Create a prompt
Custom prompts give makers the freedom to instruct the GPT model to behave in a certain way or to perform a specific task. By carefully crafting a prompt, you can generate responses that suit your specific business needs. This transforms the GPT model into a flexible tool to accomplish various tasks.
Important
- AI Builder prompts run on GPT 4o Mini and GPT 4o models powered by Azure OpenAI Service.
- This capability is limited to some regions.
- This capability might be subject to usage limits or capacity throttling.
Supported languages
The following list of supported languages for AI prompts in AI Builder is subject to be updated:
Chinese (Simplified), Czech (Czech Republic), Danish (Denmark), Dutch (Netherlands), English (United States), Finnish (Finland), French (France), German (Germany), Greek (Greece), Italian (Italy), Japanese (Japan), Korean (Korea), Polish (Poland), Portuguese (Brazil), Russian (Russia), Spanish (Spain), Swedish (Sweden), Thai (Thailand), Turkish (Türkiye)
Use specific text for more relevant responses
The goal of prompt engineering is to create an instruction that's as specific as possible to get a more relevant response from the GPT model. Your prompts should be specific to a topic and convey your intent.
A prompt might include the following information:
- The topic
- Keywords or phrases that are associated with the topic
- The tone of the response
- The target audience
If the generated text is too long or contains irrelevant information, adjust the prompt. A good prompt has the following characteristics:
- Clear and concise: It's written in clear and concise language that's easy to understand.
- Specific: It's specific enough to guide the GPT model in the right direction.
- Contextual: It provides enough context for the GPT model to generate meaningful output.
- Relevant: It's relevant to the task and provides the GPT model with enough information to generate meaningful output.
Parts of a prompt
There are generally two parts to a prompt for a GPT model: the instruction and the context.
- The instruction is the first part of the prompt. It should provide clear directions on what the GPT model should do, for example, "Summarize this email in three bullets."
- The context is the second part of the prompt. It should provide the information the GPT model needs to generate an appropriate response, for example, "The email contains customer feedback from the past week."
Example
A custom prompt can guide the GPT model to answer a question, complete text, translate languages, summarize a document, and identify tasks, to-dos, and action items in text. The complexity of a custom prompt can range from a single sentence to something more intricate, depending on the task.
Download: AI Builder prompt engineering guide
Download the guide here: AI Builder prompt engineering guide (10 pages, 10X13 in.)

Download and print the AI Builder prompt engineering guide (10 pages, 10X13 inch size) to keep it handy and get help creating prompts.
Create a GPT prompt
Prompt builder provides the flexibility to create your own custom prompt by defining input variables that enable incorporating dynamic runtime content within a prompt. It gives you the ability to validate the prompt with Test your prompt, ensuring optimal prompt performance and correctness of the response before integration into your business solutions.
Sign in to Power Apps, Power Automate, or Copilot Studio.
On the left pane, select AI prompts or Prompts > Create text with GPT using a prompt.
For Power Apps and Power Automate, you might need to first select AI hub on the left pane.
On the lower-right corner, select Create custom prompt.
Configure and test your prompt
Use the following screenshot as a guide to build and test your prompt.
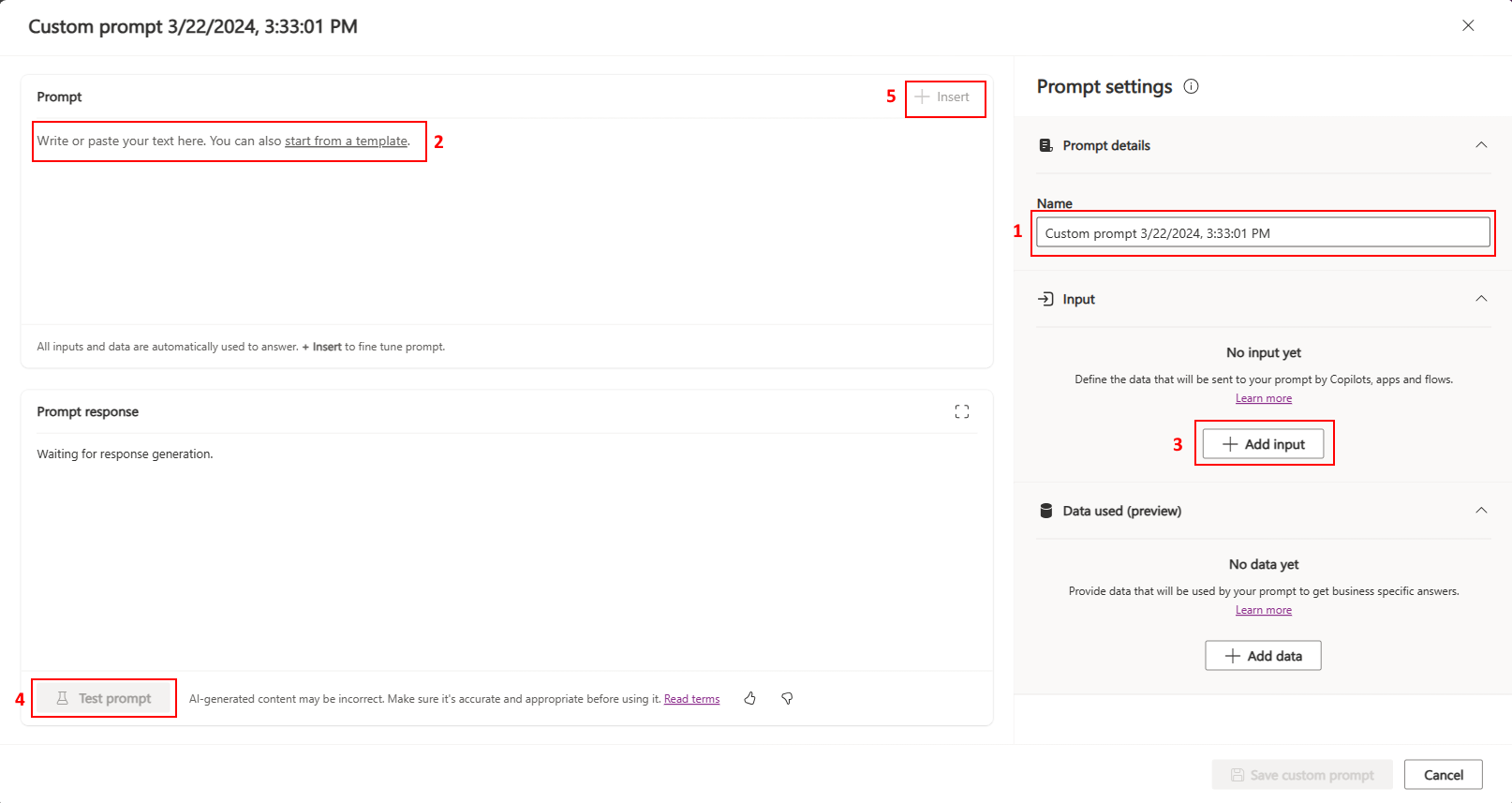
Enter a name for your prompt.
Write or paste your prompt.
Alternatively, you can build upon an existing template to give yourself a starting point.
Tip
For help finding prompts you can use, go to the Prompt directory Sample Solution Gallery.
Add a dynamic value, and then select Enter.
In the process of building prompts, makers often need to provide context data to ensure that the GPT model generates appropriate responses. To facilitate this, dynamic values are used in the prompt, serving as placeholders that get filled with actual data at runtime.
Test your prompt using the sample value.
The testing of prompts is an essential yet often under-emphasized capability. Manual testing is beneficial for iterative building experiences.
(Optional) Insert input or data references to define how it must be used in context of the prompt.
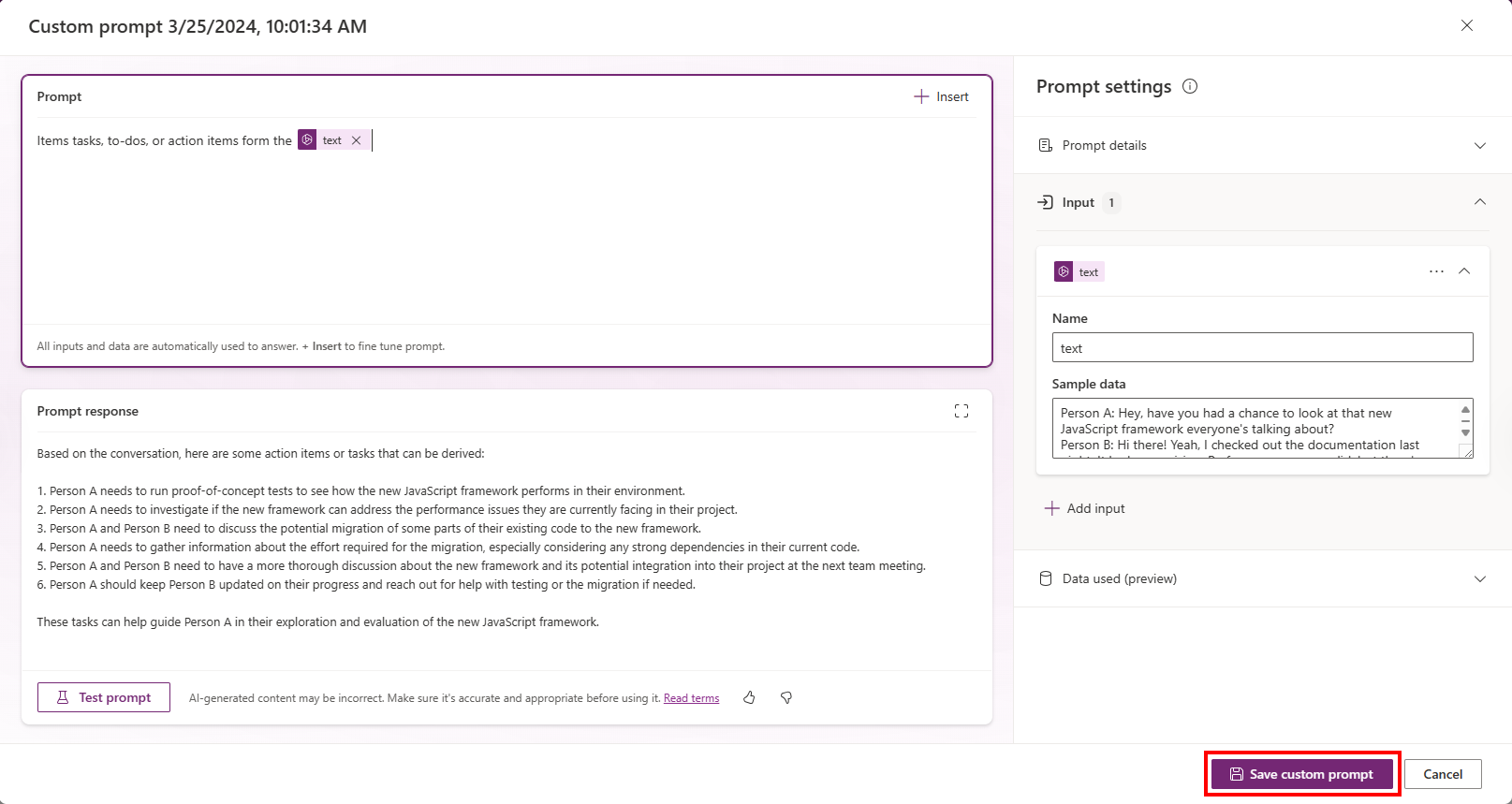
Review and save your prompt
Prompt builder allows makers to save prompts to facilitate reusability, archiving, and future improvement of prompts.
After you test your prompt with the sample value (in step 4), review it to see how well your prompt works.
When you're satisfied, select Save custom prompt.
Use your prompt in Power Apps or Power Automate
Your next step is determined by the app you plan to use with your prompt.
Use in Power Apps
- Empowers makers to incorporate existing prompts into their apps.
- Use a prompt in Power Apps
Use in Power Automate
- Empowers makers to incorporate existing prompts into their flows.
- Use a prompt in Power Automate