Before you build a category classification model
Before you build your category classification model, make sure your data is in Microsoft Dataverse and it's structured in the correct format.
Prerequisites
This model requires the training data to be available within a Dataverse table. Support for data from external sources is currently unavailable.
Make sure your administrator has assigned you a security role with Read privilege for the table that has the training data.
Make sure you have appropriate permissions to create tables in your Power Platform environment. You can use either the System Customizer or System Administrator built-in security roles.
Supported languages
AI Builder category classification supports the following languages. If you try to classify text in other languages, your model might not work properly.
- English
- French
- German
- Italian
- Spanish
- Portuguese
Data preparation
The training data used to train the model from the Dataverse table should conform to the following:
Store text and tags as two columns in the same table. Each row must have data in the Text column.
You can provide one or more tags to data in the same row in the Text column. You can also leave the Tags column empty.
If you've identified multiple tags within the text sample, provide them as delimited text in the Tags fields. Currently, commas (,), semicolons (;), and tab characters are supported separators.
Text Tags Great clean and quiet room with a free to-go breakfast Dining, Room Small but well-orchestrated room that was comfy Room I love the view from the 13th floor (none) Make sure to have a minimum of 10 distinct text samples for each tag to be extracted. Tags with fewer than 10 samples won't be trained. In the previous example, there should have been a minimum of 10 rows each that have been tagged with the Dining and Room tags.
If Room has been tagged in fewer than 10 rows in the data, it will be ignored. The model won't be trained to categorize data for that tag.
For every tag that is used, provide a minimum of 10 text samples where it isn't used.
Text Tags Great clean and quiet room with a free to go breakfast Room Small but well-orchestrated room that was comfy Room (none) Room If all rows in the table are tagged to Room, and there are no rows—or fewer than 10 rows—that have been tagged to another label, the model will fail the training process.
A table must have at least two tags, and each one must have 10 text samples.
You can define up to 200 distinct tags. Each tag is a category that will be identified and extracted from the given text.
Each sample of text data must have fewer than 5,000 characters.
If you don't have training data and want to try AI Builder category classification, follow these instructions to use sample data.
Examples of training data format
This section provides examples of the training data format in a Dataverse table.
| Columns | Data type | Size |
|---|---|---|
| Comments | Text | 3,000 |
| Tags | Text | 100 |
| Comments | Tags |
|---|---|
| During my stay, I was completely ignored. The staff failed to pick up on me aspirating and having a UTI. I also had pneumonia. |
Care |
| I was seen very soon after arriving each time and all the staff, nurse, doctor, and anesthetist were very helpful. There seems to be a good sense of teamwork. |
Staff, Check-in |
| The equipment seemed up to date. The nurse/healthcare assistant seemed quite caring. |
Facilities, Staff |
Note
If you don't have your own training data and want to try AI Builder category classification, you can get started by downloading sample data for the category classification model. More information: Use sample data to do category classification
Import your data into Dataverse
Because training data for a category classification model needs to be available as a Dataverse table, let's begin with preparing data in Dataverse table.
Dataverse includes a powerful set of connectors to help you import data from many sources. More information: Add data to a table in Microsoft Dataverse by using Power Query.
As an example, let's look at how to import training data from an Excel workbook. This example uses a file containing what's shown in the following table.
| Id | Tags | Text |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Dining | Breakfast was a bit of a hassle. |
| 2 | Dining, Room | Great clean and quiet room with a free to-go breakfast. |
| 3 | Room, Dining, Location | The staff we dealt with was very friendly and helpful. The hallways and our room were clean and comfortable. Breakfast (included) was muffins and bagels. |
| 4 | Location, Dining | Surrounding area is full of bars and restaurants. |
| 5 | Service | Staff was respectful. |
In the example, the tags are separated by a comma (,). As an alternative, you can use a semicolon (;) or tab character.
Sign in to Power Apps.
Select the environment you want to work in.

Select Data > Tables.
Select your table. If you don't have a table already, follow the steps in Create a custom table.
Select Data > Get data > Get data from Excel from the ribbon of the selected table.
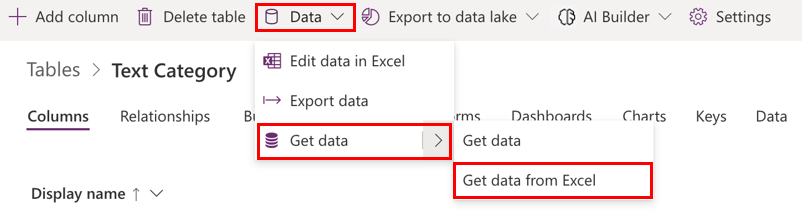
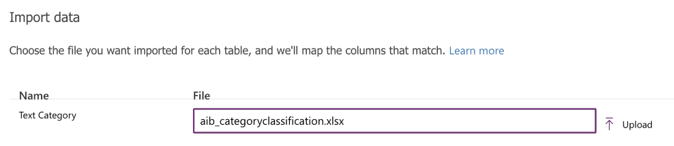
On the Import data screen, select the Excel file that has the data referred to in the Examples of training data format section earlier in this topic, and then select Upload.
To review the field mappings on the Column mappings for Text Category screen, select Map Columns.
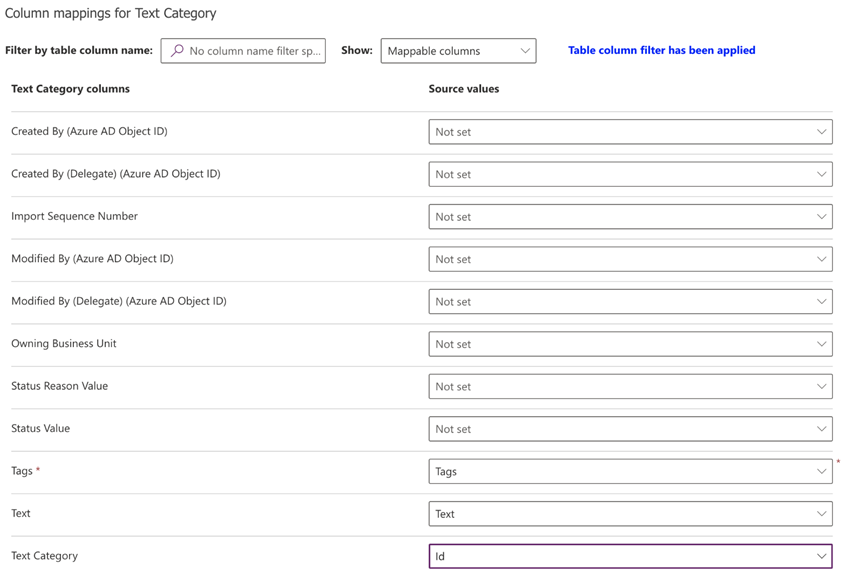
The left side lists all columns defined in the table. The dropdown list on the right shows the columns available in the Excel file.
Map the Tags, Text, and Id columns from Excel to the respective columns in the table.
After you've mapped the columns, go back to the import step by selecting Save changes in the upper-right corner.
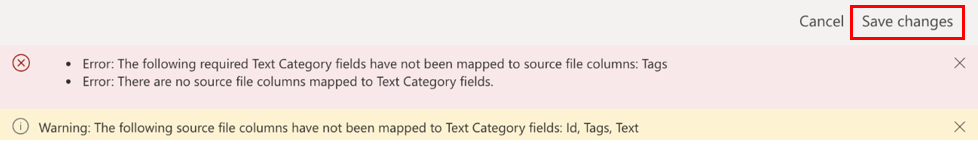
After you see the Mapping status as successful, begin the import process by selecting Import in the upper-right corner.
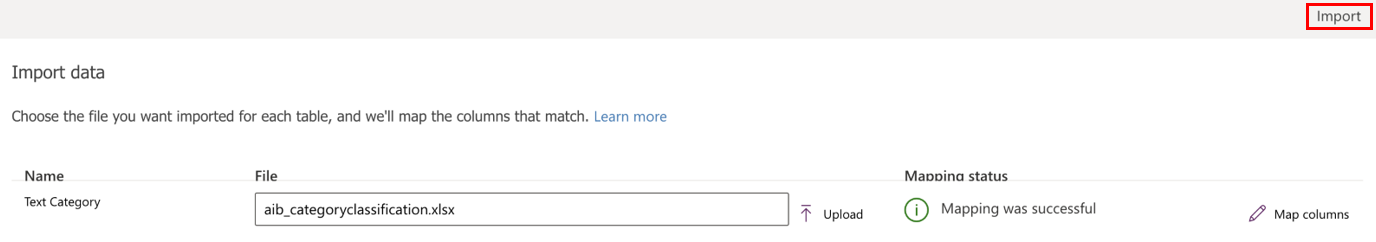
The import process might take a few minutes depending on the volume of data being imported. After a few minutes, refresh the Data tab of the table to find all the records imported from the Excel file.
You're now ready to go to the next step.