Set up an appliance for Azure Government cloud
Follow this article to deploy an Azure Migrate appliance for Azure Government cloud to perform:
- Discovery, assessment and agentless replication of servers running in VMware environment
- Discovery and assessment of servers running in Hyper-V environment
- Discovery and assessment of physical servers or servers running on other clouds like AWS, GCP, Xen etc.
If you want to set up an appliance in the public cloud, follow this article.
Note
The option to deploy an appliance using a template (for servers running in VMware or Hyper-V environment) isn't supported in Azure Government. You need to use the installer script only.
Prerequisites
You can use the script to deploy the Azure Migrate appliance on an existing physical or a virtualized server.
The server that will act as the appliance must be running Windows Server 2019 or Windows Server 2022 and meet other requirements for VMware, Hyper-V, and physical servers.
If you run the script on a server with Azure Migrate appliance already set up, you can choose to clean up the existing configuration and set up a fresh appliance of the desired configuration. When you execute the script, you will get a notification as shown below:

Set up the appliance for VMware
- To set up the appliance, you download the zipped file named AzureMigrateInstaller.zip either from the portal or from here.
- Extract the contents on the server where you want to deploy the appliance.
- Execute the PowerShell script to launch the appliance configuration manager.
- Set up the appliance and configure it for the first time.
Download the script
- In Servers, databases and web apps > Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment, select Discover.
- In Discover server > Are your servers virtualized?, select Yes, with VMware vSphere hypervisor.
- Provide an appliance name and generate a project key in the portal.
- Select Download, to download the zipped file.
Verify security
Check that the zipped file is secure, before you deploy it.
- On the server to which you downloaded the file, open an administrator command window.
- Run the following command to generate the hash for the zipped file:
C:\>CertUtil -HashFile <file_location> [Hashing Algorithm]- Example usage:
C:\>CertUtil -HashFile C:\Users\administrator\Desktop\AzureMigrateInstaller.zip SHA256
- Verify the latest appliance version and hash value:
| Download | Hash value |
|---|---|
| Latest version | 07783A31D1E66BE963349B5553DC1F1E94C70AA149E11AC7D8914F4076480731 |
Run the script
Extract the zipped file to a folder on the server that will host the appliance. Make sure you don't run the script on a server with an existing Azure Migrate appliance.
Launch PowerShell on the above server with administrative (elevated) privilege.
Change the PowerShell directory to the folder where the contents have been extracted from the downloaded zipped file.
Run the script named AzureMigrateInstaller.ps1 by running the following command:
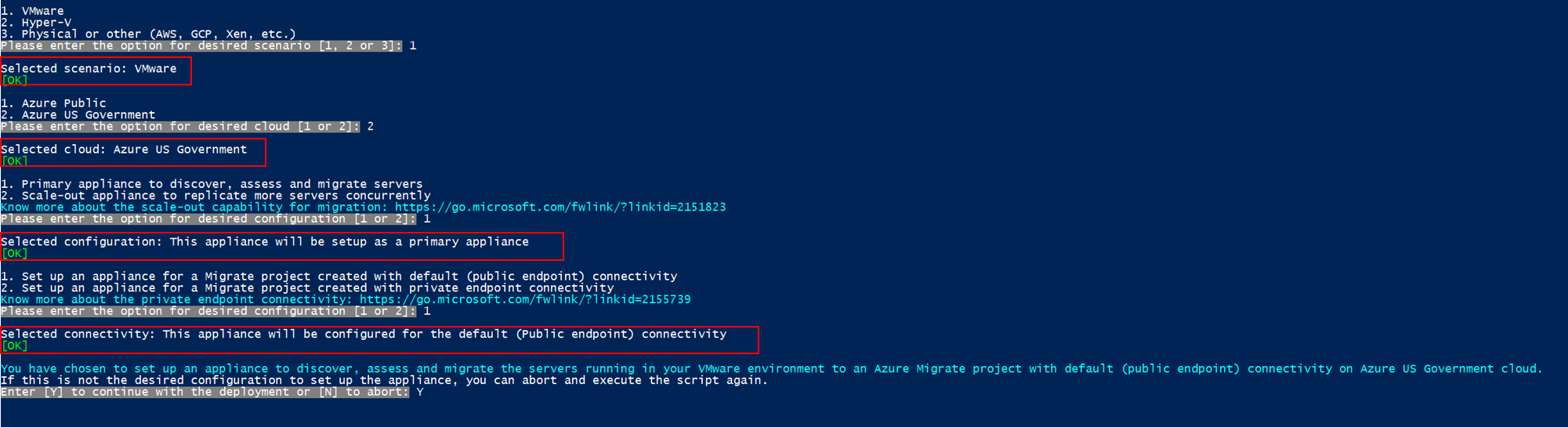
PS C:\Users\administrator\Desktop\AzureMigrateInstaller> .\AzureMigrateInstaller.ps1Select from the scenario, cloud and connectivity options to deploy an appliance with the desired configuration. For instance, the selection shown below sets up an appliance to discover, assess and migrate servers running in your VMware environment to an Azure Migrate project with default (public endpoint) connectivity on Azure Government cloud.
The installer script does the following:
- Installs agents and a web application.
- Install Windows roles, including Windows Activation Service, IIS, and PowerShell ISE.
- Download and installs an IIS rewritable module.
- Updates a registry key (HKLM) with persistent setting details for Azure Migrate.
- Creates the following files under the path:
- Config Files: %Programdata%\Microsoft Azure\Config
- Log Files: %Programdata%\Microsoft Azure\Logs
After the script has executed successfully, the appliance configuration manager will be launched automatically.
Verify access
Make sure that the appliance can connect to Azure URLs for government clouds.
Set up the appliance for Hyper-V
- To set up the appliance, you download the zipped file named AzureMigrateInstaller.zip either from the portal or from here.
- Extract the contents on the server where you want to deploy the appliance.
- Execute the PowerShell script to launch the appliance configuration manager.
- Set up the appliance and configure it for the first time.
Download the script
- In Servers, databases and web apps > Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment, select Discover.
- In Discover servers > Are your servers virtualized?, select Yes, with Hyper-V.
- Provide an appliance name and generate a project key in the portal.
- Select Download to download the zipped file.
Verify security
Check that the zipped file is secure, before you deploy it.
On the server to which you downloaded the file, open an administrator command window.
Run the following command to generate the hash for the zipped file:
C:\>CertUtil -HashFile <file_location> [Hashing Algorithm]- Example usage:
C:\>CertUtil -HashFile C:\Users\administrator\Desktop\AzureMigrateInstaller.zip SHA256
Verify the latest appliance version and hash value:
Download Hash value Latest version 07783A31D1E66BE963349B5553DC1F1E94C70AA149E11AC7D8914F4076480731
Run the script
Extract the zipped file to a folder on the server that will host the appliance. Make sure you don't run the script on a server with an existing Azure Migrate appliance.
Launch PowerShell on the above server with administrative (elevated) privilege.
Change the PowerShell directory to the folder where the contents have been extracted from the downloaded zipped file.
Run the script named AzureMigrateInstaller.ps1 by running the following command:
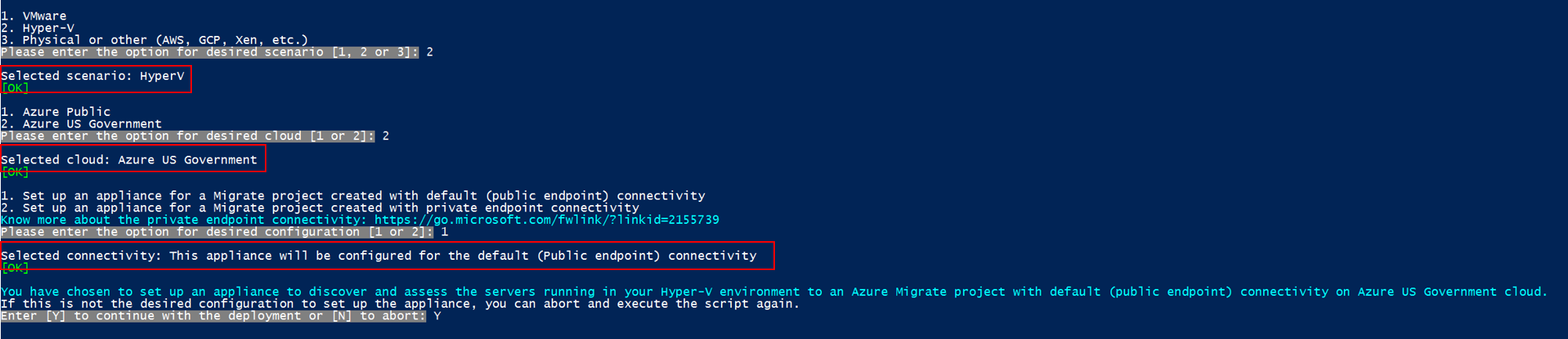
PS C:\Users\administrator\Desktop\AzureMigrateInstaller> .\AzureMigrateInstaller.ps1Select from the scenario, cloud and connectivity options to deploy an appliance with the desired configuration. For instance, the selection shown below sets up an appliance to discover and assess servers running in your Hyper-V environment to an Azure Migrate project with default (public endpoint) connectivity on Azure Government cloud.
The installer script does the following:
- Installs agents and a web application.
- Install Windows roles, including Windows Activation Service, IIS, and PowerShell ISE.
- Download and installs an IIS rewritable module.
- Updates a registry key (HKLM) with persistent setting details for Azure Migrate.
- Creates the following files under the path:
- Config Files: %Programdata%\Microsoft Azure\Config
- Log Files: %Programdata%\Microsoft Azure\Logs
After the script has executed successfully, the appliance configuration manager will be launched automatically.
Verify access
Make sure that the appliance can connect to Azure URLs for government clouds.
Set up the appliance for physical servers
- To set up the appliance, you download the zipped file named AzureMigrateInstaller.zip either from the portal or from here.
- Extract the contents on the server where you want to deploy the appliance.
- Execute the PowerShell script to launch the appliance configuration manager.
- Set up the appliance and configure it for the first time.
Download the script
- In Servers, databases and web apps > Azure Migrate: Discovery and assessment, select Discover.
- In Discover servers > Are your servers virtualized?, select Physical or other (AWS, GCP, Xen etc.).
- Select Download to download the zipped file.
Verify security
Check that the zipped file is secure, before you deploy it.
- On the server to which you downloaded the file, open an administrator command window.
- Run the following command to generate the hash for the zipped file:
C:\>CertUtil -HashFile <file_location> [Hashing Algorithm]- Example usage:
C:\>CertUtil -HashFile C:\Users\administrator\Desktop\AzureMigrateInstaller.zip SHA256
- Verify the latest appliance version and hash value:
| Download | Hash value |
|---|---|
| Latest version | 07783A31D1E66BE963349B5553DC1F1E94C70AA149E11AC7D8914F4076480731 |
Note
The same script can be used to set up Physical appliance for Azure Government cloud with either public or private endpoint connectivity.
Run the script
Extract the zipped file to a folder on the server that will host the appliance. Make sure you don't run the script on a server with an existing Azure Migrate appliance.
Launch PowerShell on the above server with administrative (elevated) privilege.
Change the PowerShell directory to the folder where the contents have been extracted from the downloaded zipped file.
Run the script named AzureMigrateInstaller.ps1 by running the following command:
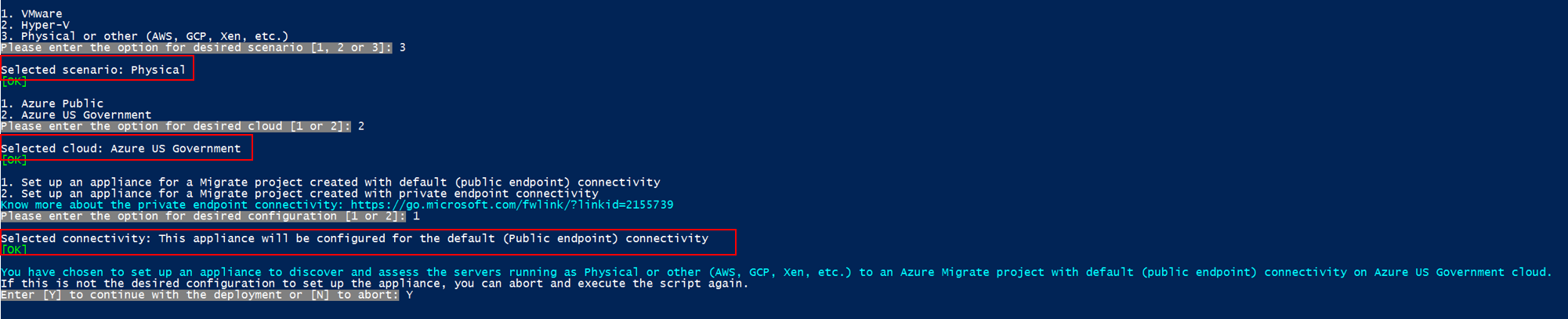
PS C:\Users\administrator\Desktop\AzureMigrateInstaller> .\AzureMigrateInstaller.ps1Select from the scenario, cloud and connectivity options to deploy an appliance with the desired configuration. For instance, the selection shown below sets up an appliance to discover and assess physical servers (or servers running on other clouds like AWS, GCP, Xen etc.) to an Azure Migrate project with default (public endpoint) connectivity on Azure Government cloud.
The installer script does the following:
- Installs agents and a web application.
- Install Windows roles, including Windows Activation Service, IIS, and PowerShell ISE.
- Download and installs an IIS rewritable module.
- Updates a registry key (HKLM) with persistent setting details for Azure Migrate.
- Creates the following files under the path:
- Config Files: %Programdata%\Microsoft Azure\Config
- Log Files: %Programdata%\Microsoft Azure\Logs
After the script has executed successfully, the appliance configuration manager will be launched automatically.
Note
If you come across any issues, you can access the script logs at C:\ProgramData\Microsoft Azure\Logs\AzureMigrateScenarioInstaller_Timestamp.log for troubleshooting.
Verify access
Make sure that the appliance can connect to Azure URLs for government clouds.
Next steps
After deploying the appliance, you need to configure it for the first time, and register it with the project.
- Set up the appliance for VMware, Hyper-V, or physical servers.