Integrate Apache Spark and Apache Hive with Hive Warehouse Connector in Azure HDInsight
The Apache Hive Warehouse Connector (HWC) is a library that allows you to work more easily with Apache Spark and Apache Hive. It supports tasks such as moving data between Spark DataFrames and Hive tables. Also, by directing Spark streaming data into Hive tables. Hive Warehouse Connector works like a bridge between Spark and Hive. It also supports Scala, Java, and Python as programming languages for development.
The Hive Warehouse Connector allows you to take advantage of the unique features of Hive and Spark to build powerful big-data applications.
Apache Hive offers support for database transactions that are Atomic, Consistent, Isolated, and Durable (ACID). For more information on ACID and transactions in Hive, see Hive Transactions. Hive also offers detailed security controls through Apache Ranger and Low Latency Analytical Processing (LLAP) not available in Apache Spark.
Apache Spark has a Structured Streaming API that gives streaming capabilities not available in Apache Hive. Beginning with HDInsight 4.0, Apache Spark 2.3.1 & above, and Apache Hive 3.1.0 have separate metastore catalogs, which make interoperability difficult.
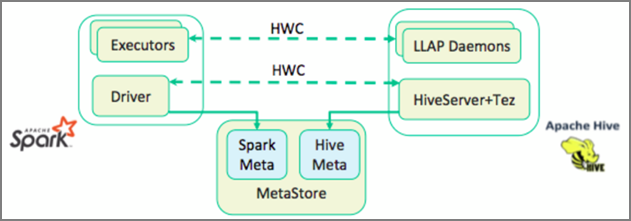
The Hive Warehouse Connector (HWC) makes it easier to use Spark and Hive together. The HWC library loads data from LLAP daemons to Spark executors in parallel. This process makes it more efficient and adaptable than a standard JDBC connection from Spark to Hive. This brings out two different execution modes for HWC:
- Hive JDBC mode via HiveServer2
- Hive LLAP mode using LLAP daemons [Recommended]
By default, HWC is configured to use Hive LLAP daemons. For executing Hive queries (both read and write) using the above modes with their respective APIs, see HWC APIs.
Some of the operations supported by the Hive Warehouse Connector are:
- Describing a table
- Creating a table for ORC-formatted data
- Selecting Hive data and retrieving a DataFrame
- Writing a DataFrame to Hive in batch
- Executing a Hive update statement
- Reading table data from Hive, transforming it in Spark, and writing it to a new Hive table
- Writing a DataFrame or Spark stream to Hive using HiveStreaming
Hive Warehouse Connector setup
Important
- The HiveServer2 Interactive instance installed on Spark 2.4 Enterprise Security Package clusters is not supported for use with the Hive Warehouse Connector. Instead, you must configure a separate HiveServer2 Interactive cluster to host your HiveServer2 Interactive workloads. A Hive Warehouse Connector configuration that utilizes a single Spark 2.4 cluster is not supported.
- Hive Warehouse Connector (HWC) Library is not supported for use with Interactive Query Clusters where Workload Management (WLM) feature is enabled.
In a scenario where you only have Spark workloads and want to use HWC Library, ensure Interactive Query cluster doesn't have Workload Management feature enabled (hive.server2.tez.interactive.queueconfiguration is not set in Hive configs).
For a scenario where both Spark workloads (HWC) and LLAP native workloads exists, You need to create two separate Interactive Query Clusters with shared metastore database. One cluster for native LLAP workloads where WLM feature can be enabled on need basis and other cluster for HWC only workload where WLM feature shouldn't be configured. It's important to note that you can view the WLM resource plans from both the clusters even if it's enabled in only one cluster. Don't make any changes to resource plans in the cluster where WLM feature is disabled as it might impact the WLM functionality in other cluster. - Although Spark supports R computing language for simplifying its data analysis, Hive Warehouse Connector (HWC) Library is not supported to be used with R. To execute HWC workloads, you can execute queries from Spark to Hive using the JDBC-style HiveWarehouseSession API that supports only Scala, Java, and Python.
- Executing queries (both read and write) through HiveServer2 via JDBC mode is not supported for complex data types like Arrays/Struct/Map types.
- HWC supports writing only in ORC file formats. Non-ORC writes (eg: parquet and text file formats) are not supported via HWC.
Hive Warehouse Connector needs separate clusters for Spark and Interactive Query workloads. Follow these steps to set up these clusters in Azure HDInsight.
Supported Cluster types & versions
| HWC Version | Spark Version | InteractiveQuery Version |
|---|---|---|
| v1 | Spark 2.4 | HDI 4.0 | Interactive Query 3.1 | HDI 4.0 |
| v2 | Spark 3.1 | HDI 5.0 | Interactive Query 3.1 | HDI 5.0 |
Create clusters
Create an HDInsight Spark 4.0 cluster with a storage account and a custom Azure virtual network. For information on creating a cluster in an Azure virtual network, see Add HDInsight to an existing virtual network.
Create an HDInsight Interactive Query (LLAP) 4.0 cluster with the same storage account and Azure virtual network as the Spark cluster.
Configure HWC settings
Gather preliminary information
From a web browser, navigate to
https://LLAPCLUSTERNAME.azurehdinsight.net/#/main/services/HIVEwhere LLAPCLUSTERNAME is the name of your Interactive Query cluster.Navigate to Summary > HiveServer2 Interactive JDBC URL and note the value. The value may be similar to:
jdbc:hive2://<zookeepername1>.rekufuk2y2ce.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:2181,<zookeepername2>.rekufuk2y2ce.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:2181,<zookeepername3>.rekufuk2y2ce.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:2181/;serviceDiscoveryMode=zooKeeper;zooKeeperNamespace=hiveserver2-interactive.Navigate to Configs > Advanced > Advanced hive-site > hive.zookeeper.quorum and note the value. The value may be similar to:
<zookeepername1>.rekufuk2y2cezcbowjkbwfnyvd.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:2181,<zookeepername2>.rekufuk2y2cezcbowjkbwfnyvd.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:2181,<zookeepername3>.rekufuk2y2cezcbowjkbwfnyvd.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:2181.Navigate to Configs > Advanced > General > hive.metastore.uris and note the value. The value may be similar to:
thrift://iqgiro.rekufuk2y2cezcbowjkbwfnyvd.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9083,thrift://hn*.rekufuk2y2cezcbowjkbwfnyvd.bx.internal.cloudapp.net:9083.Navigate to Configs > Advanced > Advanced hive-interactive-site > hive.llap.daemon.service.hosts and note the value. The value may be similar to:
@llap0.
Configure Spark cluster settings
From a web browser, navigate to
https://CLUSTERNAME.azurehdinsight.net/#/main/services/SPARK2/configswhere CLUSTERNAME is the name of your Apache Spark cluster.Expand Custom spark2-defaults.
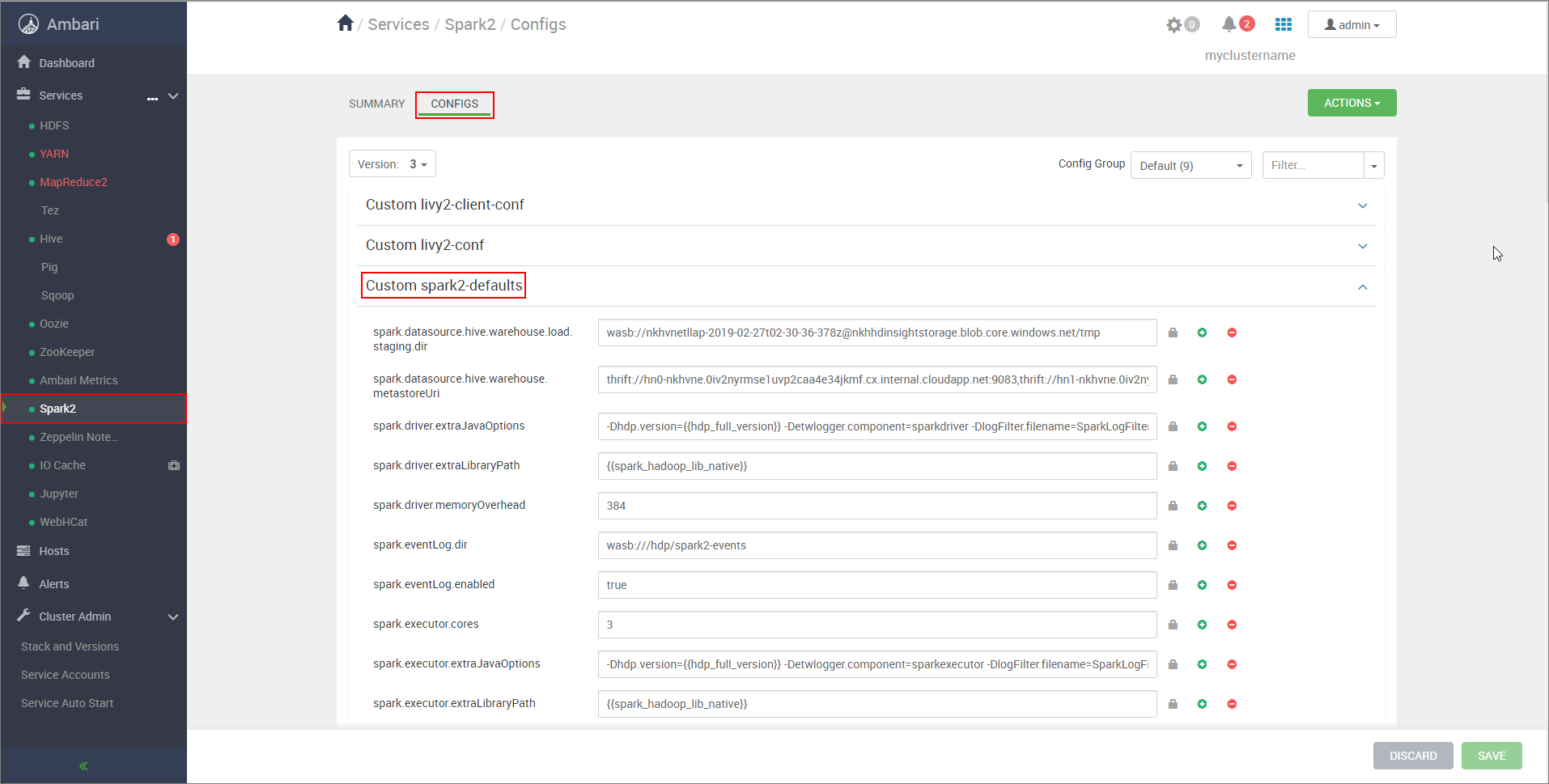
Select Add Property... to add the following configurations:
Configuration Value spark.datasource.hive.warehouse.load.staging.dirIf you're using ADLS Gen2 Storage Account, use abfss://STORAGE_CONTAINER_NAME@STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME.dfs.core.windows.net/tmp
If you're using Azure Blob Storage Account, usewasbs://STORAGE_CONTAINER_NAME@STORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAME.blob.core.windows.net/tmp.
Set to a suitable HDFS-compatible staging directory. If you've two different clusters, the staging directory should be a folder in the staging directory of the LLAP cluster's storage account so that HiveServer2 has access to it. ReplaceSTORAGE_ACCOUNT_NAMEwith the name of the storage account being used by the cluster, andSTORAGE_CONTAINER_NAMEwith the name of the storage container.spark.sql.hive.hiveserver2.jdbc.urlThe value you obtained earlier from HiveServer2 Interactive JDBC URL spark.datasource.hive.warehouse.metastoreUriThe value you obtained earlier from hive.metastore.uris. spark.security.credentials.hiveserver2.enabledtruefor YARN cluster mode andfalsefor YARN client mode.spark.hadoop.hive.zookeeper.quorumThe value you obtained earlier from hive.zookeeper.quorum. spark.hadoop.hive.llap.daemon.service.hostsThe value you obtained earlier from hive.llap.daemon.service.hosts. Save changes and restart all affected components.
Configure HWC for Enterprise Security Package (ESP) clusters
The Enterprise Security Package (ESP) provides enterprise-grade capabilities like Active Directory-based authentication, multi-user support, and role-based access control for Apache Hadoop clusters in Azure HDInsight. For more information on ESP, see Use Enterprise Security Package in HDInsight.
Apart from the configurations mentioned in the previous section, add the following configuration to use HWC on the ESP clusters.
From Ambari web UI of Spark cluster, navigate to Spark2 > CONFIGS > Custom spark2-defaults.
Update the following property.
Configuration Value spark.sql.hive.hiveserver2.jdbc.url.principalhive/<llap-headnode>@<AAD-Domain>From a web browser, navigate to
https://CLUSTERNAME.azurehdinsight.net/#/main/services/HIVE/summarywhere CLUSTERNAME is the name of your Interactive Query cluster. Click on HiveServer2 Interactive. You'll see the Fully Qualified Domain Name (FQDN) of the head node on which LLAP is running as shown in the screenshot. Replace<llap-headnode>with this value.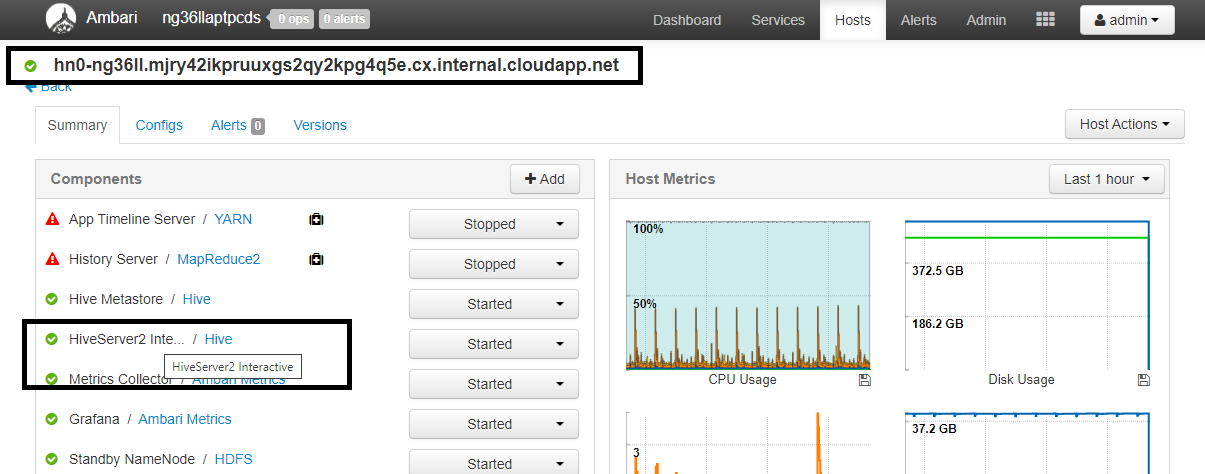
Use ssh command to connect to your Interactive Query cluster. Look for
default_realmparameter in the/etc/krb5.conffile. Replace<AAD-DOMAIN>with this value as an uppercase string, otherwise the credential won't be found.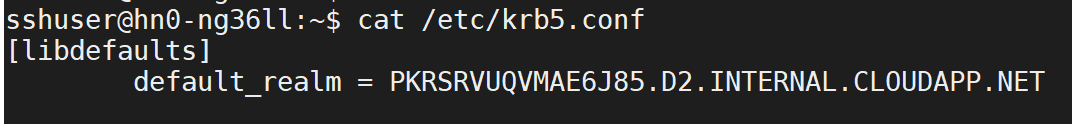
For instance,
hive/hn*.mjry42ikpruuxgs2qy2kpg4q5e.cx.internal.cloudapp.net@PKRSRVUQVMAE6J85.D2.INTERNAL.CLOUDAPP.NET.
Save changes and restart components as needed.
Hive Warehouse Connector usage
You can choose between a few different methods to connect to your Interactive Query cluster and execute queries using the Hive Warehouse Connector. Supported methods include the following tools:
Below are some examples to connect to HWC from Spark.
Spark-shell
This is a way to run Spark interactively through a modified version of the Scala shell.
Use ssh command to connect to your Apache Spark cluster. Edit the command below by replacing CLUSTERNAME with the name of your cluster, and then enter the command:
ssh sshuser@CLUSTERNAME-ssh.azurehdinsight.netFrom your ssh session, execute the following command to note the
hive-warehouse-connector-assemblyversion:ls /usr/hdp/current/hive_warehouse_connectorEdit the code below with the
hive-warehouse-connector-assemblyversion identified above. Then execute the command to start the spark shell:spark-shell --master yarn \ --jars /usr/hdp/current/hive_warehouse_connector/hive-warehouse-connector-assembly-<VERSION>.jar \ --conf spark.security.credentials.hiveserver2.enabled=falseAfter you start the spark shell, a Hive Warehouse Connector instance can be started using the following commands:
import com.hortonworks.hwc.HiveWarehouseSession val hive = HiveWarehouseSession.session(spark).build()
Spark-submit
Spark-submit is a utility to submit any Spark program (or job) to Spark clusters.
The spark-submit job will set up and configure Spark and Hive Warehouse Connector as per our instructions, execute the program we pass to it, then cleanly release the resources that were being used.
Once you build the scala/java code along with the dependencies into an assembly jar, use the below command to launch a Spark application. Replace <VERSION>, and <APP_JAR_PATH> with the actual values.
YARN Client mode
spark-submit \ --class myHwcApp \ --master yarn \ --deploy-mode client \ --jars /usr/hdp/current/hive_warehouse_connector/hive-warehouse-connector-assembly-<VERSION>.jar \ --conf spark.security.credentials.hiveserver2.enabled=false /<APP_JAR_PATH>/myHwcAppProject.jarYARN Cluster mode
spark-submit \ --class myHwcApp \ --master yarn \ --deploy-mode cluster \ --jars /usr/hdp/current/hive_warehouse_connector/hive-warehouse-connector-assembly-<VERSION>.jar \ --conf spark.security.credentials.hiveserver2.enabled=true /<APP_JAR_PATH>/myHwcAppProject.jar
This utility is also used when we have written the entire application in pySpark and packaged into .py files (Python), so that we can submit the entire code to Spark cluster for execution.
For Python applications, pass a .py file in the place of /<APP_JAR_PATH>/myHwcAppProject.jar, and add the below configuration (Python .zip) file to the search path with --py-files.
--py-files /usr/hdp/current/hive_warehouse_connector/pyspark_hwc-<VERSION>.zip
Run queries on Enterprise Security Package (ESP) clusters
Use kinit before starting the spark-shell or spark-submit. Replace USERNAME with the name of a domain account with permissions to access the cluster, then execute the following command:
kinit USERNAME
Securing data on Spark ESP clusters
Create a table
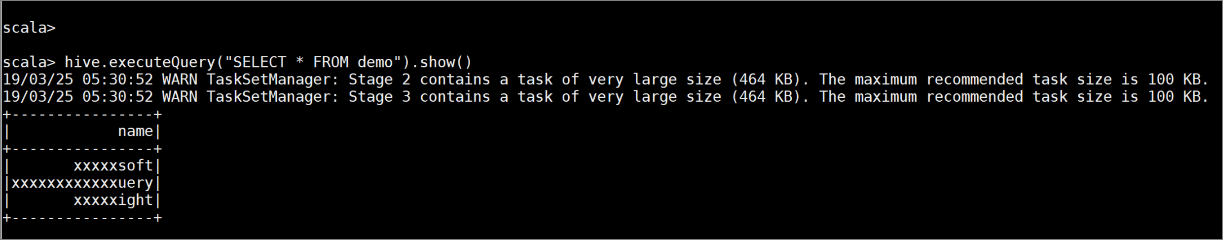
demowith some sample data by entering the following commands:create table demo (name string); INSERT INTO demo VALUES ('HDinsight'); INSERT INTO demo VALUES ('Microsoft'); INSERT INTO demo VALUES ('InteractiveQuery');View the table's contents with the following command. Before you apply the policy, the
demotable shows the full column.hive.executeQuery("SELECT * FROM demo").show()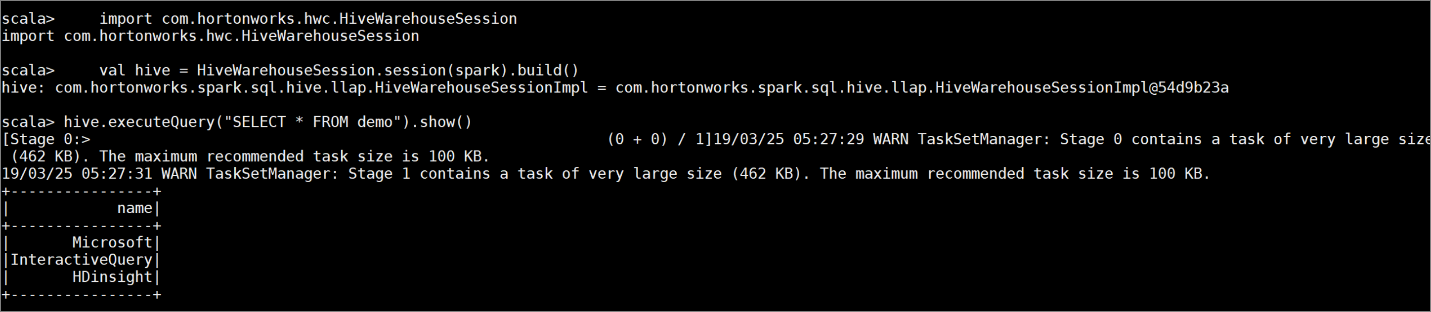
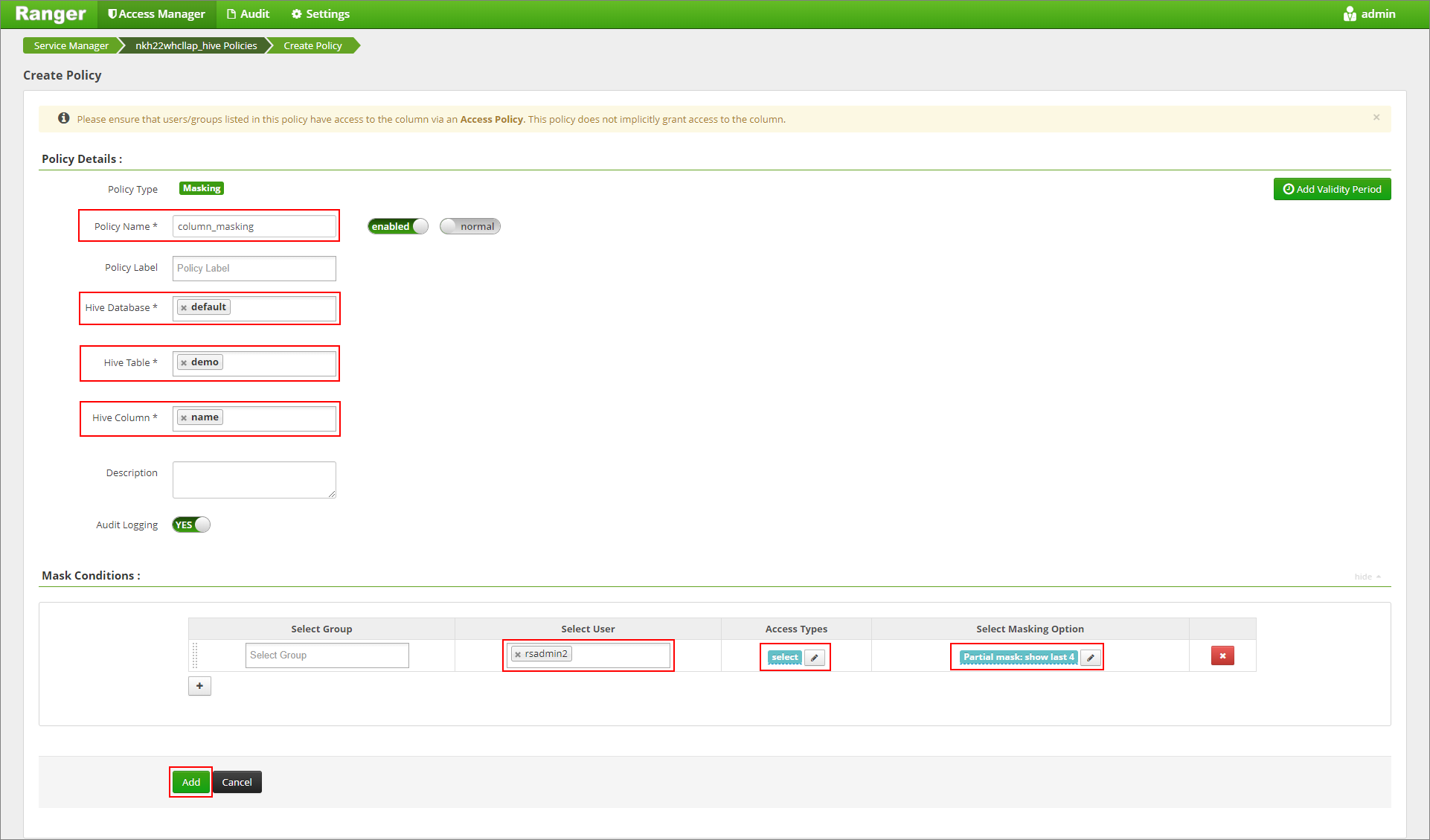
Apply a column masking policy that only shows the last four characters of the column.
Go to the Ranger Admin UI at
https://LLAPCLUSTERNAME.azurehdinsight.net/ranger/.Click on the Hive service for your cluster under Hive.
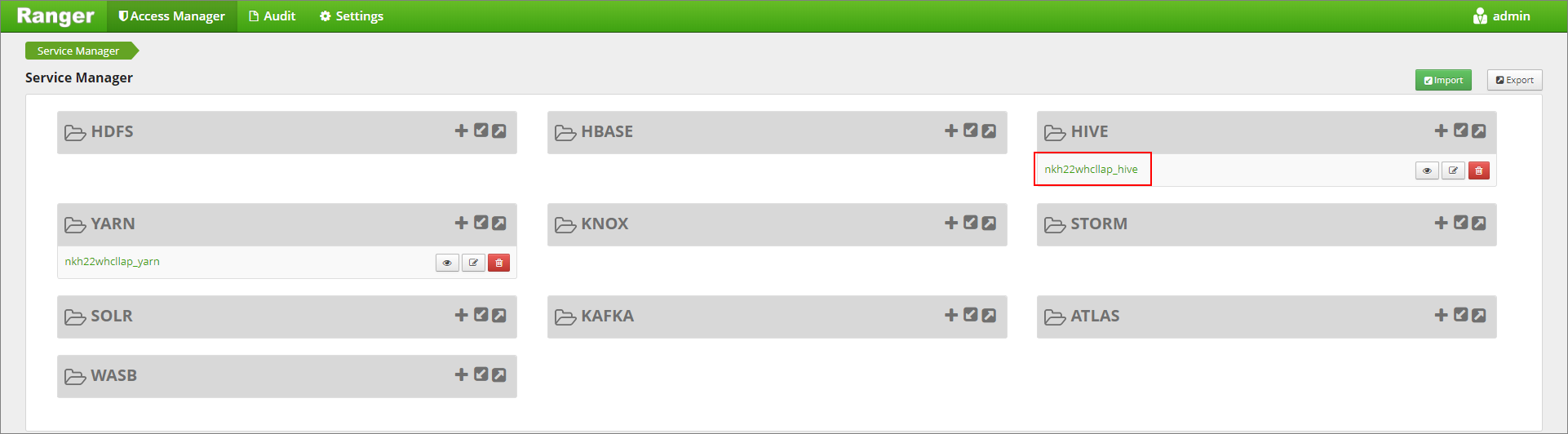
Click on the Masking tab and then Add New Policy
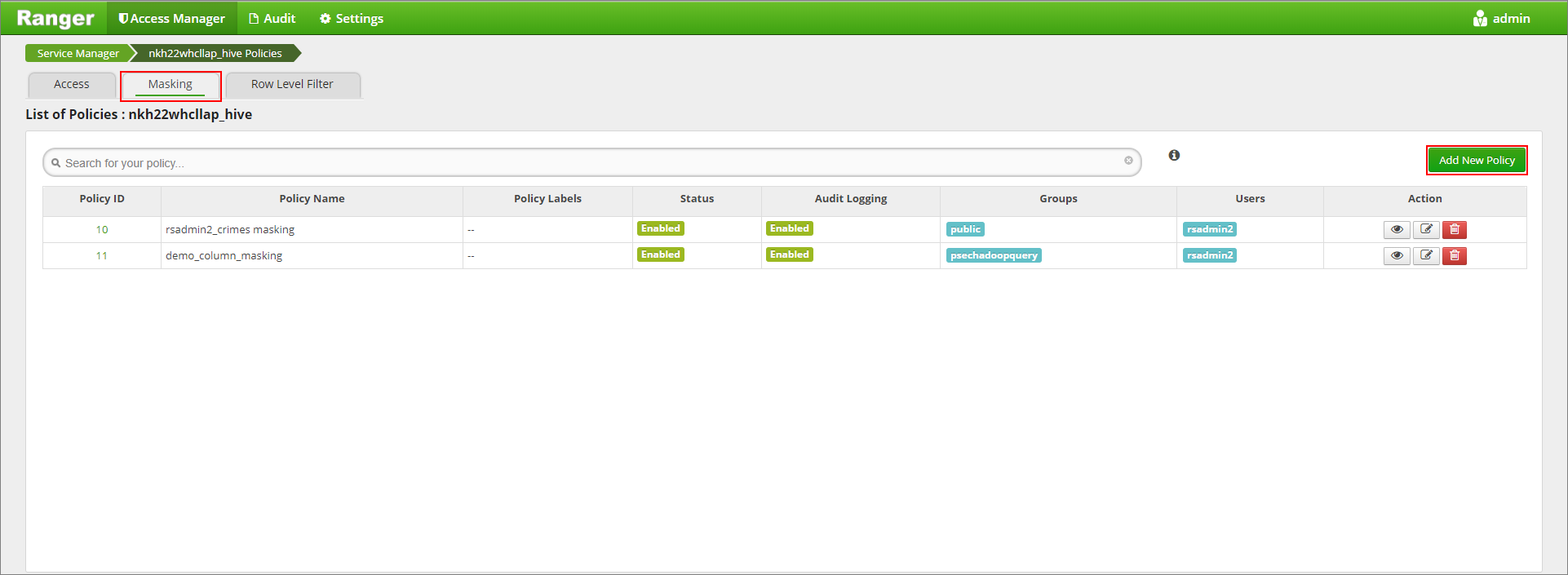
Provide a desired policy name. Select database: Default, Hive table: demo, Hive column: name, User: rsadmin2, Access Types: select, and Partial mask: show last 4 from the Select Masking Option menu. Click Add.
View the table's contents again. After applying the ranger policy, we can see only the last four characters of the column.