Learn about sensitivity labels in Microsoft Purview Data Map (preview)
Important
Labeling in the Microsoft Purview Data Map is currently in preview. The Supplemental Terms of Use for Microsoft Azure Previews include additional legal terms that apply to Azure features that are in beta, preview, or otherwise not yet released into general availability.
To get work done, people in your organization collaborate with others both inside and outside the organization. Data doesn't always stay in your cloud, and often roams everywhere, across devices, apps, and services. When your data roams, you still want it to be secure in a way that meets your organization's business and compliance policies.
Applying sensitivity labels to your content enables you to keep your data secure by stating how sensitive certain data is in your organization. It also abstracts the data itself, so you use labels to track the type of data, without exposing sensitive data on another platform.
For example, applying a sensitivity label ‘highly confidential’ to a document that contains social security number and credit card numbers helps you identify the sensitivity of the document without knowing the actual data in the document.
Benefits of labeling in Microsoft Purview
Microsoft Purview allows you to apply sensitivity labels to assets, enabling you to classify and protect your data.
- Label travels with the data: The sensitivity labels created in Microsoft Purview Information Protection can also be extended to the Microsoft Purview Data Map, SharePoint, Teams, Power BI, and SQL. When you apply a label on an office document and then scan it into the Microsoft Purview Data Map, the label will be applied to the data asset. While the label is applied to the actual file in Microsoft Purview Information Protection, it's only added as metadata in the Microsoft Purview map. While there are differences in how a label is applied to an asset across various services/applications, labels travel with the data and is recognized by all the services you extend it to.
- Overview of your data estate: Microsoft Purview provides insights into your data through precanned reports. When you scan data into the Microsoft Purview Data Map, we hydrate the reports with information on what assets you have, scan history, classifications found in your data, labels applied, glossary terms, etc.
- Automatic labeling: Labels can be applied automatically based on sensitivity of the data. When an asset is scanned for sensitive data, autolabeling policies are used to decide which sensitivity label to apply. You can create autolabeling policies for sensitivity labels, defining which classification/sensitive information types when found will apply a label automatically.
- Apply labels to files and database columns: Labels can be applied to files in storage such as Azure Data Lake or Azure Files and to table columns in Azure SQL Database.
Sensitivity labels are tags that you can apply on assets to classify and protect your data. Learn more about sensitivity labels here.
How to apply labels to assets in the Microsoft Purview Data Map
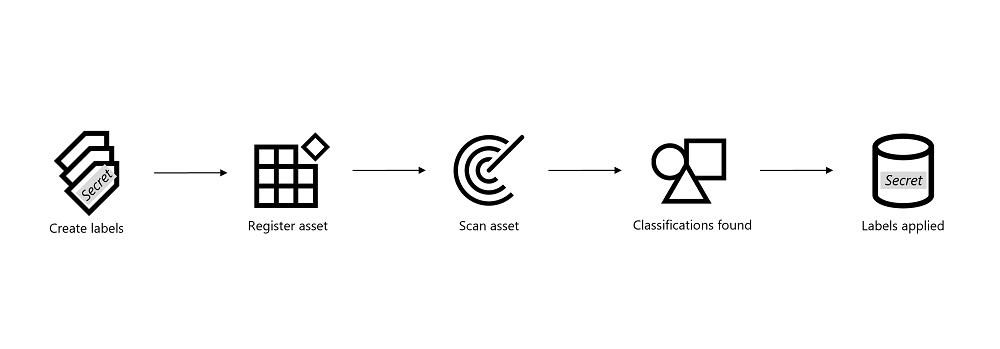
Being able to apply labels to your asset in the data map requires you to perform the following steps:
- Create new or apply existing sensitivity labels. You can apply any sensitivity label with label scope of Files & other data assets to Microsoft Purview assets.
- Register and scan your asset in the Microsoft Purview Data Map.
- Microsoft Purview applies classifications: When you schedule a scan on an asset, Microsoft Purview scans the type of data in your asset and applies classifications to it in the data map. Application of classifications is done automatically by Microsoft Purview, there's no action for you.
- Create an auto-labeling policy for non-Microsoft 365 workloads: Create an auto-labeling policy scoped to All or specific assets within the locations of "Azure Storage" or "Azure SQL". Define the out of the box classifications that once detected in the next data scan will result in the automatic labeling of the selected sensitivity label.
Note
Autolabeling policies are conditions that you specify, stating when a particular label should be applied. When the data is next scanned Purview data map will check if these conditions are met to automatically assign the label to the data. If you don't see a supported data source show up in the auto-labeling policy for selection, verify that the data source was correctly registered and shows up in data map. The locations shown for auto-labeling policy scoping depends on what assets have already been registered.
Supported data sources
You can find the data sources that support labeling on the supported sources page.
Labeling for SQL databases
Microsoft also supports labeling for SQL database columns using the SQL data classification in SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). While Microsoft Purview uses the global sensitivity labels, SSMS only uses labels defined locally.
Labeling in Microsoft Purview and labeling in SSMS are separate processes that don't currently interact with each other. Therefore, labels applied in SSMS are not shown in Microsoft Purview, and vice versa. We recommend Microsoft Purview for labeling SQL databases, because the labels can be applied globally, across multiple platforms.
For more information, see the SQL data discovery and classification documentation.