Deploy VMs on your Azure Stack Edge Pro GPU device via Azure PowerShell script
APPLIES TO:  Azure Stack Edge Pro - GPU
Azure Stack Edge Pro - GPU Azure Stack Edge Pro 2
Azure Stack Edge Pro 2 Azure Stack Edge Pro R
Azure Stack Edge Pro R Azure Stack Edge Mini R
Azure Stack Edge Mini R
This tutorial describes how to create and manage a VM on your Azure Stack Edge Pro device using an Azure PowerShell script.
Prerequisites
Before you begin creating and managing a VM on your Azure Stack Edge Pro device using this script, you need to make sure you have completed the prerequisites listed in the following steps:
For Azure Stack Edge Pro device via the local web UI
Before you can deploy VMs on your Azure Stack Edge device, you must configure your client to connect to the device via Azure Resource Manager over Azure PowerShell. For detailed instructions, see Connect to Azure Resource Manager on your Azure Stack Edge device.
Make sure that you can use the following steps to access the device from your client. You've already done this configuration when you connected to Azure Resource Manager, and now you're verifying that the configuration was successful.
Verify that Azure Resource Manager communication is working by running the following command:
To call the local device APIs to authenticate, enter:
If you configured compute for Kubernetes, you can skip this step. Otherwise, ensure that you've enabled a network interface for compute by doing the following:
a. On your local user interface, go to Compute settings.
b. Select the network interface that you want to use to create a virtual switch. The VMs you create will be attached to a virtual switch that's attached to this port and the associated network. Be sure to choose a network that matches the IP address you'll use for the VM.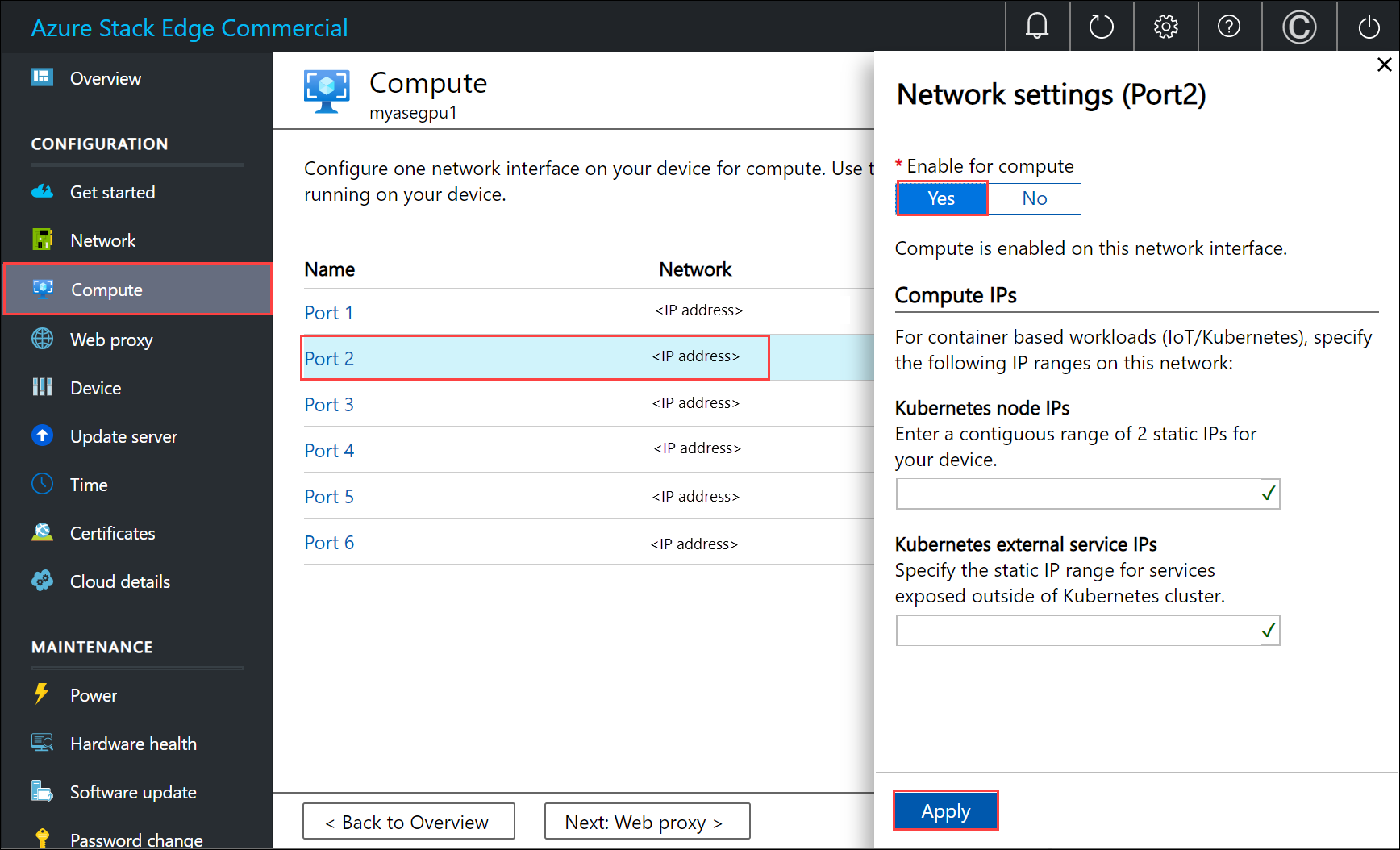
c. Under Enable for compute on the network interface, select Yes. Azure Stack Edge will create and manage a virtual switch that corresponds to that network interface. Don't enter specific IPs for Kubernetes at this time. It can take several minutes to enable compute.
Note
If you're creating GPU VMs, select a network interface that's connected to the internet. Doing so enables you to install a GPU extension on your device.
For your Windows client
Make sure that you have modified:
- The host file on the client, OR,
- The DNS server configuration
Important
We recommend that you modify the DNS server configuration for endpoint name resolution.
Start Notepad as an administrator (Administrator privileges is required to save the file), and then open the hosts file located at
C:\Windows\System32\Drivers\etc.
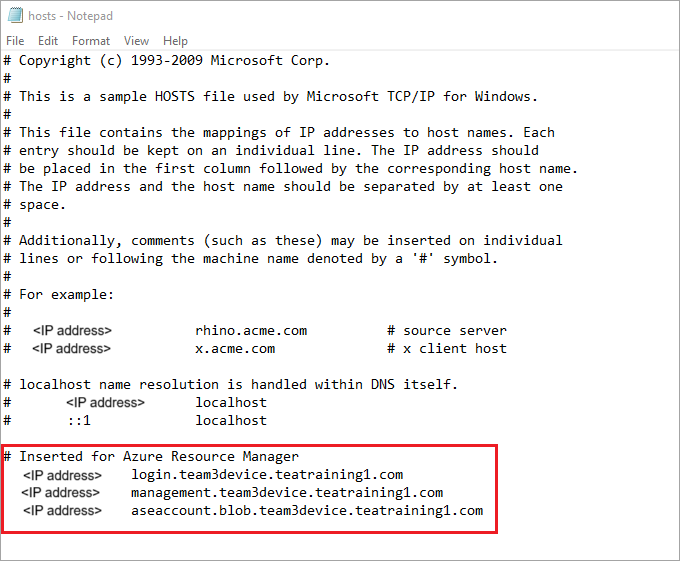
Add the following entries to your hosts file replacing with appropriate values for your device:
<device IP> login.<appliance name>.<DNS domain> <device IP> management.<appliance name>.<DNS domain> <device IP> <storage name>.blob.<appliance name>.<DNS domain>For the storage account, you can provide a name that you want the script to use later to create a new storage account. The script does not check if that storage account is existing.
Use the following image for reference. Save the hosts file.
Download the PowerShell script used in this procedure.
Make sure that your Windows client is running PowerShell 5.0 or later.
Make sure that the
Azure.Storage Module version 4.5.0is installed on your system. You can get this module from the PowerShell Gallery. To install this module, type:Install-Module -Name Azure.Storage -RequiredVersion 4.5.0To verify the version of the installed module, type:
Get-InstalledModule -name Azure.StorageTo uninstall any other version modules, type:
Uninstall-Module -Name Azure.StorageDownload AzCopy 10 to your Windows client. Make a note of this location as you will pass it as a parameter while running the script.
Make sure that your Windows client is running TLS 1.2 or later.
Create a VM
Run PowerShell as an administrator.
Go to the folder where you downloaded the script on your client.
Before you run the script, make sure you are still connected to the local Azure Resource Manager of the device and the connection has not expired.
PS C:\windows\system32> login-AzureRMAccount -EnvironmentName aztest1 -TenantId aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee Account SubscriptionName TenantId Environment ------- ---------------- -------- ----------- EdgeArmUser@localhost Default Provider Subscription aaaabbbb-0000-cccc-1111-dddd2222eeee aztest1 PS C:\windows\system32> cd C:\Users\v2 PS C:\Users\v2>Use the following command to run the script:
.\ArmPowershellClient.ps1 -NicPrivateIp <Private IP> -VHDPath <Path> -VHDFile <VHD File, with extension> -StorageAccountName <Name> -OS <Windows/Linux> -VMSize <Supported VM Size> -VMUserName <Username to be used to sign in to VM> -VMPassword <Password for the VM> --AzCopy10Path <Absolute Path>If you want the IP to be dynamically allocated to the VM, omit the
-NicPrivateIpparameter.Here are the examples when the script is run to create a Windows VM and a Linux VM.
For a Windows VM:
Here is a sample output for a Windows VM that was created.
PS C:\Users\v2> .\ArmPowershellClient.ps1 -VHDPath \\asefs\Logs\vmvhd -VHDFile WindowsServer2016Datacenter.vhd -StorageAccountName myasesatest -OS Windows -VMSize Standard_D1_v2 -VMUserName Administrator -VMPassword Password1 -AzCopy10Path C:\Users\AzCopy10\AzCopy.exe New-AzureRmResourceGroup -Name rg201221071831 -Location DBELocal -Force Successfully created Resource Group:rg201221071831 Successfully created Resource Group:StorAccRG Get-AzureRmStorageAccount -Name myasesatest -ResourceGroupName StorAccRG -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue New-AzureRmStorageAccount -Name myasesatest -ResourceGroupName StorAccRG -SkuName Standard_LRS -Location DBELocal Created New Storage Account Get-AzureRmStorageAccount -name myasesatest -resourcegroupname StorageAccountName ResourceGroupName Location SkuName Kind AccessTier CreationTime ProvisioningState EnableHttpsTrafficOnly ------------------ ----------------- -------- ------- ---- ---------- ------------ ----------------- ---------------------- myasesatest StorAccRG DBELocal StandardLRS Storage 12/22/2020 3:18:38 AM Succeeded False myasesatest StorAccRG DBELocal StandardLRS Storage 12/22/2020 3:18:38 AM Succeeded False Uploading Vhd to Storage Account New-AzureStorageContext -StorageAccountName myasesatest -StorageAccountKey hyibjhbVlOROgTlU1nQJIlxrg94eGDhF+RIQ71Z7UVZIxoOPMlHP274NUhZtA1hMxGBcpk2BVApiFasFPEhY/A== -Endpoint https://myasesatest.blob.myasegpuvm.wdshcsso.com/ New-AzureStorageAccountSASToken -Service Blob,File,Queue,Table -ResourceType Container,Service,Object -Permission SAS Token : ?sv=2017-07-29&sig=TXaGbjum9tFFaJnu3SFmDuslJuqNiNQwvuHfpPJMYN0%3D&spr=https&se=2020-12-22T04%3A18%3A43Z&srt=sco&ss=bfqt&sp=racwdl C:\Users\AzCopy10\AzCopy.exe make https://myasesatest.blob.myasegpuvm.wdshcsso.com/vmimages?sv=2017-07-29&sig=TXaGbjum9tFFaJnu3SFmDuslJuqNiNQwvuHfpPJMYN0%3D&spr=https&se=2020-12-22T04%3A18%3A43Z&srt=sco&ss=bfqt&sp=racwdl Successfully created the resource. AzCopy cp \\asefs\Logs\vmvhd\WindowsServer2016Datacenter.vhd https://myasesatest.blob.myasegpuvm.wdshcsso.com/vmimages?sv=2017-07-29&sig=TXaGbjum9tFFaJnu3SFmDuslJuqNiNQwvuHfpPJMYN0%3D&spr=https&se=2020-12-22T04%3A18%3A43Z&srt=sco&ss=bfqt&sp=racwdl INFO: Scanning... Job b6f54665-93c4-2f47-4770-5f3b7b0de2dc has started Log file is located at: C:\Users\Administrator\.azcopy\b6f54665-93c4-2f47-4770-5f3b7b0de2dc.log INFO: AzCopy.exe: A newer version 10.8.0 is available to download 99.9 %, 0 Done, 0 Failed, 1 Pending, 0 Skipped, 1 Total, (Disk may be limiting speed) Job b6f54665-93c4-2f47-4770-5f3b7b0de2dc summary Elapsed Time (Minutes): 12.7717 Total Number Of Transfers: 1 Number of Transfers Completed: 1 Number of Transfers Failed: 0 Number of Transfers Skipped: 0 TotalBytesTransferred: 13958644224 Final Job Status: Completed VHD Upload Done Creating a new managed disk = New-AzureRmDiskConfig -Location DBELocal -CreateOption Import -SourceUri Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Compute.Automation.Models.PSDisk New-AzureRmDisk -ResourceGroupName rg201221071831 -DiskName ld201221071831 -Disk ResourceGroupName : rg201221071831 ManagedBy : Sku : Microsoft.Azure.Management.Compute.Models.DiskSku Zones : TimeCreated : 12/21/2020 7:31:35 PM OsType : CreationData : Microsoft.Azure.Management.Compute.Models.CreationData DiskSizeGB : 13 EncryptionSettings : ProvisioningState : Succeeded Id : /subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/rg201221071831/providers/Microsoft.Compute/disks/ld201221071831 Name : ld201221071831 Type : Microsoft.Compute/disks Location : DBELocal Tags : {} Created a new managed disk Creating a new Image out of managed disk ResourceGroupName : SourceVirtualMachine : StorageProfile : Microsoft.Azure.Management.Compute.Models.ImageStorageProfile ProvisioningState : Id : Name : Type : Location : DBELocal Tags : New-AzureRmImage -Image Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Compute.Automation.Models.PSImage -ImageName ig201221071831 -ResourceGroupName rg201221071831 -HyperVGeneration V1 ResourceGroupName : rg201221071831 SourceVirtualMachine : StorageProfile : Microsoft.Azure.Management.Compute.Models.ImageStorageProfile ProvisioningState : Succeeded Id : /subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/rg201221071831/providers/Microsoft.Compute/images/ig201221071831 Name : ig201221071831 Type : Microsoft.Compute/images Location : dbelocal Tags : {} Created a new Image Using Vnet /subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/ASERG/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/ASEVNET Creating a new Network Interface WARNING: The output object type of this cmdlet will be modified in a future release. VirtualMachine : IpConfigurations : {ip201221071831} DnsSettings : Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Network.Models.PSNetworkInterfaceDnsSettings MacAddress : 001DD87D7216 Primary : EnableAcceleratedNetworking : False EnableIPForwarding : False NetworkSecurityGroup : ProvisioningState : Succeeded VirtualMachineText : null IpConfigurationsText : [ { "Name": "ip201221071831", "Etag": "W/\"27785dd5-d12a-4d73-9495-ffad7847261a\"", "Id": "/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/rg201221071831/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/nic201221071831/ipConfigurations/ip201221071831", "PrivateIpAddress": "10.57.51.61", "PrivateIpAllocationMethod": "Dynamic", "Subnet": { "Id": "/subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/ASERG/providers/Microsoft.Network/virtualNetworks/ASEVNET/subnets/ASEVNETsubNet", "ResourceNavigationLinks": [], "ServiceEndpoints": [] }, "ProvisioningState": "Succeeded", "PrivateIpAddressVersion": "IPv4", "LoadBalancerBackendAddressPools": [], "LoadBalancerInboundNatRules": [], "Primary": true, "ApplicationGatewayBackendAddressPools": [], "ApplicationSecurityGroups": [] } ] DnsSettingsText : { "DnsServers": [], "AppliedDnsServers": [], "InternalDomainNameSuffix": "qgotb4hjdh4efnhn0vz5adtb3f.a--x.internal.cloudapp.net" } NetworkSecurityGroupText : null ResourceGroupName : rg201221071831 Location : dbelocal ResourceGuid : e6327ab9-0855-4f04-9b36-17bbf31b5bd8 Type : Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces Tag : TagsTable : Name : nic201221071831 Etag : W/"27785dd5-d12a-4d73-9495-ffad7847261a" Id : /subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/rg201221071831/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/nic201221071831 Created Network Interface Creating a new VM New-AzureRmVMConfig -VMName VM201221071831 -VMSize Standard_D1_v2 Set-AzureRmVMOperatingSystem -VM Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Compute.Models.PSVirtualMachine -Windows -ComputerName COM201221071831 -Credential System.Management.Automation.PSCredential Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Compute.Models.PSVirtualMachine = Set-AzureRmVMOSDisk -VM Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Compute.Models.PSVirtualMachine -Name osld201221071831 -Caching ReadWrite -CreateOption FromImage -Windows -StorageAccountType StandardLRS Add-AzureRmVMNetworkInterface -VM Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Compute.Models.PSVirtualMachine -Id /subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/rg201221071831/providers/Microsoft.Network/networkInterfaces/nic201221071831.Id Set-AzureRmVMSourceImage -VM Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Compute.Models.PSVirtualMachine -Id /subscriptions/aaaa0a0a-bb1b-cc2c-dd3d-eeeeee4e4e4e/resourceGroups/rg201221071831/providers/Microsoft.Compute/images/ig201221071831 New-AzureRmVM -ResourceGroupName rg201221071831 -Location DBELocal -VM Microsoft.Azure.Commands.Compute.Models.PSVirtualMachine -Verbose WARNING: Since the VM is created using premium storage or managed disk, existing standard storage account, myasesa1, is used for boot diagnostics. VERBOSE: Performing the operation "New" on target "VM201221071831". Ticks : 1533424841 Days : 0 Hours : 0 Milliseconds : 342 Minutes : 2 Seconds : 33 TotalDays : 0.00177479726967593 TotalHours : 0.0425951344722222 TotalMilliseconds : 153342.4841 TotalMinutes : 2.55570806833333 TotalSeconds : 153.3424841 RequestId : IsSuccessStatusCode : True StatusCode : OK ReasonPhrase : OK PS C:\Users\v2>For a Linux VM:
Here is the sample of the command that was used to create a Linux VM.
.\ArmPowershellClient.ps1 -VHDPath \\asefs\Logs\vmvhd -VHDFile ubuntu13.vhd -StorageAccountName myasesatest -OS Linux -VMSize Standard_D1_v2 -VMUserName Administrator -VMPassword Password1 -AzCopy10Path C:\Users\AzCopy10\AzCopy.exe New-AzureRmResourceGroup -Name rg201221075546 -Location DBELocal -ForceOnce you have successfully created the VMs, these VMs should show up in the list of virtual machines in the Azure portal. To view the VMs, in the Azure Stack Edge resource for your device in Azure portal, go to Edge services > Virtual machines.
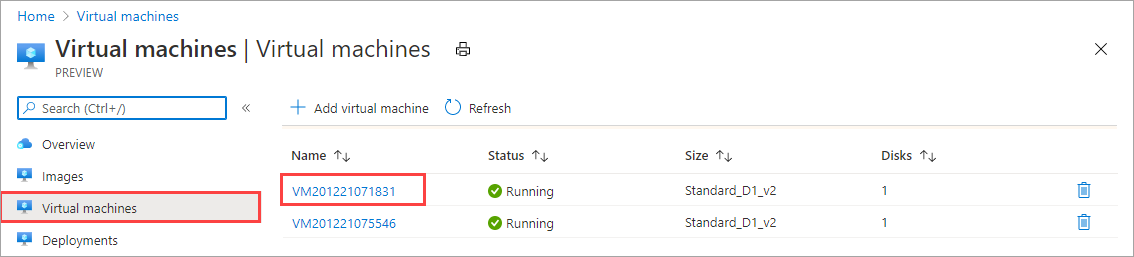
To view the details of a VM, select the VM name. Note the dynamic allocation of IP for this VM.
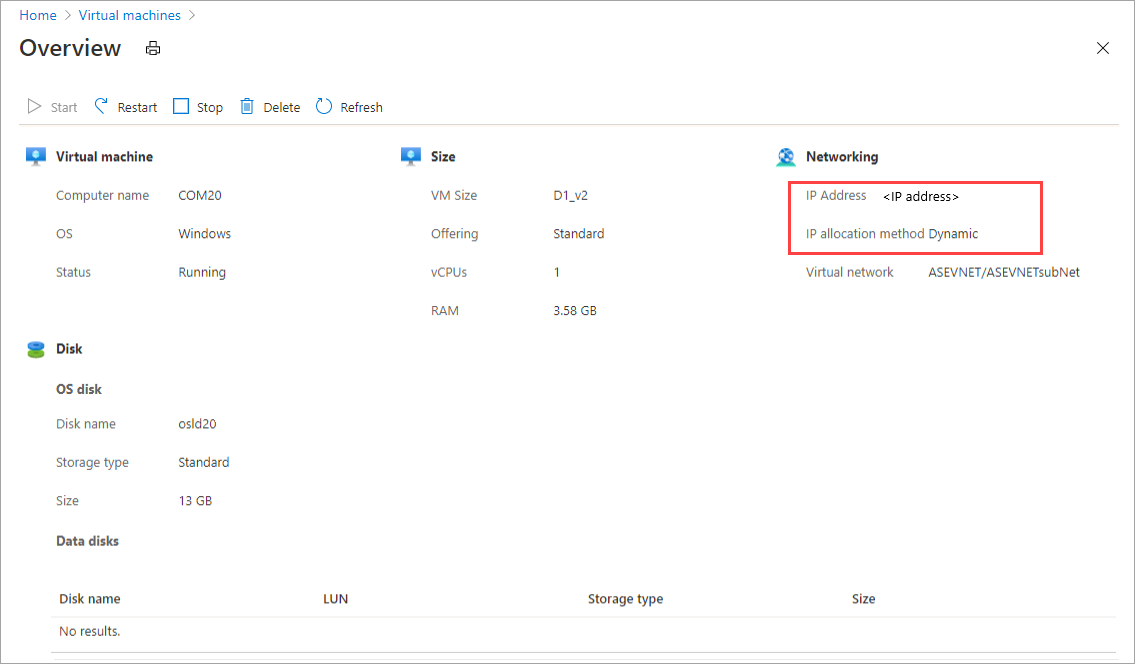
To clean up the resources that the script created, use the following commands:
Get-AzureRmVM | Remove-AzureRmVM -Force Get-AzureRmNetworkInterface | Remove-AzureRmNetworkInterface -Force Get-AzureRmImage | Remove-AzureRmImage -Force Get-AzureRmDisk | Remove-AzureRmDisk -Force Get-AzureRmStorageAccount | Remove-AzureRmStorageAccount -Force