Office 365: Trusting application emails sent through internal relay…
In todays connected environments there are several applications that send email through designated internal relay servers. The messages may originate from application servers that generate notifications, scans from multifunction printers, or other network connected devices. An excellent target for internal relay servers are the hybrid servers implemented for Office 365 integration or any Exchange 2010 or newer server.
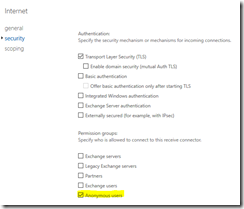
In some installations a connector is created that allows for anonymous access. This is definitely the case when the Exchange server receives email from the internet.
In many cases the internet or anonymous connector is what is utilized for internal relay applications. This works for accepting and sending email within the environment – but there are several limitations. Any email that is received through only the anonymous permission is considered not authenticated. Here are some implications:
- Sender addresses are not resolved to email addresses in the global address list.
- Email to distribution lists requiring authentication will not be processed.
- Message limits of the on premises organization are applied to the messages relayed.
In this example telnet was utilized to submit a message through the anonymous connector. The message header indicates the message was received as anonymous.
21
X-MS-Exchange-Organization-AuthAs
Anonymous
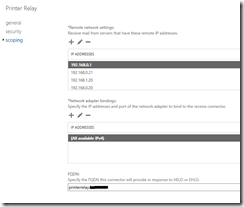
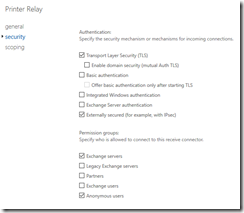
In order for internal applications to reliably deliver email it may be necessary to trust these messages. The messages must come from an authenticated source. To allow this to occur a receive connector can be created the implements the following:
- IP restrictions to the sending applications or devices.
- Authentication using “Externally Secured”.
Exchange by default will always utilize the most restrictive connector. When the device connects and the IP address is within scope of the connector the externally secured permissions will be applied. When the connector with externally secured is selected this results in the authentication settings for the email being set as INTERNAL.
In this example telnet was utilized to submit a message through the externally secured connector. The message header indicates the message was received as internal.
19
X-MS-Exchange-Organization-AuthAs
Internal
For more information on the connector security settings please review the following article –> https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/mt668454(v=exchg.160).aspx