Lync Server 2013 Guidance Series: Can I partition Global Address List?
As part of designing Lync Server 2013 infrastructure, one frequently comes across the common question from the customer "Can I have two global address list for user?" The reason cited is I have corporate and business function office I don’t want user from the corporate office be able to search for users from the business function and visa-versa.
The answer is YES you can partition your global address list into 2 or more partitions. In today’s blog we are going to understand how to best partition your global address list, the advantage, disadvantages and limitations. What are the best practices and how to get it done?
For illustration we shall use 6 Lync user start Luser1 until Luser6 all enabled for sip domain @contoso.com we have grouped the users into two logical group representing two departments within and organization
Group Even |
Group Odd |
Other |
Luser2 |
Luser1 |
Luser7 |
Luser4 |
Luser3 |
Luser8 |
Luser6 |
Luser5 |
Table 1 Test User Setup
Post the Office communication server 2007 R2, starting with Lync Server 2010 we moved to Central Management store and Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS) model for the management and storage of settings for user or server objects. The re-engineering of this feature takes into account that many organizations have a very rich structure of OUs, and limiting users to siloes based on OUs became a boundary that was no longer feasible as a user management practice. Users need to have visibility beyond their OU. Lync Server 2010 adds an attribute onto user objects. This attribute, msRTCSIP-GroupingID, can be populated with the Globally Unique Identification (GUID) unique to users that need to be able to search for each other. Unless the user is a member of the tagged group, the search results will not display the user contacts.
Note: Even though a user may not be able to receive search results for specific users by means of the Address Book, this does not prevent them from using email contact information or manual entry of contact sip address or phone number information.
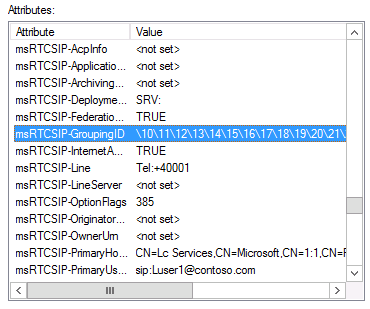
What is msRTCSIP-GroupingID attribute?
Figure 1 msRTCSIP-GroupingID attribute
MsRTCSIP-GroupingID attribute is user/contact attribute which by default is not set when a user/contact account is enabled for Lync Server pool. The use of the attribute only simulates a grouping of users in logical partitions, and does not create a true partition in which the security and privacy of the tenants can be tightly controlled. Hence the attribute msRTCSIP-GroupingID should not be used in a commercial hosting environment and is not supported by Microsoft due to the privacy and security risks when providing multi-tenancy in a hosting environment
Understanding msRTCSIP-GroupingID
Before we discuss how to populate the msRTCSIP-GroupingID with value. Let look at the advantages and disadvantages of using msRTCSIP-GroupingID.
Advantage of using msRTCSIP-GroupingID
As discussed msRTCSIP-GroupingID creates logical partitions that facilitates the Address book Search to search within between the users that share the same value.
Disadvantage of using msRTCSIP-GroupingID
Once the value has been set for msRTCSIP-GroupingID for group of user, user who do not share the msRTCSIP-GroupingID value or have msRTCSIP-GroupingID no set cannot search for these users
From the above example if Group Even has the msRTCSIP-GroupingID unique value set for its user and Group Odd have msRTCSIP-GroupingID unique value set and group other who do not have msRTCSIP-GroupingID value set. Users from Group Odd will not be able to search for users from Group Even using the Lync GAL and visa-versa.
Group Name |
Group Even |
Group Odd |
Other |
msRTCSIP-GroupingID Value Set |
Yes |
Yes |
No |
Can Search user Part of Group Even |
Yes |
No |
No |
Can Search user Part of Group Odd |
No |
Yes |
No |
Can Search user Part of Other |
No |
No |
Yes |
Table 3 How msRTCSIP-GroupingID works
Notes: Once the msRTCSIP-GroupingID attribute is set we cannot have Lync enabled user that can search the entire Lync Address List
Figure 2 Group odd search when the msRTCSIP-GroupingID Attribute is set
Figure 3 Group even search when the msRTCSIP-GroupingID Attribute is set
Notes: Address book segregation or partition doesn’t means that, user from one address book cannot send message to user in another address book. In order to prevent user from one address book communicate with users that part of another address book with a single Lync environment and third party ethical firewall solution is required.
Set msRTCSIP-GroupingID Value
Setting the msRTCSIP-GroupingID requires making change to the end User Active Directory Attributes, hence is recommended to back up Active Directory and you Lync server 2013. For more information on backing up Lync server please refer https://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/hh202160.aspx.
Before implementing these steps in production environment, please ensure proper testing has been done in Lab or test environment
Notes: Based on the number of partition you want to create in your Lync Server setup please choose that many number of unique Hexadecimal Guid.
Manual Method
Open Active directory user and computer snap-in enable advance features in view
Go into user properties in the attribute editor tab and set the unique hexadecimal value for the users who are part of the same group
Group Name |
Group Even |
Group Odd |
Member |
Luser2 Luser4 Luser6 |
Luser1 Luser3 Luser5 |
Hexadecimal Guid |
A1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
B1 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 |
Figure 4 Sample Hexadecimal
Script Method
Partitioning Lync Address Book using msRTCSIP-GroupingID and OU Based Separation
Please refer to the following script
https://gallery.technet.microsoft.com/office/Partitioning-Lync-Address-2450e01d
Verify msRTCSIP-GroupingID has been set
Open Active directory user and computer snap-in enable advance features in view
Go into user properties in the attribute editor tab verify if the msRTCSIP-GroupingID has been displayed as follow
Figure 5: msRTCSIP-GroupingID value set
Additional steps
Server Side
- Open the Lync Management shell as administrator
- Run "Update-CsAddressBook" Cmdlet
Client side
Sign out exist the Lync client Delete the SIP profile
For Lync 2010, open <user profile>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Communicator\
For Lync 2013, <user profile>\AppData\Local\Microsoft\Office\15.0\Lync\
For multiple users you can also use a script
Summary
MsRTCSIP-GroupingID attribute only simulates a grouping of users in logical partitions, and does not create a true partition in which the security and privacy of the tenants can be tightly controlled. Prior to configuring msRTCSIP-GroupingID it’s important to understand its advantages and disadvantages. Even though a user may not be able to receive search results for specific users by means of the Address Book, this does not prevent them from using email contact information or manual entry of contact sip address or phone number information. Once the msRTCSIP-GroupingID Attribute is set we cannot have Lync enabled user that can search the entire Lync Address List. Lync Address book segregation or partition doesn’t means that, user from one address book cannot send message to user in another address book.