Add an artifact repository to a lab
This article tells you how to add an artifact repository to your lab in Azure DevTest Labs. Artifacts are tools or applications to install on virtual machines (VMs). You define artifacts in a JSON file that you load from a GitHub or Azure Repos Git repository.
The public DevTest Labs GitHub artifact repository provides many common artifacts for Windows and Linux. The artifacts in this public repository are available by default in DevTest Labs. For information about adding artifacts to VMs, see Add artifacts to DevTest Labs VMs.
You can also create custom artifacts that aren't available in the public artifact repository. To learn about creating custom artifacts, see Create custom artifacts. You can add your custom artifacts to your own artifact repository, and add the repository to your lab so all lab users can use the artifacts.
This article shows you how to add an artifact repository to your lab by using the Azure portal, an Azure Resource Management (ARM) template, or Azure PowerShell. You can also use an Azure PowerShell or Azure CLI script to automate adding an artifact repository to a lab.
Note
We recommend that you use the Azure Az PowerShell module to interact with Azure. To get started, see Install Azure PowerShell. To learn how to migrate to the Az PowerShell module, see Migrate Azure PowerShell from AzureRM to Az.
Add an artifact repo
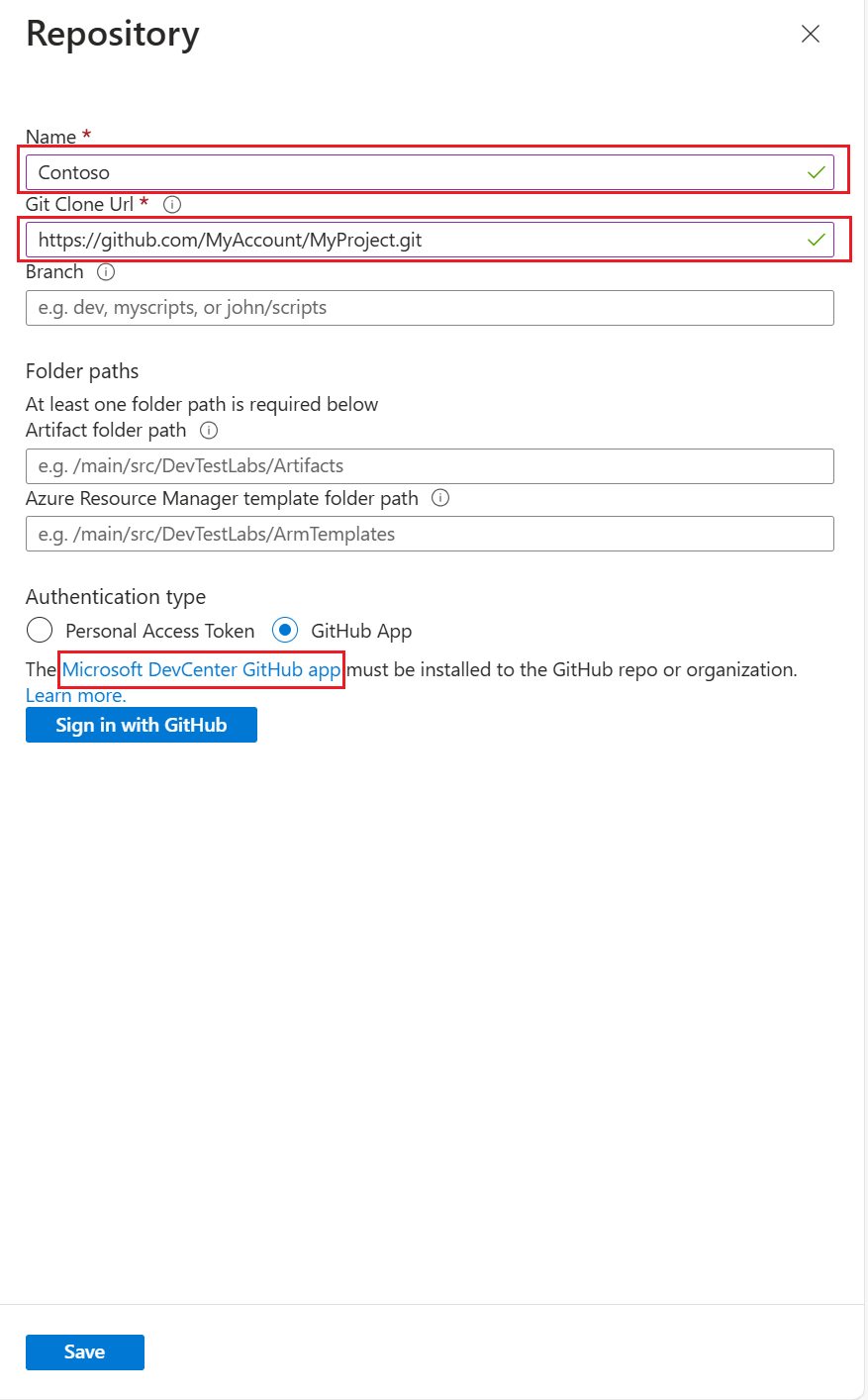
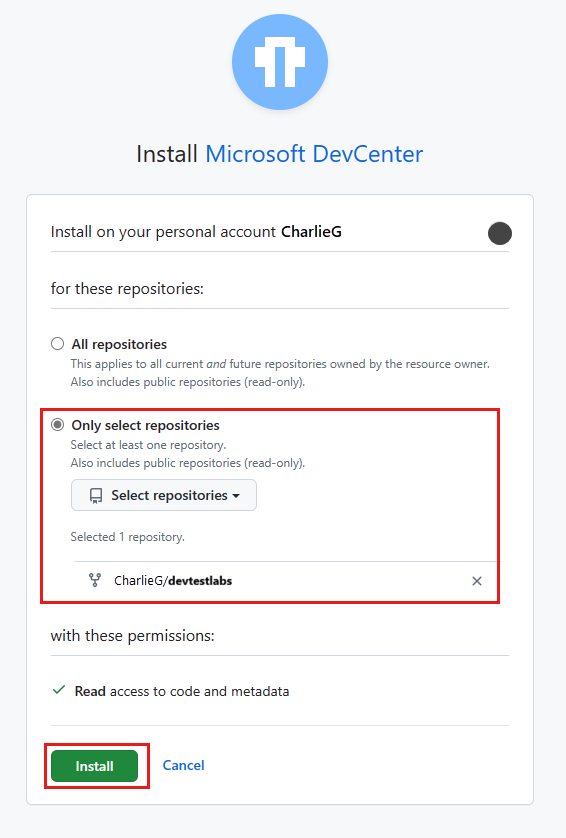
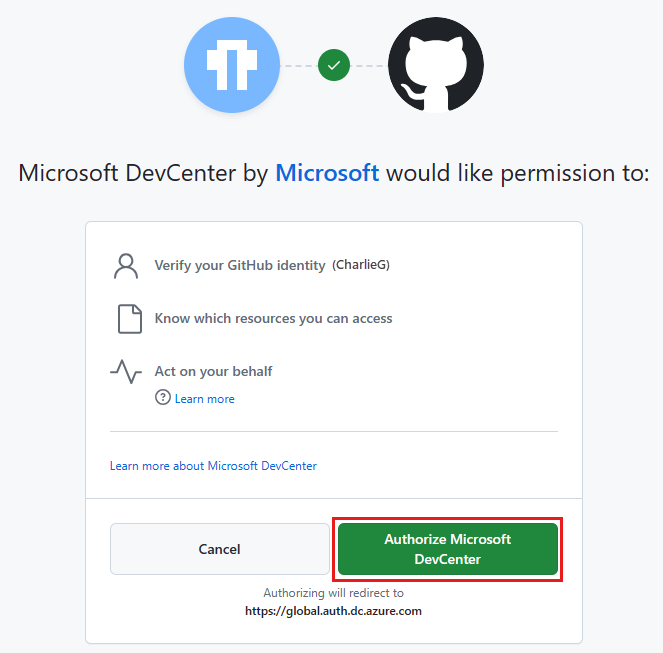
You can add an artifact repo from an Azure Repos repository or a GitHub repository. You can choose to authenticate by assigning permissions to a managed identity, by using GitHub app authentication, or by using a PAT. To learn more about managed identities, see What are managed identities for Azure resources?
Select the tab for the type of repository and authentication you want to use.
To add an artifact repo, complete the following tasks:
- Assign permissions in Azure Repos for the managed identity.
- Add your artifact repository.
Assign permissions in Azure Repos for the managed identity
You must give the managed identity permissions to the repository in Azure Repos.
Sign in to your Azure DevOps organization.
Note
Your Azure DevOps organization must be in the same directory as the Azure subscription that contains your lab.
Select Organization settings.
On the Overview page, select Users.
On the Users page, select Add users.
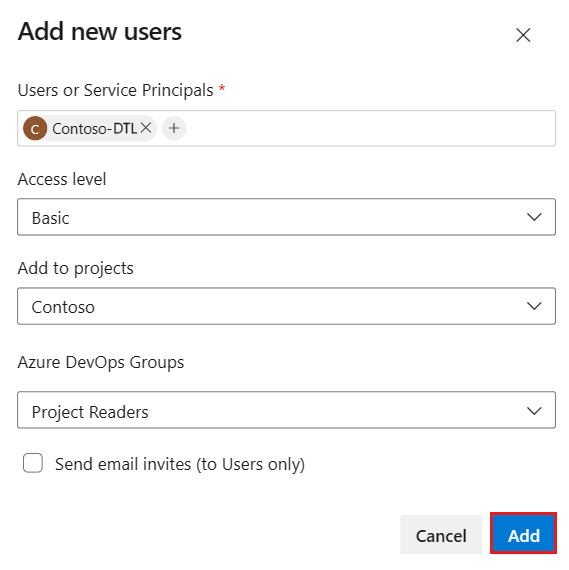
Complete Add new users by entering or selecting the following information, and then select Add:
Name Value Users or Service Principals Enter the name of your lab.
When you use a system-assigned MSI, specify the name of the lab, not the object ID of the managed account. When you use a user-assigned MSI, use the name of the managed account.Access level Select Basic. Add to projects Select the project that contains your repository. Azure DevOps Groups Select Project Readers. Send email invites (to Users only) Clear the checkbox.
Add an Azure DevOps artifact repository to a lab in the Azure portal
On the lab's Overview page, select Configuration and policies from the left navigation.
On the Configuration and policies page, select Repositories under External resources in the left navigation.
On the Repositories page, the Public Artifact Repo is automatically present and connects to the DevTest Labs public GitHub repository. If this repo isn't enabled for your lab, you can enable it by selecting the checkbox next to Public Artifact Repo, and then selecting Enable on the top menu bar.
To add your artifact repository to the lab, select Add in the top menu bar.
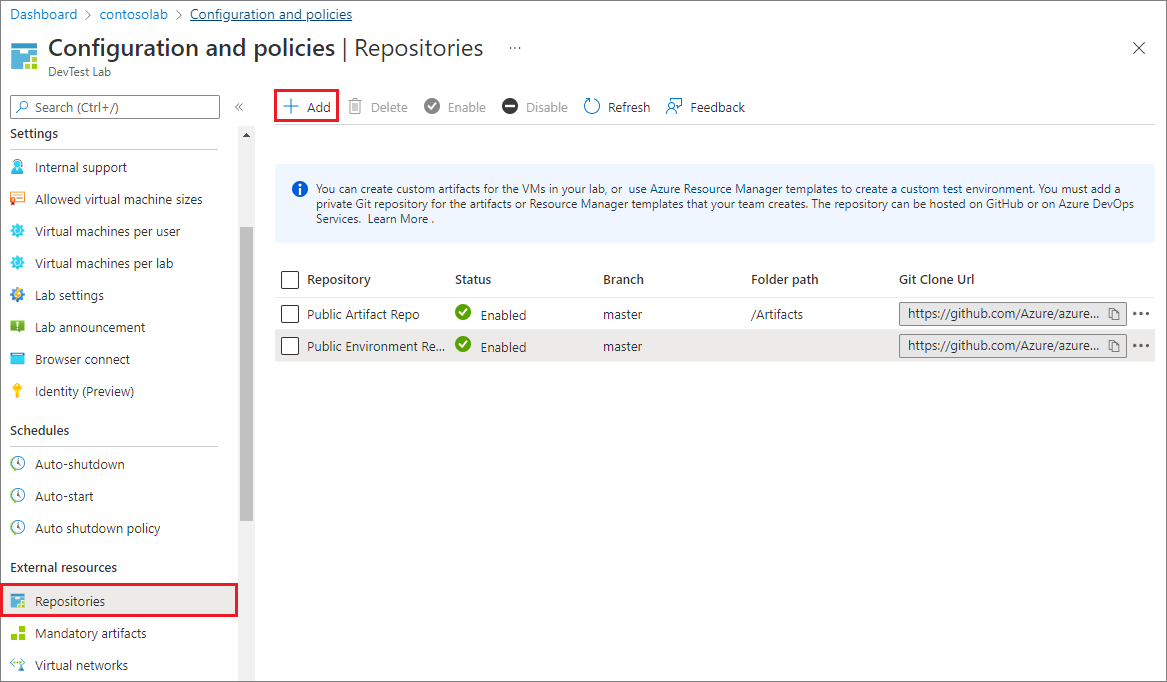
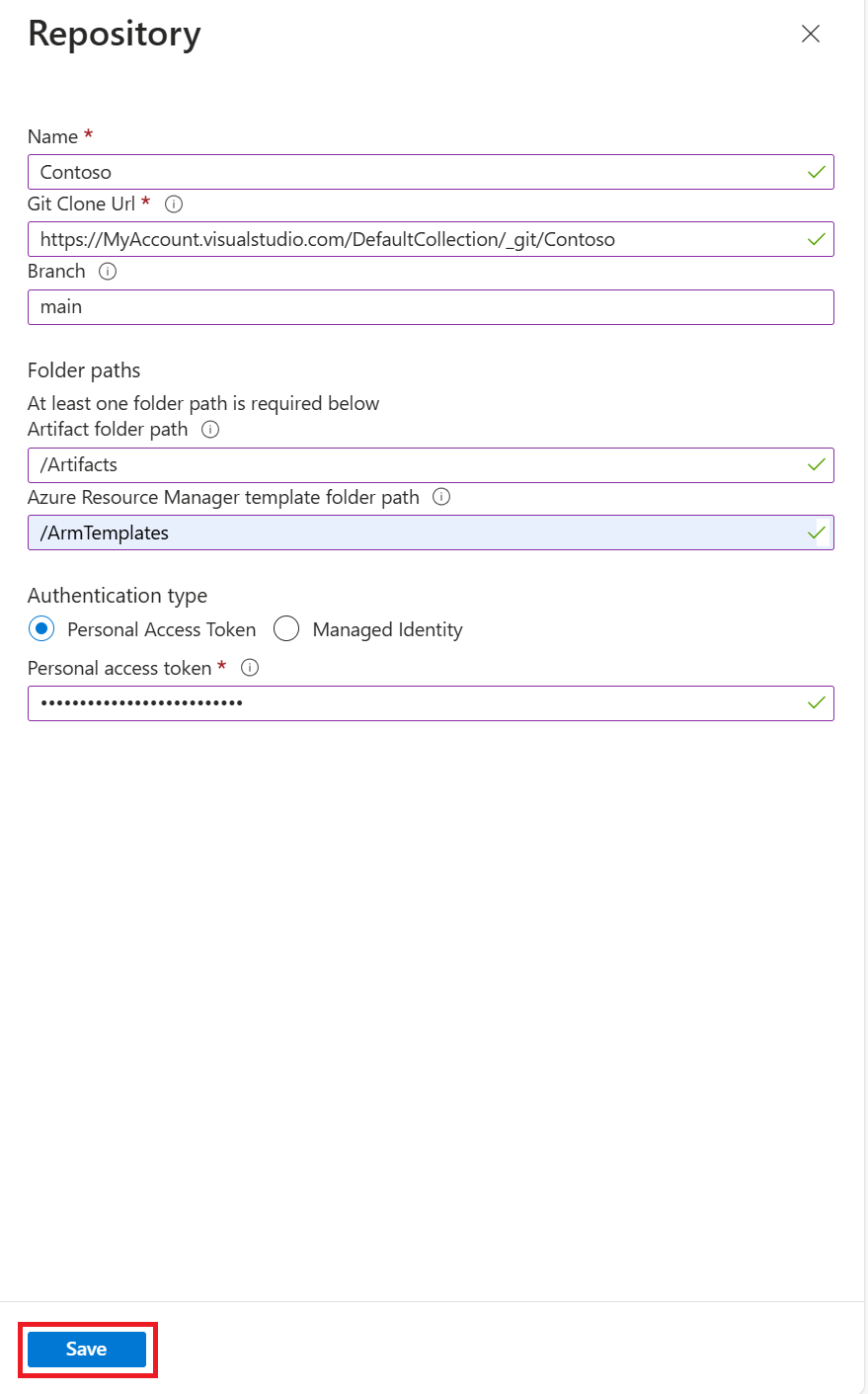
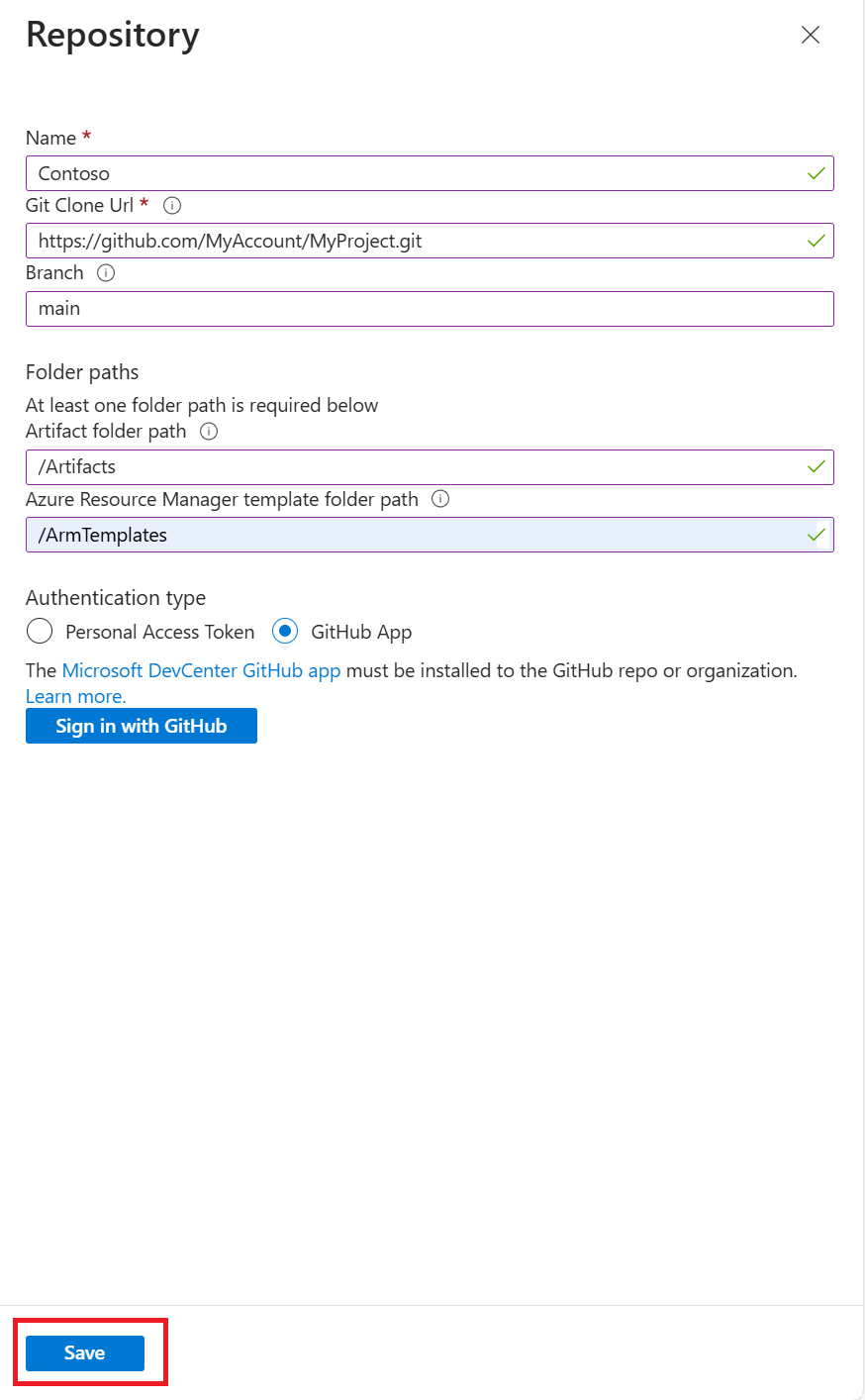
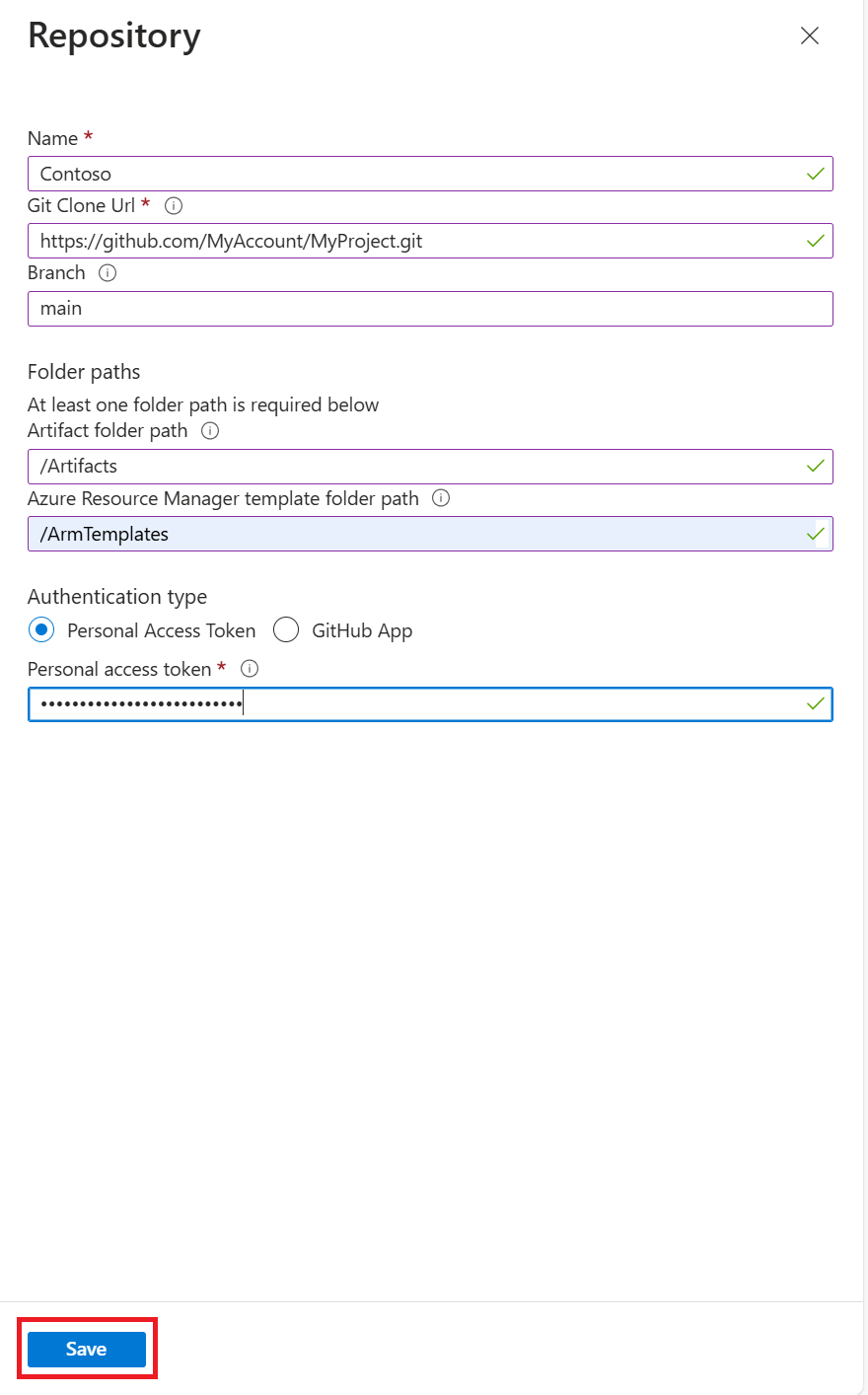
In the Repository pane, enter the following information:
- Name: A repository name to use in the lab.
- Git clone URL: The Git HTTPS clone URL from Azure Repos.
- Branch (optional): The branch that has your artifact definitions.
- Folder paths: The folder for your ARM template definitions, relative to the Git clone URL. Be sure to include the initial forward slash in the folder path.
- Managed Identity: Use this option to leverage the Managed Identity for authentication.
Select Save.
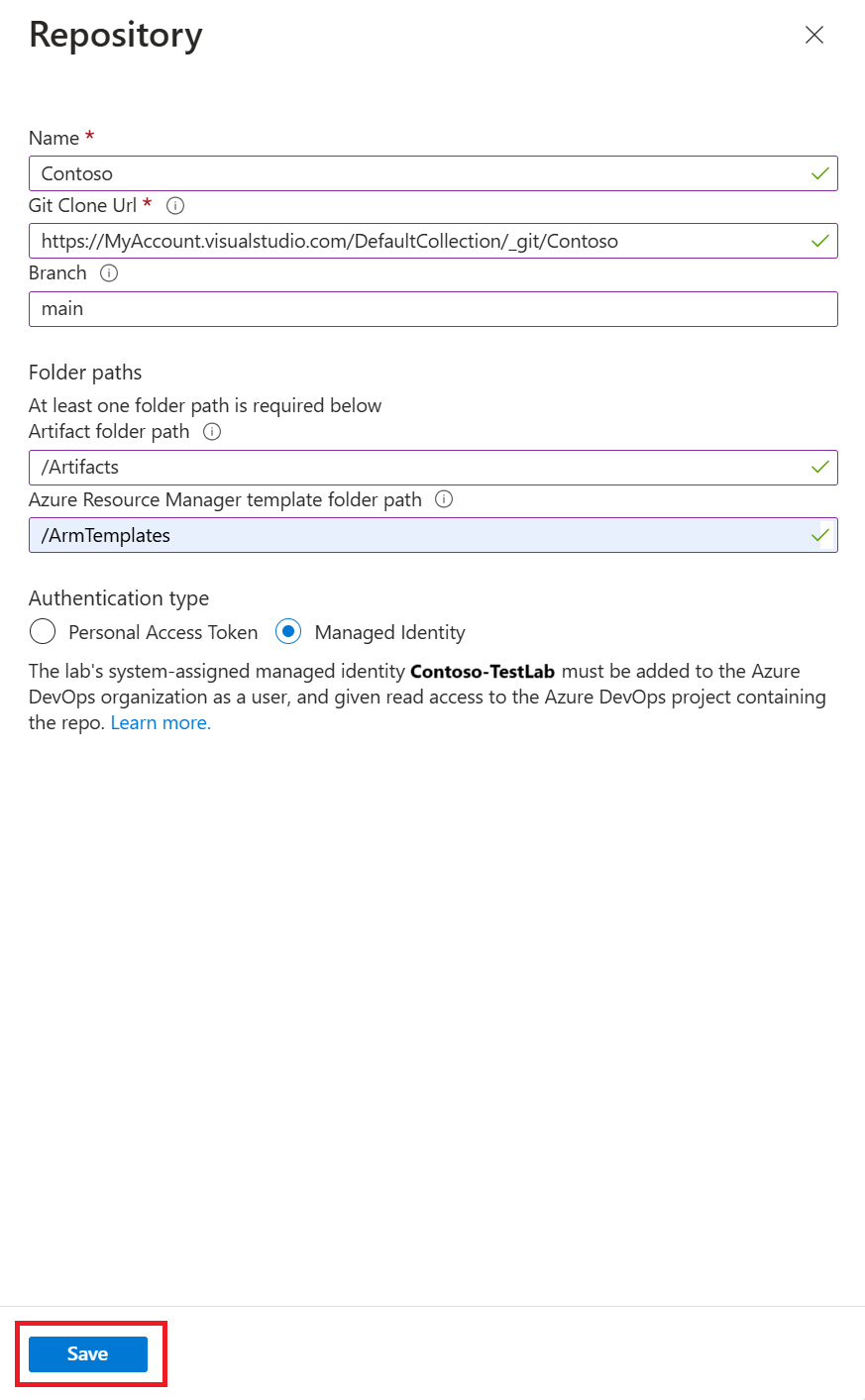
The repository now appears in the Repositories list for the lab.
Add an artifact repository by using an ARM template
ARM templates are JSON files that describe Azure resources to create. For more information about ARM templates, see Understand the structure and syntax of ARM templates.
The following ARM template adds an artifact repository to a lab. The template creates the lab if it doesn't already exist.
Review the ARM template
The sample template gathers the following information in parameters. Some of the parameters have defaults, but the deployment command must specify the lab name, artifact repository URI, repository type, and repository personal access token.
- Lab name.
- Display name for the artifact repository in DevTest Labs. The default value is
Team Repository. - URI of the artifact repository, which you copied earlier.
- Repository branch that contains the artifacts. The default value is
main. - Name of the folder that contains the artifacts. The default value is:
/Artifacts. - Repository type. The allowed values are
VsoGit, for Azure Repos, orGitHub. - Personal access token for the repository, which you copied earlier.
{
"$schema": "https://schema.management.azure.com/schemas/2015-01-01/deploymentTemplate.json#",
"contentVersion": "1.0.0.0",
"parameters": {
"labName": {
"type": "string"
},
"artifactRepositoryDisplayName": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "Team Repository"
},
"artifactRepoUri": {
"type": "string"
},
"artifactRepoBranch": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "main"
},
"artifactRepoFolder": {
"type": "string",
"defaultValue": "/Artifacts"
},
"artifactRepoType": {
"type": "string",
"allowedValues": ["VsoGit", "GitHub"]
},
"artifactRepoSecurityToken": {
"type": "securestring"
}
},
"variables": {
"artifactRepositoryName": "[concat('Repo-', uniqueString(subscription().subscriptionId))]"
},
"resources": [{
"apiVersion": "2016-05-15",
"type": "Microsoft.DevTestLab/labs",
"name": "[parameters('labName')]",
"location": "[resourceGroup().location]",
"resources": [
{
"apiVersion": "2016-05-15",
"name": "[variables('artifactRepositoryName')]",
"type": "artifactSources",
"dependsOn": [
"[resourceId('Microsoft.DevTestLab/labs', parameters('labName'))]"
],
"properties": {
"uri": "[parameters('artifactRepoUri')]",
"folderPath": "[parameters('artifactRepoFolder')]",
"branchRef": "[parameters('artifactRepoBranch')]",
"displayName": "[parameters('artifactRepositoryDisplayName')]",
"securityToken": "[parameters('artifactRepoSecurityToken')]",
"sourceType": "[parameters('artifactRepoType')]",
"status": "Enabled"
}
}
]
}
]
}
Deploy the template
There are several ways to deploy ARM templates to create or update Azure resources. For information and instructions, see the following articles:
- Deploy resources with ARM templates and Azure PowerShell
- Deploy resources with ARM templates and Azure CLI
- Deploy resources with ARM templates in the Azure portal
- Deploy resources with ARM templates and Resource Manager REST API
For this example, deploy the template by using Azure PowerShell.
Note
The cmdlets that deploy the template are context-specific, so they use the current tenant and subscription. If you need to change the context, use Set-AzContext before you deploy the template
Create a resource group by using New-AzResourceGroup. If the resource group you want to use already exists, skip this step.
New-AzResourceGroup -Name MyLabResourceGroup1 -Location westusCreate a deployment to the resource group by using New-AzResourceGroupDeployment. You can make several resource deployments to the same resource group. If you're deploying several times to the same resource group, make sure each deployment name is unique.
New-AzResourceGroupDeployment ` -Name MyLabResourceGroup-Deployment1 ` -ResourceGroupName MyLabResourceGroup1 ` -TemplateFile azuredeploy.json ` -TemplateParameterFile azuredeploy.parameters.json
After New-AzResourceGroupDeployment runs successfully, the output shows important information like the provisioning state, which should be succeeded, and any outputs for the template.
Add an artifact repository by using Azure PowerShell
The following sample PowerShell script, New-DevTestLabArtifactRepository.ps1, adds an artifact repository to a lab. The full script includes some verbose messages and comments.
<#
.SYNOPSIS
This script creates a new custom repository and adds it to an existing DevTest Lab.
.PARAMETER LabName
The name of the lab.
.PARAMETER LabResourceGroupName
The name of the resource group that contains the lab.
.PARAMETER ArtifactRepositoryName
Name for the new artifact repository. The script creates a random name for the repository if not specified.
.PARAMETER ArtifactRepositoryDisplayName
Display name for the artifact repository.
This name appears in the list of artifact repositories for a lab.
.PARAMETER RepositoryUri
Uri to the artifact repository.
.PARAMETER RepositoryBranch
Branch that contains the artifact files. Defaults to 'main'.
.PARAMETER FolderPath
Folder that contains the artifact files. Defaults to '/Artifacts'
.PARAMETER PersonalAccessToken
Personal access token for the GitHub or Azure Repos repository.
.PARAMETER SourceType
Whether the artifact repository is a VSOGit (Azure Repos) or GitHub repository.
.EXAMPLE
Set-AzContext -SubscriptionId aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e
.\New-DevTestLabArtifactRepository.ps1 -LabName "mydevtestlab" -LabResourceGroupName "mydtlrg" -ArtifactRepositoryName "MyTeam Repository" -RepositoryUri "https://github.com/<myteam>/<nameofrepo>.git" -PersonalAccessToken "1111...." -SourceType "GitHub"
.NOTES
The script uses the current Azure context. To set the context, use Set-AzContext.
#>
[CmdletBinding()]
Param(
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
$LabName,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
$LabResourceGroupName,
$ArtifactRepositoryName,
$ArtifactRepositoryDisplayName = 'Team Artifact Repository',
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
$RepositoryUri,
$RepositoryBranch = 'main',
$FolderPath = '/Artifacts',
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
$PersonalAccessToken ,
[Parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[ValidateSet('VsoGit', 'GitHub')]
$SourceType
)
# Set artifact repository internal name if not specified.
if ($ArtifactRepositoryName -eq $null){
$ArtifactRepositoryName = "PrivateRepo" + (Get-Random -Maximum 999)
}
# Sign in to Azure.
Connect-AzAccount
#Get Lab Resource.
$LabResource = Get-AzResource -ResourceType 'Microsoft.DevTestLab/labs' -ResourceName $LabName -ResourceGroupName $LabResourceGroupName
Write-Verbose "Lab Name: $($LabResource.Name)"
Write-Verbose "Lab Resource Group Name: $($LabResource.ResourceGroupName)"
Write-Verbose "Lab Resource Location: $($LabResource.Location)"
Write-Verbose "Artifact Repository Internal Name: $ArtifactRepositoryName"
#Prepare properties object for the call to New-AzResource.
$propertiesObject = @{
uri = $RepositoryUri;
folderPath = $FolderPath;
branchRef = $RepositoryBranch;
displayName = $ArtifactRepositoryDisplayName;
securityToken = $PersonalAccessToken;
sourceType = $SourceType;
status = 'Enabled'
}
Write-Verbose "Properties to be passed to New-AzResource:$($propertiesObject | Out-String)"
#Add resource to the current subscription.
$resourcetype = 'Microsoft.DevTestLab/labs/artifactSources'
$resourceName = $LabName + '/' + $ArtifactRepositoryName
Write-Verbose "Az ResourceType: $resourcetype"
Write-Verbose "Az ResourceName: $resourceName"
Write-Verbose "Creating artifact repository '$ArtifactRepositoryDisplayName'..."
$result = New-AzResource -Location $LabResource.Location -ResourceGroupName $LabResource.ResourceGroupName -properties $propertiesObject -ResourceType $resourcetype -ResourceName $resourceName -ApiVersion 2016-05-15 -Force
#Alternate implementation:
# Use resourceId rather than resourcetype and resourcename parameters.
# Using resourceId lets you specify the $SubscriptionId rather than using the
# subscription id of Get-AzContext.
#$resourceId = "/subscriptions/$SubscriptionId/resourceGroups/$($LabResource.ResourceGroupName)/providers/Microsoft.DevTestLab/labs/$LabName/artifactSources/$ArtifactRepositoryName"
#$result = New-AzResource -properties $propertiesObject -ResourceId $resourceId -ApiVersion 2016-05-15 -Force
# Check the result.
if ($result.Properties.ProvisioningState -eq "Succeeded") {
Write-Verbose ("Successfully added artifact repository source '$ArtifactRepositoryDisplayName'")
}
else {
Write-Error ("Error adding artifact repository source '$ArtifactRepositoryDisplayName'")
}
#Return the newly created resource to use in later scripts.
return $result
Parameters
The PowerShell script takes the following parameters:
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
LabName |
The name of the lab. |
ArtifactRepositoryName |
Name for the new artifact repository. The script creates a random name for the repository if it isn't specified. |
ArtifactRepositoryDisplayName |
Display name that appears in the lab's artifact repository list. |
RepositoryUri |
URI of the artifact repository, which you copied earlier. |
RepositoryBranch |
Repository branch that contains the artifacts. The default value is main. |
FolderPath |
Folder that contains the artifacts. The default value is: /Artifacts. |
PersonalAccessToken |
Security token for accessing the repository, which you copied earlier. |
SourceType |
Whether the artifact repository is a VSOGit (Azure Repos) or GitHub repository. |
The repository needs an internal name for identification, which is different than the display name in the Azure portal. You don't see the internal name when using the Azure portal, but you see it when using Azure REST APIs or Azure PowerShell. The script creates a random name if the deployment command doesn't specify one.
#Set artifact repository name, if not set by user
if ($ArtifactRepositoryName -eq $null){
$ArtifactRepositoryName = "PrivateRepo" + (Get-Random -Maximum 999)
}
PowerShell commands
The script uses the following PowerShell commands:
| Command | Notes |
|---|---|
| Get-AzResource | Gets details about the lab, such as its location. You create the artifact repository source in the same location and under the same resource group as the lab. |
| New-AzResource | Adds the Azure resource. There's no specific command for adding artifact repositories. This cmdlet needs either the ResourceId or the ResourceName and ResourceType pair to know the type of resource to create. The current script uses the ResourceName and ResourceType pair. |
A good way to discover resource name and resource type information is to use the Azure REST API Browser website. DevTest Labs Artifact Sources shows REST APIs for creating and managing DevTest Labs artifact sources. The current script uses the following resource ID:
https://management.azure.com/subscriptions/{subscriptionId}/resourceGroups/{resourceGroupName}/providers/Microsoft.DevTestLab/labs/{labName}/artifactsources/{name}
The resource type is everything listed after providers in the URI, except for items in curly brackets. The resource name is everything in the curly brackets. If you use more than one item for the resource name, separate each item with a slash:
$resourcetype = 'Microsoft.DevTestLab/labs/artifactSources'
$resourceName = $LabName + '/' + $ArtifactRepositoryName
Run the PowerShell script
Run the PowerShell script, substituting your own values for the example values in LabName, LabResourceGroupName, ArtifactRepositoryName, RepositoryUri, PersonalAccessToken, and SourceType:
Set-AzContext -SubscriptionId <Your Azure subscription ID>
.\New-DevTestLabArtifactRepository.ps1 -LabName "mydevtestlab" -LabResourceGroupName "mydtlrg" -ArtifactRepositoryName "myteamrepository" -RepositoryUri "https://github.com/myteam/myteamrepository.git" - "1111...." -SourceType "GitHub"