap:0 PCMU/8000a=rtpmap:101 telephone-event/8000a=fmtp:101 0-15a=ptime:20a=sendrecv
Most of the Unified Messaging call answering issues can be resolved by analyzing the first SIP INVITE request from the IP gateway. The first SIP INVITE request gives you a good idea about the rest of the call flow. Consider the following:
- Make sure the request Uniform Resource Identifier (URI) has the IP address of the Unified Messaging server and a valid SIP extension. Also note the transport mechanism.
- The IP address of the To header must match the UM IP Gateway object, and the extension must match a pilot number in a UM hunt group.
- The user's UM dial plan is determined by the UM dial plan linked to the UM hunt group determined in the previous step.
- The From header is used for caller ID resolution.
- The SDP header contains the media endpoint and supported media codec information.
For the full Exchange 2007 UM troubleshooting whitepaper download it here.
Comments
- Anonymous
January 01, 2003
There is nicely written whitepaper to help you troubleshoot and understand how Exchange 2007 Unified