Update Azure Network Watcher extension to the latest version
Azure Network Watcher is a network performance monitoring, diagnostic, and analytics service that monitors Azure networks. The Network Watcher Agent virtual machine (VM) extension is a requirement for capturing network traffic on demand and using other advanced functionality on Azure VMs. It's used by connection monitor, connection troubleshoot, and packet capture.
Prerequisites
- An Azure account with an active subscription. If you don't have one, create a free account.
- An Azure virtual machine (VM) that has the Network Watcher extension installed.
Latest version
The latest version of the Network Watcher extension is 1.4.3422.1.
Identify latest version
Use az vm extension image list command to identify the latest version of the Network Watcher extension for your VM's operating system.
# Identify latest version of Network Watcher extension for Linux.
az vm extension image list --name 'NetworkWatcherAgentLinux' --publisher 'Microsoft.Azure.NetworkWatcher' --latest --location 'eastus'
Update your extension using a PowerShell script
If you have large deployments, use a PowerShell script to update multiple VMs at once. The following PowerShell script updates Network Watcher extension of all Windows VMs in a subscription:
<#
.SYNOPSIS
This script will scan all VMs in the provided subscription and upgrade any out of date AzureNetworkWatcherExtensions
.DESCRIPTION
This script should be no-op if AzureNetworkWatcherExtensions are up to date
Requires Azure PowerShell 4.2 or higher to be installed (e.g. Install-Module AzureRM).
.EXAMPLE
.\UpdateVMAgentsInSub.ps1 -SubID F4BC4873-5DAB-491E-B713-1358EF4992F2 -NoUpdate
#>
[CmdletBinding()]
param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string] $SubID,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[Switch] $NoUpdate = $false,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$false)]
[string] $MinVersion = "1.4.2.1"
)
function NeedsUpdate($version)
{
if ([Version]$version -lt [Version]$MinVersion)
{
$lessThan = $true
}else{
$lessThan = $false
}
return $lessThan
}
Write-Host "Scanning all VMs in the subscription: $($SubID)"
Set-AzContext -SubscriptionId $SubID
$vms = Get-AzVM
$foundVMs = $false
Write-Host "Starting VM search, this may take a while"
foreach ($vmName in $vms)
{
# Get Detailed VM info
$vm = Get-AzVM -ResourceGroupName $vmName.ResourceGroupName -Name $vmName.name -Status
$isitWindows = $vm.OsName -like "*Windows*"
foreach ($extension in $vm.Extensions)
{
if ($extension.Name -eq "AzureNetworkWatcherExtension")
{
if (NeedsUpdate($extension.TypeHandlerVersion))
{
$foundVMs = $true
if (-not ($NoUpdate))
{
Write-Host "Found VM that needs to be updated: subscriptions/$($SubID)/resourceGroups/$($vm.ResourceGroupName)/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/$($vm.Name) -> Updating " -NoNewline
Remove-AzVMExtension -ResourceGroupName $vm.ResourceGroupName -VMName $vm.Name -Name "AzureNetworkWatcherExtension" -Force
Write-Host "... " -NoNewline
$type = if ($isitWindows) { "NetworkWatcherAgentWindows" } else { "NetworkWatcherAgentLinux" }
Set-AzVMExtension -ResourceGroupName $vm.ResourceGroupName -Location $vmName.Location -VMName $vm.Name -Name "AzureNetworkWatcherExtension" -Publisher "Microsoft.Azure.NetworkWatcher" -Type $type -typeHandlerVersion $MinVersion
Write-Host "Done"
}
else
{
Write-Host "Found $(if ($isitWindows) {"Windows"} else {"Linux"}) VM that needs to be updated: subscriptions/$($SubID)/resourceGroups/$($vm.ResourceGroupName)/providers/Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/$($vm.Name)"
}
}
}
}
}
if ($foundVMs)
{
Write-Host "Finished $(if ($NoUpdate) {"searching"} else {"updating"}) out of date AzureNetworkWatcherExtension on VMs"
}
else
{
Write-Host "All AzureNetworkWatcherExtensions up to date"
}
Update your extension manually
To update your extension, you need to know your extension version.
Check your extension version
You can check your extension version by using the Azure portal, the Azure CLI, or PowerShell.
Use the Azure portal
- Go to the Extensions pane of your VM in the Azure portal.
- Select the AzureNetworkWatcher extension to see the details pane.
- Locate the version number in the Version field.
Use the Azure CLI
Run the following command from an Azure CLI prompt:
az vm get-instance-view --resource-group "SampleRG" --name "Sample-VM"
Locate "AzureNetworkWatcherExtension" in the output and identify the version number from the “TypeHandlerVersion” field in the output.
Information about the extension appears multiple times in the JSON output. The full version number of the extension is available under the Extensions block.
You should see something like the below:
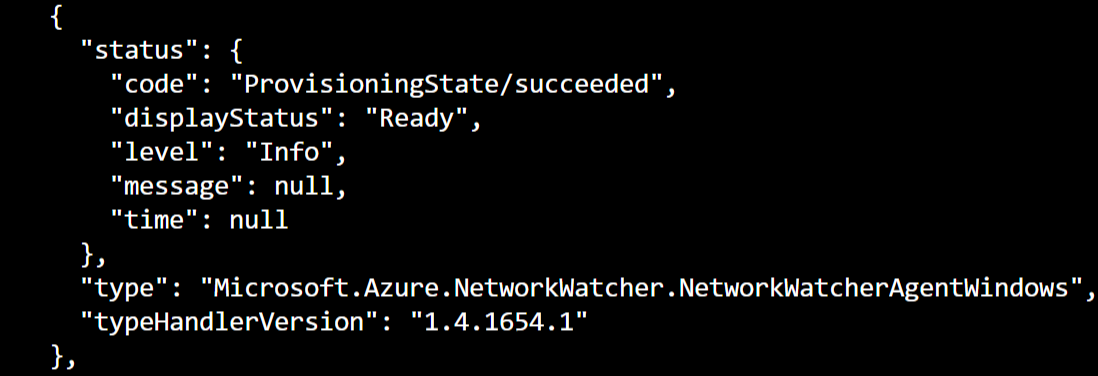
Use PowerShell
Run the following commands from a PowerShell prompt:
Get-AzVM -ResourceGroupName "SampleRG" -Name "Sample-VM" -Status
Locate the Azure Network Watcher extension in the output and identify the version number from the “TypeHandlerVersion” field in the output.
You should see something like the below:
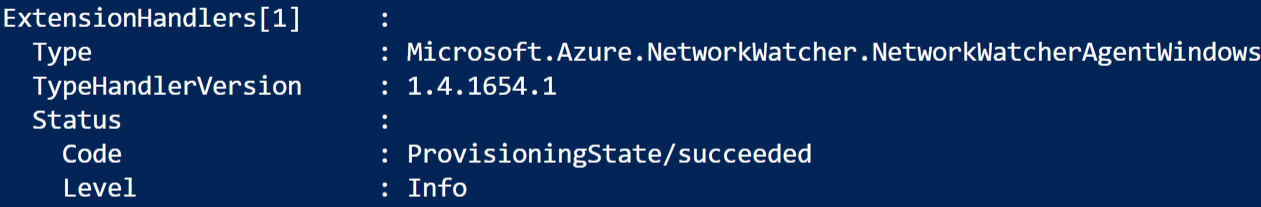
Update your extension
If your version is below the latest version mentioned above, update your extension by using any of the following options.
Option 1: Use PowerShell
Run the following commands:
#Linux command
Set-AzVMExtension -ResourceGroupName "myResourceGroup1" -Location "WestUS" -VMName "myVM1" -Name "AzureNetworkWatcherExtension" -Publisher "Microsoft.Azure.NetworkWatcher" -Type "NetworkWatcherAgentLinux"
#Windows command
Set-AzVMExtension -ResourceGroupName "myResourceGroup1" -Location "WestUS" -VMName "myVM1" -Name "AzureNetworkWatcherExtension" -Publisher "Microsoft.Azure.NetworkWatcher" -Type "NetworkWatcherAgentWindows" -ForceRerun "True"
If that doesn't work. Remove and install the extension again, using the steps below, to install latest version.
Removing the extension
#Same command for Linux and Windows
Remove-AzVMExtension -ResourceGroupName "SampleRG" -VMName "Sample-VM" -Name "AzureNetworkWatcherExtension"
Installing the extension again
#Linux command
Set-AzVMExtension -ResourceGroupName "SampleRG" -Location "centralus" -VMName "Sample-VM" -Name "AzureNetworkWatcherExtension" -Publisher "Microsoft.Azure.NetworkWatcher" -Type "NetworkWatcherAgentLinux" -typeHandlerVersion "1.4"
#Windows command
Set-AzVMExtension -ResourceGroupName "SampleRG" -Location "centralus" -VMName "Sample-VM" -Name "AzureNetworkWatcherExtension" -Publisher "Microsoft.Azure.NetworkWatcher" -Type "NetworkWatcherAgentWindows" -typeHandlerVersion "1.4"
Option 2: Use the Azure CLI
Force an upgrade.
#Linux command
az vm extension set --resource-group "myResourceGroup1" --vm-name "myVM1" --name "NetworkWatcherAgentLinux" --publisher "Microsoft.Azure.NetworkWatcher" --force-update
#Windows command
az vm extension set --resource-group "myResourceGroup1" --vm-name "myVM1" --name "NetworkWatcherAgentWindows" --publisher "Microsoft.Azure.NetworkWatcher" --force-update
If that doesn't work, remove and install the extension again, and follow these steps to automatically add the latest version.
Remove the extension.
#Same for Linux and Windows
az vm extension delete --resource-group "myResourceGroup1" --vm-name "myVM1" -n "AzureNetworkWatcherExtension"
Install the extension again.
#Linux command
az vm extension set --resource-group "DALANDEMO" --vm-name "Linux-01" --name "NetworkWatcherAgentLinux" --publisher "Microsoft.Azure.NetworkWatcher"
#Windows command
az vm extension set --resource-group "DALANDEMO" --vm-name "Linux-01" --name "NetworkWatcherAgentWindows" --publisher "Microsoft.Azure.NetworkWatcher"
Option 3: Reboot your VMs
If you have auto-upgrade set to true for the Network Watcher extension, reboot your VM installation to the latest extension.
Support
If you need more help at any point in this article, see the Network Watcher extension documentation for Linux or Windows. You can also contact the Azure experts on the MSDN Azure and Stack Overflow forums. Alternatively, file an Azure support incident. Go to the Azure support site, and select Get support. For information about using Azure Support, read the Microsoft Azure support FAQ.