Deliver events to webhooks using namespace topics - Azure CLI (preview)
The article provides step-by-step instructions to publish events to Azure Event Grid in the CloudEvents JSON format and deliver those events by using the push delivery model. To be specific, you use Azure CLI and Curl to publish events to a namespace topic in Event Grid and push those events from an event subscription to a webhook handler destination. For more information about the push delivery model, see Push delivery overview.
Note
The Azure CLI Event Grid extension doesn't yet support namespaces and any of the resources it contains. We will use Azure CLI resource to create Event Grid resources.
If you don't have an Azure subscription, create an Azure free account before you begin.
Prerequisites
Use the Bash environment in Azure Cloud Shell. For more information, see Quickstart for Bash in Azure Cloud Shell.
If you prefer to run CLI reference commands locally, install the Azure CLI. If you're running on Windows or macOS, consider running Azure CLI in a Docker container. For more information, see How to run the Azure CLI in a Docker container.
If you're using a local installation, sign in to the Azure CLI by using the
az logincommand. To finish the authentication process, follow the steps displayed in your terminal. For other sign-in options, see Sign in with the Azure CLI.When you're prompted, install the Azure CLI extension on first use. For more information about extensions, see Use extensions with the Azure CLI.
Run az version to find the version and dependent libraries that are installed. To upgrade to the latest version, run az upgrade.
This article requires version 2.0.70 or later of the Azure CLI. If using Azure Cloud Shell, the latest version is already installed.
Enable the Event Grid resource provider
If you haven't previously used Event Grid in your Azure subscription, you might need to register the Event Grid resource provider. Run the following command to register the provider:
az provider register --namespace Microsoft.EventGridIt might take a moment for the registration to finish. To check the status, run the following command:
az provider show --namespace Microsoft.EventGrid --query "registrationState"When
registrationStateisRegistered, you're ready to continue.
Create a resource group
Create an Azure resource group with the az group create command. You use this resource group to contain all resources created in this article.
The general steps to use Cloud Shell to run commands are:
- Select Open Cloud Shell to see an Azure Cloud Shell window on the right pane.
- Copy the command and paste into the Azure Cloud Shell window.
- Press ENTER to run the command.
Declare a variable to hold the name of an Azure resource group. Specify a name for the resource group by replacing
<your-resource-group-name>with a value you like.resource_group="<your-resource-group-name>"location="<your-resource-group-location>"Create a resource group. Change the location as you see fit.
az group create --name $resource_group --location $location
Create a namespace
An Event Grid namespace provides a user-defined endpoint to which you post your events. The following example creates a namespace in your resource group using Bash in Azure Cloud Shell. The namespace name must be unique because it's part of a Domain Name System (DNS) entry. A namespace name should meet the following rules:
- It should be between 3-50 characters.
- It should be regionally unique.
- Only allowed characters are a-z, A-Z, 0-9 and -
- It shouldn't start with reserved key word prefixes like
Microsoft,System, orEventGrid.
Declare a variable to hold the name for your Event Grid namespace. Specify a name for the namespace by replacing
<your-namespace-name>with a value you like.namespace="<your-namespace-name>"Create a namespace. You might want to change the location where it's deployed.
az eventgrid namespace create -g $resource_group -n $namespace -l $location
Create a namespace topic
Create a topic that's used to hold all events published to the namespace endpoint.
Declare a variable to hold the name for your namespace topic. Specify a name for the namespace topic by replacing
<your-topic-name>with a value you like.topic="<your-topic-name>"Create your namespace topic:
az eventgrid namespace topic create -g $resource_group -n $topic --namespace-name $namespace
Create a message endpoint
Before subscribing to the namespace topic, let's create the endpoint for the event message. Typically, the endpoint takes actions based on the event data. To simplify this quickstart, you deploy a prebuilt web app that displays the event messages. The deployed solution includes an App Service plan, an App Service web app, and source code from GitHub.
Copy the following command, specify a name for the web app (Event Grid Viewer sample), and press ENTER to run the command. Replace
<your-site-name>with a unique name for your web app. The web app name must be unique because it's part of the DNS entry.sitename="<your-site-name>"Run the
az deployment group createto deploy the web app using an Azure Resource Manager template.az deployment group create \ --resource-group $resource_group \ --template-uri "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Azure-Samples/azure-event-grid-viewer/master/azuredeploy.json" \ --parameters siteName=$sitename hostingPlanName=viewerhost
The deployment might take a few minutes to complete. After the deployment has succeeded, view your web app to make sure it's running. In a web browser, navigate to: https://<your-site-name>.azurewebsites.net. You should see the site with no messages currently displayed.
Deliver events to Azure Event Grid Viewer webhook
Create a push delivery event subscription to the namespace using the webhook for Azure Event Grid Viewer.
Define a variable to hold the name of the event subscription.
event_subscription="<your_event_subscription_name>"Replace
EVENTGRIDWEBSITENAMEwith the name of the Event Grid Viewer web site. For example:contosoegridviewer.az resource create --api-version 2024-06-01-preview --resource-group $resource_group --namespace Microsoft.EventGrid --resource-type eventsubscriptions --name $event_subscription --parent namespaces/$namespace/topics/$topic --location $location --properties "{\"eventDeliverySchema\": \"CloudEventSchemaV1_0\",\"deliveryConfiguration\":{\"deliveryMode\":\"Push\",\"push\":{\"destination\":{\"endpointType\":\"WebHook\",\"properties\":{\"endpointUrl\":\"https:\/\/$sitename.azurewebsites.net\/api/updates\"}}}}}"
Send events to your topic
Now, send a sample event to the namespace topic by following steps in this section.
List namespace access keys
Get the access keys associated with the namespace you created. You use one of them to authenticate when publishing events. To list your keys, you need the full namespace resource ID first. Get it by running the following command:
namespace_resource_id=$(az eventgrid namespace show -g $resource_group -n $namespace --query "id" --output tsv)Get the first key from the namespace:
key=$(az eventgrid namespace list-key -g $resource_group --namespace-name $namespace --query "key1" --output tsv)
Publish an event
Retrieve the namespace hostname. You use it to compose the namespace HTTP endpoint to which events are sent. The following operations were first available with API version
2023-06-01-preview.publish_operation_uri="https://"$(az eventgrid namespace show -g $resource_group -n $namespace --query "topicsConfiguration.hostname" --output tsv)"/topics/"$topic:publish?api-version=2023-06-01-previewCreate a sample CloudEvents compliant event:
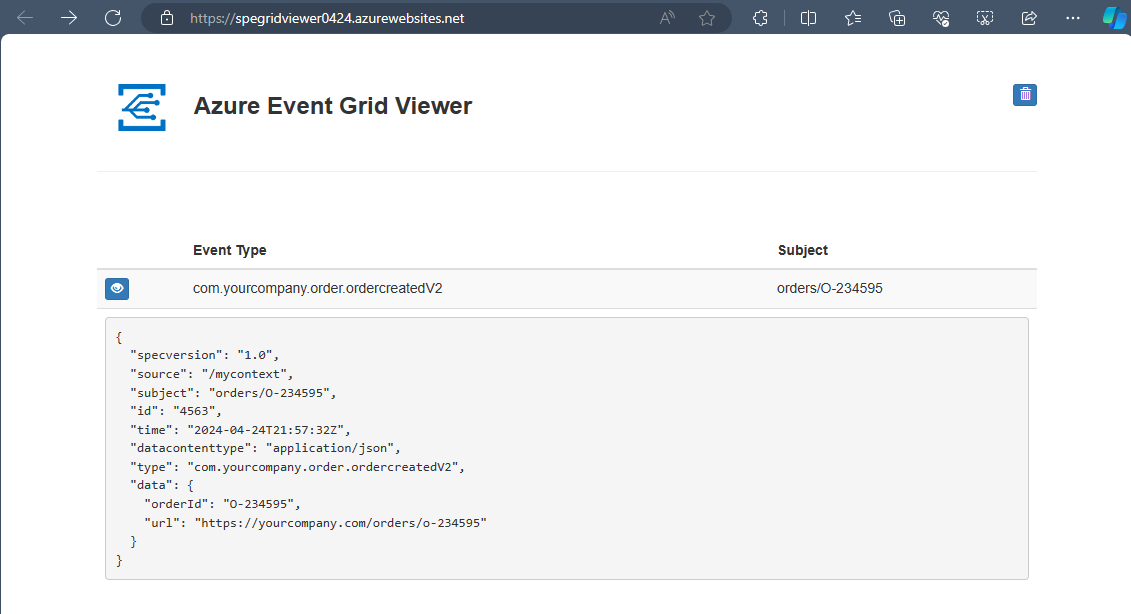
event=' { "specversion": "1.0", "id": "'"$RANDOM"'", "type": "com.yourcompany.order.ordercreatedV2", "source" : "/mycontext", "subject": "orders/O-234595", "time": "'`date +%Y-%m-%dT%H:%M:%SZ`'", "datacontenttype" : "application/json", "data":{ "orderId": "O-234595", "url": "https://yourcompany.com/orders/o-234595"}} 'The
dataelement is the payload of your event. Any well-formed JSON can go in this field. For more information on properties (also known as context attributes) that can go in an event, see the CloudEvents specifications.Use CURL to send the event to the topic. CURL is a utility that sends HTTP requests.
curl -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/cloudevents+json" -H "Authorization:SharedAccessKey $key" -d "$event" $publish_operation_uri
Verify that Azure Event Grid Viewer received the event
Verify that the Azure Event Grid Viewer web app shows the events it received from Event Grid.
Related content
In this quickstart, you used a webhook as an event handler. For quickstart that uses an Azure event hub as an event handler, see Deliver events to Azure Event Hubs using namespace topics.
