MDM Adapter - Extending Dynamics AX 2012 R3 Master Data Management
AX 2012 R3 Master Data Management (MDM) subsystem features a set of powerful functionalities, such as data synchronization between AX instances, conflict management, single/multi master modes, policy based data filtering, etc. It provides a great platform to build a robust enterprise-level MDM strategy.
Out of box, R3 MDM supports managing master data among AX instances. This blog entry gives a simple example on how one can extend existing MDM functionalities to support managing master data between AX and non-AX systems. We have also included a sample app, attached to this post as zip, to demonstrate the topics covered(more details in Appendix). Since R3 MDM is built on top of DIXF, we assume readers have experience with DIXF and R3 MDM. If you don’t, you can learn and read about it here and here.
Disclaimer: design and code mentioned in this blog post are only for demonstrating purposes. Please do not use it in your production environment. This post only demonstrates one possible way to connect other systems with SQL Server MDS to leverage MDM functionalities built in AX 2012 R3.
First, let’s take a look at high level architecture of R3 MDM and the sample MDM adapter.
R3 MDM is built on top of DIXF. During data synchronization, synchronization batch job running on AOS communicates with DIXF service to create SSIS packages, which integrates data between MDS and AX DB. MDM adapter follows a similar pattern. It communicates with the same DIXF service to create SSIS packages, which performs integration between MDS and non-AX DB.
When AX client performs synchronization with MDS, it first exports local changes made since the last time synchronization was performed. It then imports changes from MDS. Import is also incremental such that only changed data gets imported back. During export, DIXF writes changes from target table into staging table and performs integration between staging table and MDS. During import, data first flow from MDS into staging table in AX. DIXF then moves the data from staging table to target table, as depicted by the diagram below.
When MDM adapter performs synchronization with MDS, it only integrate data to and from staging table. During export, a staging writer is responsible for writing change data from target table into staging table. MDM adapter then integrates the data from staging table to MDS. During import, MDM adapter integrates data from MDS to staging table. An entity writer is responsible for moving data from staging table to target table.
Data synchronization sequence
As mentioned before, MDM adapter follows very similar pattern for performing data synchronization between MDS and non-AX DB. It follows these steps.
- Call StagingWriter to gather all the changes took place since last sync and write them into the staging table.
- Call DMFEntityProxy::CreateAndExecuteExportPackageToMDS to generate SSIS packages that pushes data from staging table to MDS.
- Call DMFEntityProxy::CreateAndExecuteImportPackageFromMDS to generate SSIS packages that pulls data from MDS to staging table.
- Call CleanUpStaging to remove imported records that conflict with local changes.
- Call EntityWriter to write data from staging table to target tables.
Set up and configuration
- Make sure the user account running DIXF web service has access to non-AX DB.
- On the machine where DIXF service is running, make sure port 7000 is open for inbound traffic.
- Create staging tables in the non-AX DB. They should be based on the DMF*Entity staging tables in AX. Non-AX staging table creation scripts can be generated from corresponding staging tables in AX. In the sample implementation, we are using the same DMF*Entity schema from AX as our staging table schema. The SSIS packages generated by DIXF looks for matching column names between MDS deployed schema and staging schema in the non-AX system, columns will be mapped for integration if their names match. So, as long as you match the column names in your non-AX staging table to the ones deployed in MDS, integration should happen properly. Your staging table can share exactly the same number of fields with the deployed DMF*Entity schema, or it could be a subset or a superset.
- The SSIS packages generated by DIXF calls the following three stored procedures in the target non-AX DB. Creation scripts can be generated from existing AX DB.
- sp_GetNextRecId – called to get new RecId for generating DMF entities in staging tables. This stored proc uses a table called SystemSequences, which is used to keep track of RecIds generated for each table. Therefore, if sample implementation is used, a table named SystemSequences need to be created in the non-AX DB.
- UpdateMDSVersionNumber – update the last AXVersion synchronized by the client. In MDS DB, a table, named AxVersionTable, tracks all the synchronization happened between all AOS instances and MDS.
- UpdateMDSExtraVersionNumber – update the last MDS change tracking version synchronized by the client. This is for scenario where data steward makes changes directly in MDS.
Now, let’s look at the major components used in the data synchronization process. Most of the components used here share the same structure and functionality with their counterparts in AX. Since MDM adapter lives outside of AX, these concepts need to be implemented on top of the framework of your choice.
MDMSyncGroup
This is the same concept used in AX to keep track of groups of entities to perform synchronization for. Sync group name should be used to link MDMEntities back to the owning MDMsynGroup. This table needs to be created in the non-AX DB. Please refer to MDMEntity in AX for implementation details.
MDMEntity
MDMEntity is used to keep track of the following information related to data synchronization, exactly the same way it is used in AX R3 MDM. This table needs to be created in the non-AX DB. Please refer to MDMEntity in AX for implementation details.
- Sync group name
- Local change tracking version number
- MDS change tacking version number
- Synchronization type
- Name of the entity
- Name of the subscription view
- Conflict management related info
- Import definition group name
- Export definition group name
- Last exported execution id
- Last imported execution id
Staging tables
Besides the fields used to store master data information, the following fields also need to be tracked.
- Definition group name
- Execution id
- AXMDMCODE – this maps to the natural key on the corresponding entity. MDS uses this code to uniquely identify each record. Please refer to DMF*Entity::insert() in AX for implementation details.
Together with the information stored on MDMEntity, one can figure out which records in the staging table need to be moved from staging to target and which ones need to be exported from staging to MDS, exactly the same way the same concepts and mechanisms are used in AX R3 MDM. Please refer to DMF*Entity tables for details.
StagingWriter
StagingWriter writes into staging table the changes took place in target tables since the last sync . This is where the heavy lifting is done and things can get pretty complicated depending on the complexity of your data model. One could implement a simple time stamp based change tracking, where each modification is tagged with a timestamp, which is used to compare against last sync timestamp during synchronization. Or, as implemented in AX, SQL change tracking can be enabled on the target entity table and local change tracking version number should be stored on the MDMEntity that corresponds to the entity being exported. Please refer to DMFStagingWriter and MDMChangeTracking in AX for details on how to implement. For demo purposes, the sample implementation uses the simple timestamp approach.
EntityWriter
EntityWriter moves data in staging table to target tables. The execution id attached to each record in staging table acts as marker indicating which records to move for a given synchronization. Things should be pretty straight forward when there is a one to one mapping between staging and target entities. The complexity comes when one staging entity could be mapped to multiple target entities. Please refer to DMFEntityWriter in AX for details on how to implement.
DMFEntityProxy
Namespace: Microsoft.Dynamics.AX.Framework.Tools.DMF.ServiceProxy
Assembly:
\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Dynamics AX\6.3\Client\Bin\Microsoft.Dynamics.AX.Framework.Tools.DMF.ServiceProxy.dll
Dependent assembly:
\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Dynamics AX\6.3\Client\Bin\Microsoft.Dynamics.IntegrationFramework.dll
This class is the gateway to reaching all the rich functionality exposed by the DIXF service. The following sample code shows how to instantiate this class.
private static DmfEntityProxy CreateDmfEntityProxy()
{
DmfEntityProxy dmfEntityProxy = new DmfEntityProxy();
ServiceContractClient helperClient;
string configFilePath = ServiceReference.GetConfigFilePath(typeof(ServiceContractClient), "");
helperClient = (ServiceContractClient)ServiceReference.CreateServiceClient(typeof(ServiceContractClient), configFilePath);
dmfEntityProxy.ClientProxy = helperClient;
return dmfEntityProxy;
}
NOTE
Since this is the proxy that accesses the DIXF web service, the client configuration file, Microsoft.Dynamics.AX.Framework.Tools.DMF.ServiceProxy.dll.config, need to be included as part of your client application. This configuration file can be found under \Program Files\Microsoft Dynamics AX\6.3\Server\AxaptaDev\bin.
Functionalities exposed by DMFEntityProxy
- CreateAndExecuteExportPackageToMDS
- CreateAndExecuteImportPackageFromMDS
- GetListOfSubscriptionViewsForEntityInMDS
- GetListOfDMFEntitiesInMDS
- GetEntityNumberOfConflictsInMDS
Here’s some sample code on how to use these functionalities from your client application.
public static ICollection<string> GetListOfSubscriptionViewsForEntityInMDS(string entityName)
{
ICollection<string> subscriptionViews = new List<string>();
DmfEntityProxy dmfEntityProxy = MdmImportExport.CreateDmfEntityProxy();
MDSClientConnectionObject connectionObj = CreateMDSClientConnectionObject();
try
{
subscriptionViews = dmfEntityProxy.GetListOfSubscriptionViewsForEntityInMDS(connectionObj, entityName);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
throw new ApplicationException(ex.Message, ex);
}
return subscriptionViews;
}
private static MDSClientConnectionObject CreateMDSClientConnectionObject()
{
MDSClientConnectionObject connectionObj = new MDSClientConnectionObject();
connectionObj.mdsWebServiceEndpoint = MDMCONFIGURATION.GetMDSWebServiceEndPoint();
connectionObj.mdsDatabaseName = MDMCONFIGURATION.GetMDSDatabase();
connectionObj.mdsDbServerName = MDMCONFIGURATION.GetMDSServer();
connectionObj.axDbServerName = MDMCONFIGURATION.GetNonAXServer();
connectionObj.axDatabaseName = MDMCONFIGURATION.GetNonAXDatabase();
return connectionObj;
}
Export
By using DMFMDMSSISPackageHelper, the export process sets up source and destination settings so that DIXF service knows where to pull data from and push data to. Here’s some sample code that uses DMFEntityProxy to export data from staging to MDS. It is based on the AX implementation in MdmAxToMdsExporter::createAndExecuteExportPackageToMDS.
private static string CreateAndExecuteExportPackageToMDS(MDMENTITY entity, string executionId)
{
string result = string.Empty;
if (entity != null)
{
DmfEntityProxy dmfEntityProxy = CreateDmfEntityProxy();
DMFMDMSSISPackageHelper dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper = new DMFMDMSSISPackageHelper();
string destinationTableName = string.Format("[stg].[{0}_Leaf]", entity.ENTITYTABLENAME); //entity.ENTITYTABLENAME is the name of the corresponding staging table, e.g., DMFCustomerEntity
string SSISCONNECTIONSTRING = "Provider=SQLOLEDB.1;Integrated Security=SSPI;Initial Catalog={0};Data Source={1};";
dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper.SourceConnectionString = string.Format(SSISCONNECTIONSTRING, MDMCONFIGURATION.GetNonAXDatabase(), MDMCONFIGURATION.GetNonAXServer());
dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper.SourceTable = entity.ENTITYTABLENAME;
dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper.DestinationConnectionString = string.Format(SSISCONNECTIONSTRING, MDMCONFIGURATION.GetMDSDatabase(), MDMCONFIGURATION.GetMDSServer());
dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper.DestinationTable = destinationTableName;
dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper.MDSStagingStoredProcName = string.Format("[stg].[udp_{0}_Leaf]", entity.ENTITYTABLENAME);
dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper.DMFEntityName = entity.ENTITYNAME;
dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper.DMFStagingTableId = entity.ENTITYTABLEID; //This is used by PackageGenerator to call storeproc sp_GetNextRecId to get the next unique identifier for inserting entities into the staging table
dmfEntityProxy.UpdatePackageVariable(dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper, "DefinitionGroup", entity.EXPORTDEFINITIONGROUP);
dmfEntityProxy.UpdatePackageVariable(dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper, "ExecutionID", string.Format("{0}", executionId));
dmfEntityProxy.UpdatePackageVariable(dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper, "ImportType", IMPORTTYPEZERO);
dmfEntityProxy.UpdatePackageVariable(dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper, "LastSyncVersionNumber", entity.MDSSYNCVERSION);
dmfEntityProxy.UpdatePackageVariable(dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper, "MdsChangeTrackingVersionNumber", entity.MDSSYNCVERSIONEXT);
dmfEntityProxy.UpdatePackageVariable(dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper, "BatchTag", string.Format("{0}_{{{1}}}", System.Environment.MachineName.Substring(0, 11), Guid.NewGuid()));
result = dmfEntityProxy.CreateAndExecuteExportPackageToMDS(dMFMDMSSISPackageHelper);
}
return result;
}
Import
By using DMFMDMSSISPackageHelper, the import process sets up source and destination settings so that DIXF service knows where to pull data from and push data to. Import process should use DMFEntityProxy to import data from MDS to staging by calling DMFEntityProxy::createAndExecuteImportPackageFromMDS. Please refer to MdmMdsToAxImporter::createAndExecuteImportPackageFromMDS in AX for implementation details.
Summary
We’ve covered all the key architecture components and processes for implementing MDM adapter on top of the existing R3 MDM functionalities. Essentially, the idea is to re-create how AX manages data synchronization with DIXF service outside of AX. This approach takes advantage of all the existing functionalities exposed by the DIXF web service, giving developers a very quick way to integrate non-AX systems as part of the overall MDM solution.
While extending existing DIXF functionalities can integrate data to and from your staging table, the heavy lifting is done by your application specific StagingWriter and EntityWriter for moving data between staging table and your target tables. Based on the complexity of your system, one staging entity could be mapped to either one target entity or multiple target entities. Majority of your development time would probably end up being spent here.
The design documented here takes advantage of existing DIXF functionalities, but comes with the cost of flexibility. If you want more flexibility interacting with MDS, you can build directly on top of MDS. However, most of the concepts we talked about here, staging to/from target, version control, conflict management, data filtering, still apply.
Note
Due to limitation of DIXF, integration with other non-AX systems is limited to systems running on SQL server only. However, for systems running on other type of DB, such as Oracle, there is nothing preventing one from performing integration with SQL MDS by using custom SSIS packages. Most of the concepts covered in this blog post would still apply.
Appendix
Instructions on how to deploy the sample MDM adapter app.
Disclaimer: This sample app is only configured to perform synchronization on Customers. However, it should be quit straight forward to extend it to include support for additional entities. This sample code is only to demo concepts discussed in this blog post. It is not production quality and please do not use this code in your production environment.
Pre-requisites
- One box setup with AX 2012 R3, DIXF, MDS, and SQL
- R3 MDM enabled with at least one AX instance connected with MDS. Specific steps can be found here: MDM in Dynamics AX 2012 R3
- Customer is deployed to MDS from AX and synchronized
- Visual Studio 2012
Set up and configuration
- Download zip file attached to this post.
- Create sample database, NONAX_DB, by restoring from file NONAX_DB.bak found in the sample code zip file.
- Make sure the user account running DIXF web service has access to NONAX_DB.
- On the machine where DIXF service is running, make sure port 7000 is open for inbound traffic.
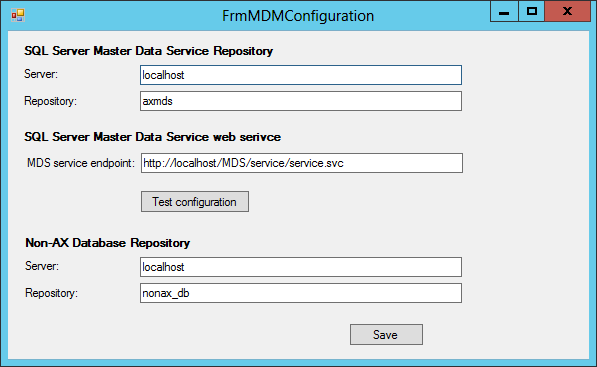
- Open the solution in visual studio and run. One can also run MDMSyncManager.exe from the bin\debug
- Click on Configure on menu bar to configure MDS and local DB related info.
- Click Test configuration is make sure the connection to MDS is working properly.
- Click Save to save changes and close the configuration form.
Please refer to the sample configuration screen below for a sample configuration.
Data synchronization
- On sync group form, input sync group name and click Save.

- Click on Entities to bring up the sync group detail form.
- Input “1“ as sync sequence number, “Customer” as the entity name, and click Save.

- On sync group form, click Sync to sync data between MDS and non-AX client.

- Click Customer, customer form should pop up, displaying customers synced from MDS.
Conflict management
- In AX, go to AR\Customers, edit one customer, change customer name, save change and sync changes to MDS.
- In non-AX client customer form, modify the same customer, change to a different name and hit enter to confirm change, click save to save the change.
- On sync group form, click “View conflict”, it should show no conflict, which is expected because we haven't sync yet.
- Click Sync. After sync is done, click “View conflict”, it should show one conflict for customer.

- Go to Excel master data add-in and resolve the conflict.
- On sync group form, click Sync. One customer should be synced back from MDS and conflict should be resolved.
Data filtering
- Create a subscription view in MDS for customers who belongs to a given CUSTGROUP, say 10.
- On sync group form, click Entities.
- On sync group details form, select an entity and click on Settings.
- One can change synchronization type to be “Push and pull” or “Pull only”. To illustrate filtered pull, change subscription view to the view created in step 1. Save change.

- In AX, make change to two customers, each belong to a different CUSTGROUP, say 10 and 20. Sync change to MDS.
- On sync group form, click Sync, only one customer belong to CUSTGROUP 10 should be imported
Comments
Anonymous
September 25, 2014
Sorry, I did not read everything you have in this article.But, the basic idea is ones you have MDS then any applications can utilize it as MDM platform for their master information needs.You can utilize it via subscription views, web services or ETL in your downstream applications including AX. My question is can I substitute MDS with another MDM platform and still configure AX to use it.In another words, I want to tell AX to use Informatica or IBM (examples) MDM instead.Can I do that?Thanks.Anonymous
October 01, 2014
Hi Joel,Yes, you got the basic idea correctly. MDS is being used as the master data repository in AX2012 R3 MDM solution.There is absolutely nothing preventing you from using repositories other than SQL MDS as your single source of truth repository. You just have to manage change tracking, data synchronization and conflict resolution, etc, on your own.Thanks,PaulAnonymous
October 07, 2014
I had created two instance AX & AX2 and i had transferd data from AX1 TO AX2 Through MDS , the next day after starting service to repeat the same transfer , i found that instance name had changed to AX1 Restore and the service connection is not oeprating . Can you please advice what should i do?ThanskAnonymous
October 09, 2014
Hi Mohamed,This blog post focuses on extending R3 AX MDM with external applications and your question is really on the R3 MDM feature itself. While I would refer you seeking help through proper Microsoft support channel, here are some pointers I can offer you.You can go to Manage synchronization formConfigure and see if your connection to SQL MDS is still alive.Make sure SQL MDS web application is running, e.g., you can access it with a browser. Make sure DIXF is working properly by going to setup/DIXF parameters and click Validate. Please also refer to technet.microsoft.com/.../dn720451.aspx for a TechNet article on MDM for more deployment details.Thanks,PaulAnonymous
October 20, 2014
The comment has been removedAnonymous
October 20, 2014
Hi Simone,The exception means the application is not able to connect to MDS. It could be number of reasons. Can you please double check that you have set up everything according to the instructions listed under AppendixSet up and configuration? The MDM adapter uses DIXF service to integrate data between MDS and external applications. If your AX MDM is working and syncing correctly, which means the DIXF service is working properly, it might have been the connection string you specified in the sample app's configuration page is incorrect.Hope this helps.Thanks,PaulAnonymous
October 21, 2014
Dear Paul,Thanks for your quick response. Unfortunately, I still am unable to get the sample adapter working. R3 DIXF & MDM are working, and the service address is exactly the same. Any further ideas on what might cause the error? I have checked all dll / config files, but they seem to be configured correctly. Might it be due to the demo environment? Can you provide me with details on the configuration which was used to develop this adapter?Kind regards,SimoneAnonymous
October 23, 2014
The comment has been removedAnonymous
December 02, 2014
Hi Paul,I hope you can help me with my questions concerning MDM and Non-AX DBs.We are looking for the best mechanism to integrate an AX database to our existing SQL Server environment (Non-AX). Lots of applications are already reading and writing directly from/to the SQL database. What we need here is a multi master mode.Sadly we won't be able to modify the existing Non-AX applications (time, cost, ...). Is it still possible to synchronize the AX database with our existing SQL Server database using the AX MDM Adapter?If not, do you have another solution that may solve our problem?Thanks,ManuelAnonymous
December 04, 2014
Hi Manuel,Current AX 2012R3 MDM topology requires SQL MDS as the data hub where single copy of truth master data is stored. If you are going to use R3 MDM, you would have to link your non-AX application to MDS, just like the sample I showed in this blog post. That would require you to modify your non-AX applications to implement the adapter interfaces such as change tracking, version tracking, etc. The adapter I showed in this blog is written to demonstrate the possibility of doing such integration with the sample application. You have to write your own adapter for your non-AX applications for this to work.As you know, integration is a complicated problem and without more insights into your exact scenario, I would not be able to give you any useful direction. As a general guideline, when integrate data in and out of AX, we recommend building your integration process on top of DIXF.Thanks,Paul