GPT in Windows
GUID Partition Table or GPT is a standard that’s been around for a while but is still not completely understood by the masses. So I wanted to do a quick blog to address some of the common questions we hear from day to day.
Previously in my blog entitled Understanding the 2 TB Limit in Windows Storage I briefly mentioned using GPT disks to bypass one of the common 2 TB limitations. If you haven’t already read that blog, you might want to review it before continuing….I’ll wait.
Welcome back. One of the things that tend to trip people up on this subject is terminology. So let’s address that first.
People will hear about GPT disks and think that it is just the next in a line of progression like this…
Basic disks >> Dynamic disks >> GPT disks
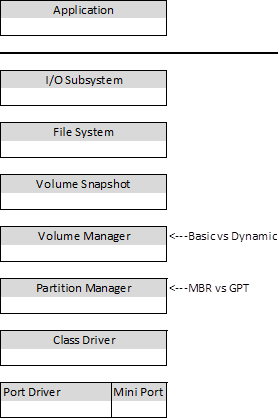
While this logic is understandable, it is incorrect as GPT disks can be either Basic or Dynamic. Let’s take a look at the Microsoft Windows storage stack (simplified).
The determination of whether a disk is Basic or Dynamic is made at the Volume Manager level, while the determination of whether a disk is MBR or GPT is made at the Partition Manager level. So a disk can be any of the following combinations…
· MBR and Basic
· MBR and Dynamic
· GPT and Basic
· GPT and Dynamic
To understand this, you must first understand the subtle differentiation between partitions and volumes. This can be difficult to visualize as they are often the same thing. The way I keep it straight is I use the following rules…
· If it is just a box – It is a partition
· If it contains a single file system – It is a volume
As this would qualify as a completely different subject, I’ll cover that in a later blog. For now, just understand that there is a difference between partitions and volumes.
For the sake of discussion I will display hard drives as a collection of sectors on a number line. It will start with sector 0 and end with the last sector of the drive. Using this logic, examples of MBR disks and GPT disks would look like this.
MBR Style (basic)-
Sector zero will house the Master Boot Record (MBR), which contains the partition table. The partition table will tell us where the partition will start and how big it is. Once the partition is formatted a volume is created. The volume starts at the first boot sector and ends at the last boot sector (aka backup boot sector).
GPT Style (basic)-
Sector zero will house the Protective MBR. This structure is only present to identify the disk as GPT and protect the new partition array from legacy disk utilities that are not GPT-aware.
Instead of having a four line partition table, there is a 32 sector partition array. This allows us to have more partitions as well as much larger partitions. Also, there is a backup Partition Array out at the end of the drive. This gives us partition information redundancy that MBR disks just don’t have.
The MS Reserved Partition marks off an area of the disk for Windows to use to store metadata that is not part of the file system. Previously this metadata was stored in unprotected regions of the disk.
The volume is just like it was before. It starts at the first boot sector and ends at the last.
Keep in mind that in using GPT we are just changing how we define the box, not the contents of the box. Assuming that you are using NTFS, the file system is the same in both examples. I can’t stress this enough. There is no difference in NTFS between MBR and GPT. In fact if you create a GPT disk smaller than 2 TB in size, a clever person could change the box with a sector editor, turn it into an MBR disk, and never alter the volume itself. NTFS is blissfully unaware of what type box it lives in.
NOTE: I recommend that you do NOT use a sector editor, ever. Doing so without a full understanding of how on-disk structures function can cause data loss.
GPT Style (dynamic) -
The big change for a dynamic disk is the location of the LDM database. This metadata was stored at the end of the drive on an MBR disk. On a GPT disk, we carve out part of the MS Reserved Partition and store the LDM database there. This puts it in a protected region and moves it into an area of the disk that is easier to get to. Previously the LDM was stored after the disk’s geometric size boundary.
That’s the basics for how GPT disks work. They bring us the following changes
· More partitions possible
· Larger partitions possible
· Partition data now has redundancy
· Metadata now stored in a protected region
All this while not changing how the file system operates
Robert Mitchell
Senior Support Escalation Engineer
Microsoft Enterprise Platforms Support
Want to know more about Microsoft storage? Check out my other blogs...
https://blogs.technet.com/askcore/archive/2009/10/16/the-four-stages-of-ntfs-file-growth.aspx
https://blogs.technet.com/askcore/archive/2009/12/30/ntfs-metafiles.aspx
https://blogs.technet.com/b/askcore/archive/2010/08/25/ntfs-file-attributes.aspx
Comments
- Anonymous
January 01, 2003
Tom,Yes, but it isn't posted publicly that I know of. The utility is called DMPSS.EXE and is avaiable by request. I think the reason we don't just post it for people is that we want to make sure its being used correctly. You can do a lot of damage with it if you don't understand what you are doing.Anyway, it has a switch in it called 'dumpconfig' which will allow you to dump out the LDM database to a file. Also, there is a 'restoreconfig' switch that allows you to copy the information in the file back to the LDM. Since the database exists outside the file system, conventional backup software will not back it up. However, block level backups that are done on the SAN side (where applicable) do backup everything. As does cloning. - Anonymous
January 01, 2003
You are welcome. I'm glad you enjoyed it. - Anonymous
January 01, 2003
Sorry for the late answer, Marco. I don't monitor my old blogs that closely. But no. Only dynamic disks will have the LDM partition. What happens is when you convert the disk to dynamic, Windows carves out space from the Microsoft Reserved partition and uses that to create the LDM partition. Disks that are still basic will have no need for an LDM partition.
Think of it as a 'just in time' partition. - Anonymous
January 01, 2003
DISKPART> sel disk 2Disk 2 is now the selected disk.DISKPART> convert gptDiskPart successfully converted the selected disk to GPT format.Then you can create partitions the same as you did with MBR disks. - Anonymous
October 10, 2010
Great introduction into GPT thank you very much. - Anonymous
October 28, 2010
Thanks a lot! Even though this article is in not in native language it's rather simple to understand for me - Anonymous
February 07, 2011
Great article!But how do I create GPT-style partitions by using DISKPART?Thanks! - Anonymous
April 21, 2012
I tell you, basing from experience, this is the BEST GPT WEBSITE EVER! Just click on the link to register.www.hidelinks.com - Anonymous
October 26, 2012
are there any tools to backup the ldm from each disk? - Anonymous
June 04, 2014
Hi...Great Blog!!!
i can find the LDM partition only in the gpt dynamic disk? in the gpt basic disk?
thank you! - Anonymous
September 24, 2014
Is there a difference between NTFS between GPT Basic and Dynamic partitions? - Anonymous
August 06, 2015
IL2, The file system, for the most part, is unaware of what type of container it is stored in. NTFS is the same, whether it is stored on GPT disk, MBR disk, basic volumes, dynamic volumes, primary partitions, extended partitions, or storage spaces. The file system rides on a layer above all of that. It functions the same. The only difference in GPT is that that partitions can be larger....so NTFS can be larger. - Anonymous
August 27, 2015
I would like more learning material on the subjects discussed here, are there any titles you would suggest? - Anonymous
December 26, 2015
The comment has been removed - Anonymous
September 23, 2016
The comment has been removed