Windows 7 Application Compatibility Issues ...Demystified !!!
UAC , PCA , Shims ,Compatibility Mode ,limited permission, Access denied, Virtual store … Are these terms really annoying and mysterious !!!.
Let’s demystify these terms which turns every geek’s smile to a confused novice.


As the saying goes “Every change is for something good” ,Windows 7 features are meant for user friendly , process improvement and security experiences. Changes in UI , access permission level, user’s data related folders have helped in achieving the appreciation among the community and users.
Below are few information/solutions which make Windows 7 experience very user friendly, ease to use and secure.
1. User Access Control (UAC) :
Many a times user is prompted with UAC during software installation or for application specific operations.
By default, when Microsoft Window XP is installed on User machine, the Windows XP Setup creates all user accounts as local administrators. This type of users can install, update, and run software since an administrator account has system-wide access. When a user is added to the local administrators group, that user is automatically granted every Windows privilege. Once user get admin privileges it is very easy for any security attacks as all applications runs with admin privileges. So in order to mitigate the impact of security attack such as malwares etc. all users should run as standard user.
A standard user on a Windows XP computer must use Run as or log on with an administrator account in order to install/uninstall applications. There was no built-in method within the Windows operating system for a user to “elevate” in flow from a standard user account to an administrator account without logging off, using Run as or switching users. So most user continue to browse the Web as an administrator which opens the gate for security attack. With the introduction of UAC in Vista and Windows 7 this security vulnerable has been overcome. With the built-in UAC elevation component, standard users can easily perform an administrative task by entering valid credentials for a local administrator account.

UAC is by default enabled in Windows 7 . As a result, user might encounter some compatibility problems with different applications that have not yet been updated for the Windows 7 UAC component. If an application requires an administrator access token user can run the program as an administrator by using the Run as administrator option on the context menu (right-click).
In extreme situation, though it is not recommended, user can disable UAC through the User Account tool in the Control Panel. You've to reboot after the changes. Also through registry settings user can disable it. HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Policies\System
Users have to set EnableLUA to 0.

Some of the useful sites regarding UAC - https://windows.microsoft.com/en-US/windows7/products/features/user-account-control
2. Visit the Windows 7 compatibility Center
Perform the below task to get more information regarding the Windows 7 compatbility of the software/application/drivers/devices.
a) Determine which software and devices are and are not compatible with Windows 7. Also visit the vendor site to get more information.
b) Locate links to drivers and upgrades that will make your computer/application compatible.
Windows 7 compatibility ceter - https://www.microsoft.com/windows/compatibility/windows-7/en-us/Default.aspx?type=Software
3. Run the program as an administrator
Does an application not work properly or does it throw error message every time it is used, try to run it with additional rights. By default, an application is not started with those additional rights, but this can be done manually by right clicking (the shortcut to) the application and to select Run as administrator. Those administrator rights can also be added by default by right clicking the shortcut to the application and to select Properties, tab Shortcut, Advanced button and to activate the option Run as administrator.

Some of the useful sites - https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/ff431742.aspx
4. Limited Permission Issue
Sometimes user is denied access to store/write to certain restricted locations.
The issues concerning the limited permissions are related to administrator rights. Without the permission to modify files in a certain location, an application is not able to save a file in this folder (e.g. C:\Program Files). In most cases this problem can be solved by running an application with administrator rights. A better alternative is adding permissions to modify the concerning folder. This cab be done by right clicking the folder and then Properties, Security tab, Edit button(or the button Advanced) and provide Full control for the concerning user account.

5. Compatibility issues with older software
Windows 7 manages the running applications differently as compared to previous windows platforms. This might cause compatibility issues for old software/applications. Few of the issues can be solved by running the application with “Widow XP compatibility mode”. Below are the steps to achieve the same.
Application -> Right Click -> Properties -> Compatibility tab -> select the compatibility mode from the dropdown - > check “Run this program in compatibility mode for” option.

For more information regarding compatibility mode please refer below sites.
https://windows.microsoft.com/en-US/windows-vista/Make-older-programs-run-in-this-version-of-Windows
https://windows.microsoft.com/en-US/windows7/install-and-use-windows-xp-mode-in-windows-7
6. Virtual Store
In Windows 7, many folders are made secured , which makes it impossible for an application/malware to make changes to the files in the folders. e.g. the folder C:\Program Files is secured. An application with administrator rights can only modify the files. Many older applications continuously try to store/modify files in this folder. To solve this issue, Windows 7 uses virtualization of files i.e. files will be stored in the Virtual Store. The applications are not aware of this virtualization, and thinks the files are stored on the same location. Virtualization is done separately for every user .Files are stored in C:\Users\<loginname > \AppData\Local\VirtualStore location . Program Files is one of the folders in the Virtual Store, which contains the user specific settings for the applications. All users must change the settings of the virtualized applications separately. This is an advantage as well because the changes won't affect the other users. In case user wants to disable virtualization they can do it by providing Full Control to the specific folder or by running the application with admin privileges

.
Few useful liks - https://social.msdn.microsoft.com/Forums/en/windowscompatibility/thread/a432f1ab-4b0c-439c-b20a-f35e2c0d18a3
7. Troubleshoot Compatibility
Sometimes applications running in Windows XP or Windows Vista throws error on Windows 7. Windows 7 has a little-known feature that helps you troubleshoot application compatibility. Here's how to use it:
a) Right-click the shortcut of the app that's not working properly, then click Troubleshootcompatibility.

b) Windows will try to detect compatibility issues, then give you two options: Try recommended settings and Troubleshoot program.
I recommend trying the first option first; if it doesn't work, you can always return and try the second (which gives you the choice of which previous version of Windows you want compatibility with).
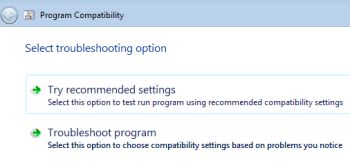
c) After Windows applies the selected settings, click StartProgram and see if that solves the problem. Either way, click Nextto have Windows apply the settings "permanently" or try again with
different settings.
8. Program Compatibility Assistant( PCA )
The Program Compatibility Assistant prompt appears if a software, device or driver didn't register correctly in Programs and Features in Control Panel during installation.
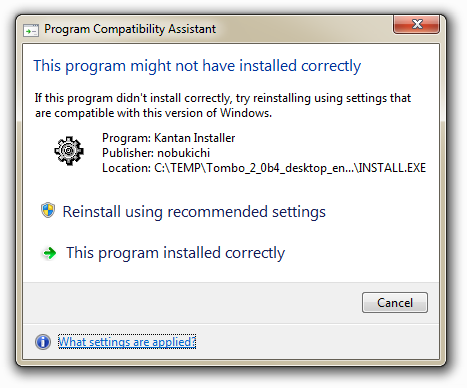
The Program Compatibility Assistant (PCA) runs automatically and detects known compatibility issues in older programs. During the installation of older software/application in Windows 7 , PCA notifies the user if there is a problem and offers to fix it the next time you run the program. User needs to apply the settings by clicking on “Reinstall using recommended settings” option. By applying the settings, no changes are made to the program, itself. for example, the PCA can resolve conflicts with User Account Control(UAC) , it can run the program in a mode that simulates earlier versions of Windows. The changes that Program Compatibility Assistant makes are done automatically, so users don’t need to make them. If the compatibility issue is serious, the Program Compatibility Assistant might warn you or block the program from running. Use “This program installed correctly” option to close the Program Compatibility Assistant.
Though it is not recommended, PCA can be disabled from the following location - Start -> Run->gpedit.msc - >Administrative Templates ->Windows Components->Application Compatibility ->"Turn of Program Compatibility Assistant" policy
PCA runs automatically but there is one more option where user can run "Program Compatibility Wizard" manually for fixing the compatibility issues . location for the same -
Control Panel->Programs -> Under Programs and Features ->Run programs made for previous versions of Windows
Few useful links-
https://windows.microsoft.com/en-US/windows7/Program-Compatibility-Assistant-frequently-asked-questions
https://blogs.technet.com/b/askperf/archive/2007/10/05/the-program-compatibility-assistant-part-one.aspx
https://blogs.technet.com/b/askperf/archive/2007/10/05/the-program-compatibility-assistant-part-two.aspx
9. Shims
Shim Technology is an elegant technique that is used to fool some applications into running on versions of the operating system they may not have been designed for. It’s a method of 'hooking' the Win32 APIs that are called by a particular application program. Once installed, such hooks permit developers and support engineers to install alternate (stub) functions to be called in place of the original functions. The actions taken by the stub function comprise the fix for a particular application compatibility problem.
There are around 360 plus shims currently available. Shims can be applied for different compatibility issues like OS version lie, registry fix, correct file path etc. Some of the important shims are RunAsAdmin, RunAsHighest, CorrectFilePaths, and WinXpSP2VersionLie etc…

For more information regarding shims please refer: https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd837644(WS.10).aspx
10. Advanced Options for troubleshooting
Below are few tools which can be used for advance debugging and fixing application compatibility issues.
i) Application Compatibility Toolkit ( ACT ) :
ACT is a used to support older version of applications in latest windows OS. It solves the compatibility issues of the newer windows application platforms.
For example, the windows 7 OS will not allow IEV6 to get installed in it. But using this tool kit you can install and use the IEV6 in windows 7.
Few versions of ACT – ACT 4.1, 5.0, 5.5,5.6 etc.

Few useful links -
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/dd562082(VS.85).aspx
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc722055(WS.10).aspx
ii) Least-privileged User Account (LUA)
The LUA approach ensures that users follow the principle of least privilege and always log on with limited user accounts.
This strategy also aims to limit the use of administrative credentials to administrators, and then only for administrative tasks.
Few useful links -
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/cc700846.aspx
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/edge/ff944922
iii) Sysinternals tools
Sysinternals tools is a suite of tools which helps in revealing rootkits, provide kernel level information ,track down and terminate runaway processes,
remove unwanted programs from system start up and provide registry level information for troubleshooting etc.
Few important tools are – Process Monitor , debug view, Pskill, Logon Sessions etc.

Few useful links -
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb842062
https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/default.aspx
iv) Windows Debugger (WinDbg )
The Microsoft Windows Debugger (WinDbg) can be used to debug both user-mode and kernel-mode programs. It uses Microsoft Visual Studio debug symbol formats for source-level debugging.
It displays function names and variables for any modules compiled using the COFF (common object file format) linker option. It permits you to do the following:
a. Step through your program, viewing the source code
b. Set breakpoints in your code
c. View CPU registers and flags
d. View a disassembly of your program
e. Watch the values of program variables
f. View the runtime stack
g. Display blocks of memory
h. Perform remote debugging across a network

Few useful links -
https://www.microsoft.com/whdc/devtools/debugging/installx86.mspx
Hope all these tricks and information will bring every app-compat techy's smile back :) ..... Keep watching for the next post "ACT , ProcMon & IE Compatibility in Nutshell …”
Comments
- Anonymous
January 16, 2011
Nice information to begin with a remediaton.. thanks chinmay. - Anonymous
February 07, 2011
Great post with lots of useful links....thanks a lot it has helped me overcome some really annoying issues with some older applications.Cheers - Anonymous
December 01, 2013
molto intressantr anche per un ptincipiantr come me - Anonymous
March 02, 2014
It’s superb blog please go through this url and solve your query . We provide Best online Services.check this site .windows7support.blogspot.in/.../fix-windows-7-error-1068.htmlThank youAalia lyon