Copy data from and to Oracle by using Azure Data Factory or Azure Synapse Analytics
APPLIES TO:  Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory  Azure Synapse Analytics
Azure Synapse Analytics
Tip
Try out Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric, an all-in-one analytics solution for enterprises. Microsoft Fabric covers everything from data movement to data science, real-time analytics, business intelligence, and reporting. Learn how to start a new trial for free!
This article outlines how to use the copy activity in Azure Data Factory to copy data from and to an Oracle database. It builds on the copy activity overview.
Supported capabilities
This Oracle connector is supported for the following capabilities:
| Supported capabilities | IR |
|---|---|
| Copy activity (source/sink) | ① ② |
| Lookup activity | ① ② |
| Script activity | ① ② |
① Azure integration runtime ② Self-hosted integration runtime
For a list of data stores that are supported as sources or sinks by the copy activity, see the Supported data stores table.
Specifically, this Oracle connector supports:
- The following versions of an Oracle database for version 2.0:
- Oracle Database 19c or later
- The following versions of an Oracle database for version 1.0:
- Oracle 19c R1 (19.1) and higher
- Oracle 18c R1 (18.1) and higher
- Oracle 12c R1 (12.1) and higher
- Oracle 11g R1 (11.1) and higher
- Oracle 10g R1 (10.1) and higher
- Oracle 9i R2 (9.2) and higher
- Oracle 8i R3 (8.1.7) and higher
- Oracle Database Cloud Exadata Service
- Parallel copying from an Oracle source. See the Parallel copy from Oracle section for details.
Note
Oracle proxy server isn't supported.
Prerequisites
If your data store is located inside an on-premises network, an Azure virtual network, or Amazon Virtual Private Cloud, you need to configure a self-hosted integration runtime to connect to it.
If your data store is a managed cloud data service, you can use the Azure Integration Runtime. If the access is restricted to IPs that are approved in the firewall rules, you can add Azure Integration Runtime IPs to the allow list.
You can also use the managed virtual network integration runtime feature in Azure Data Factory to access the on-premises network without installing and configuring a self-hosted integration runtime.
For more information about the network security mechanisms and options supported by Data Factory, see Data access strategies.
The integration runtime provides a built-in Oracle driver. Therefore, you don't need to manually install a driver when you copy data from and to Oracle.
Get started
To perform the Copy activity with a pipeline, you can use one of the following tools or SDKs:
- The Copy Data tool
- The Azure portal
- The .NET SDK
- The Python SDK
- Azure PowerShell
- The REST API
- The Azure Resource Manager template
Create a linked service to Oracle using UI
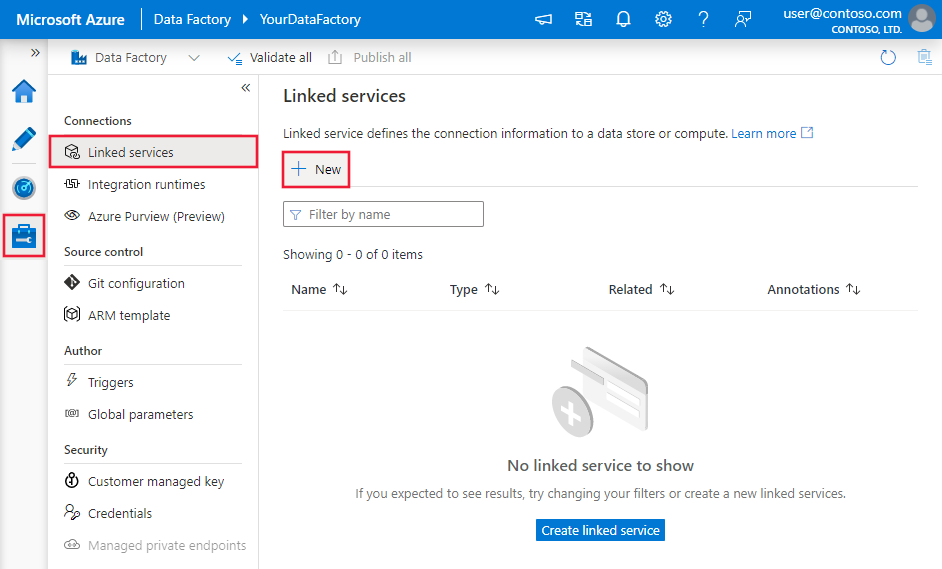
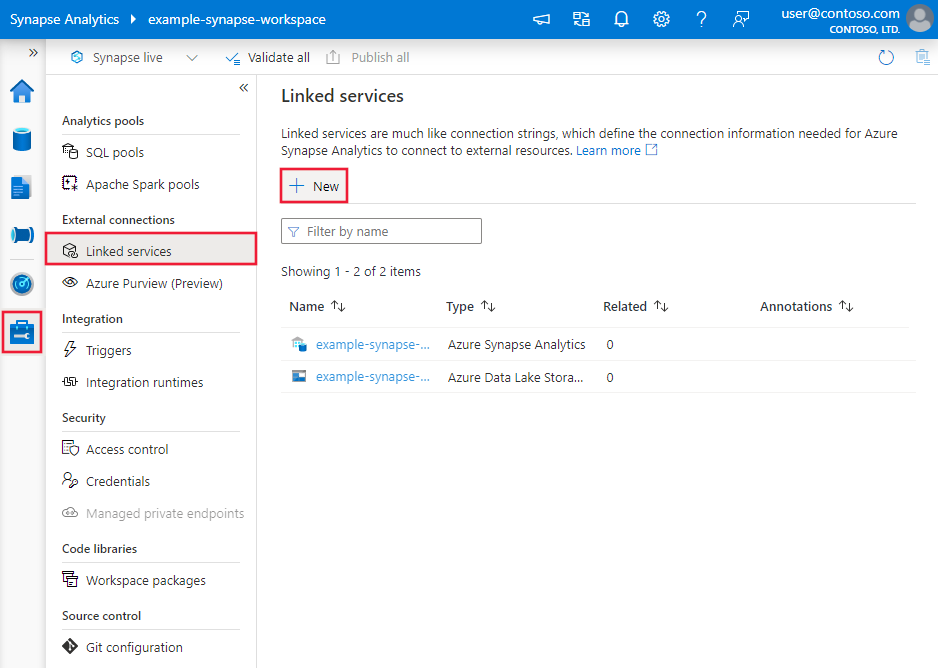
Use the following steps to create a linked service to Oracle in the Azure portal UI.
Browse to the Manage tab in your Azure Data Factory or Synapse workspace and select Linked Services, then click New:
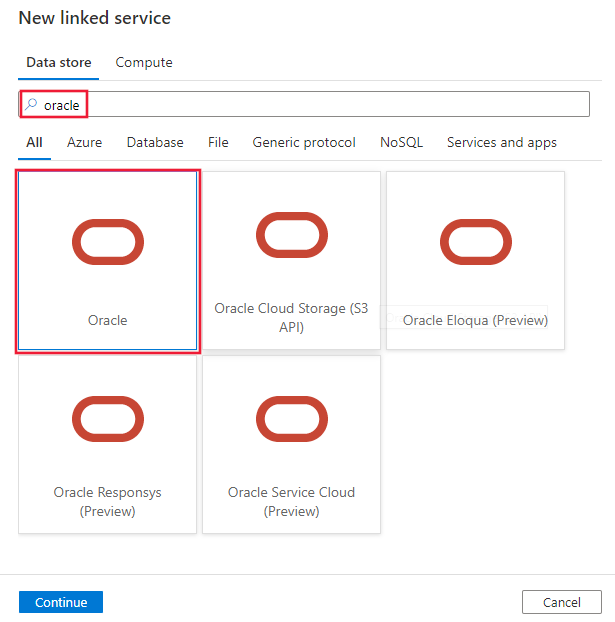
Search for Oracle and select the Oracle connector.
Configure the service details, test the connection, and create the new linked service.
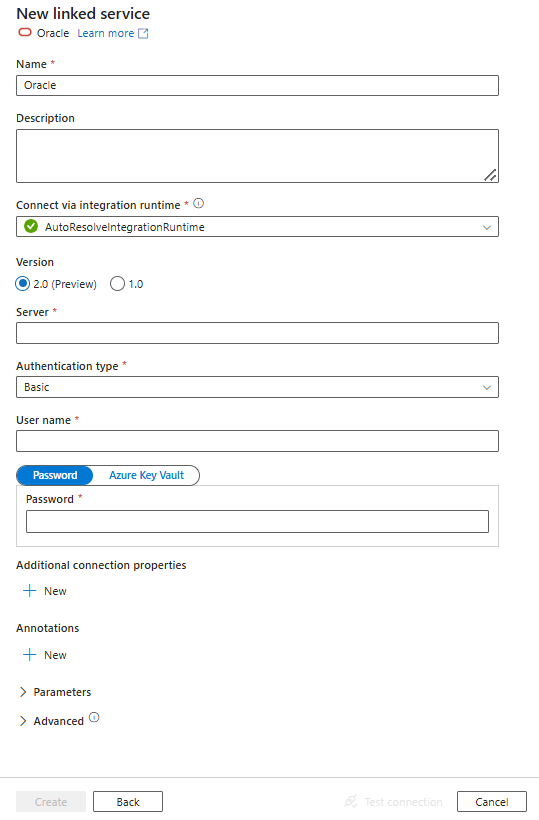
Connector configuration details
The following sections provide details about properties that are used to define entities specific to the Oracle connector.
Linked service properties
The Oracle connector now supports version 2.0. Refer to this section to upgrade your Oracle connector version from version 1.0. For the property details, see the corresponding sections.
Version 2.0
The Oracle linked service supports the following properties when apply version 2.0:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to Oracle. | Yes |
| version | The version that you specify. The value is 2.0. |
Yes |
| server | The location of Oracle database you want to connect to. You can refer to server property configuration to specify it. | Yes |
| authenticationType | Authentication type for connecting to the Oracle database. Only Basic auth is supported now. | Yes |
| username | The Oracle database username. | Yes |
| password | The Oracle database password. Mark this field as SecureString to store it securely. Or, you can reference a secret stored in Azure Key Vault. | Yes |
| connectVia | The integration runtime to be used to connect to the data store. Learn more from Prerequisites section. If not specified, the default Azure Integration Runtime is used. | No |
More connection properties you can set in linked service per your case:
| Property | Description | Required | Default value |
|---|---|---|---|
| encryptionClient | Specifies the encryption client behavior. Supported values are accepted, rejected, requested, or required. Type: string |
No | required |
| encryptionTypesClient | Specifies the encryption algorithms that client can use. Supported values are AES128, AES192, AES256, 3DES112, 3DES168. Type: string |
No | (AES256) |
| cryptoChecksumClient | Specifies the desired data integrity behavior when this client connects to a server. Supported values are accepted, rejected, requested, or required. Type: string |
No | required |
| cryptoChecksumTypesClient | Specifies the crypto-checksum algorithms that client can use. Supported values are SHA1, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512. Type: string |
No | (SHA512) |
| initialLobFetchSize | Specifies the amount that the source initially fetches for LOB columns. Type: int | No | 0 |
| fetchSize | Specifies the number of bytes that the driver allocates to fetch the data in one database round-trip. Type: int | No | 10 MB |
| statementCacheSize | Specifies the number of cursors or statements to be cached for each database connection. Type: int | No | 0 |
| initializationString | Specifies a command that is issued immediately after connecting to the database to manage session settings. Type: string | No | null |
| enableBulkLoad | Specifies whether to use bulk copy or batch insert when loading data into the database. Type: boolean | No | true |
| supportV1DataTypes | Specifies whether to use the version 1.0 data type mappings. Do not set this to true unless you want to keep backward compatibility with version 1.0's data type mappings. Type: boolean | No, this property is for backward compatibility use only | false |
| fetchTswtzAsTimestamp | Specifies whether the driver returns column value with the TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE data type as DateTime or string. This setting is ignored if supportV1DataTypes is not true. Type: boolean | No, this property is for backward compatibility use only | true |
Example:
{
"name": "OracleLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "Oracle",
"version": "2.0",
"typeProperties": {
"server": "<server name>",
"username": "<user name>",
"password": "<password>",
"authenticationType": "<authentication type>"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Example: store password in Azure Key Vault
{
"name": "OracleLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "Oracle",
"version": "2.0",
"typeProperties": {
"server": "<server name>",
"username": "<user name>",
"authenticationType": "<authentication type>",
"password": {
"type": "AzureKeyVaultSecret",
"store": {
"referenceName": "<Azure Key Vault linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"secretName": "<secretName>"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
server property configuration
For server property, you can specify it in one of the following three formats:
| Format | Example |
|---|---|
| Connect Descriptor | (DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=sales-server)(PORT=1521))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=sales.us.acme.com))) |
| Easy Connect (Plus) Naming | salesserver1:1521/sales.us.example.com |
| Oracle Net Services Name (TNS Alias) (only for the self-hosted integration runtime) | sales |
The following list shows the supported parameters used in server. If you use parameters that are not in the following list, your connection fails.
When using the Azure integration runtime:
HOST
PORT
PROTOCOL
SERVICE_NAME
SID
INSTANCE_NAME
SERVER
CONNECT_TIMEOUT
RETRY_COUNT
RETRY_DELAY
SSL_VERSION
SSL_SERVER_DN_MATCH
SSL_SERVER_CERT_DNWhen using the self-hosted integration runtime:
HOST
PORT
PROTOCOL
ENABLE
EXPIRE_TIME
FAILOVER
LOAD_BALANCE
RECV_BUF_SIZE
SDU
SEND_BUF_SIZE
SOURCE_ROUTE
TYPE_OF_SERVICE
COLOCATION_TAG
CONNECTION_ID_PREFIX
FAILOVER_MODE
GLOBAL_NAME
HS
INSTANCE_NAME
POOL_BOUNDARY
POOL_CONNECTION_CLASS
POOL_NAME
POOL_PURITY
RDB_DATABASE
SHARDING_KEY
SHARDING_KEY_ID
SUPER_SHARDING_KEY
SERVER
SERVICE_NAME
SID
TUNNEL_SERVICE_NAME
SSL_CLIENT_AUTHENTICATION
SSL_CERTIFICATE_ALIAS
SSL_CERTIFICATE_THUMBPRINT
SSL_VERSION
SSL_SERVER_DN_MATCH
SSL_SERVER_CERT_DN
WALLET_LOCATION
CONNECT_TIMEOUT
RETRY_COUNT
RETRY_DELAY
TRANSPORT_CONNECT_TIMEOUT
RECV_TIMEOUT
COMPRESSION
COMPRESSION_LEVELS
Version 1.0
The Oracle linked service supports the following properties when apply version 1.0:
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property must be set to Oracle. | Yes |
| connectionString | Specifies the information needed to connect to the Oracle Database instance. You can also put a password in Azure Key Vault, and pull the password configuration out of the connection string. Refer to the following samples and Store credentials in Azure Key Vault with more details. Supported connection type: You can use Oracle SID or Oracle Service Name to identify your database: - If you use SID: Host=<host>;Port=<port>;Sid=<sid>;User Id=<username>;Password=<password>;- If you use Service Name: Host=<host>;Port=<port>;ServiceName=<servicename>;User Id=<username>;Password=<password>;For advanced Oracle native connection options, you can choose to add an entry in TNSNAMES.ORA file on the machine where the self-hosted integration runtime is installed, and in Oracle linked service, choose to use Oracle Service Name connection type and configure the corresponding service name. |
Yes |
| connectVia | The integration runtime to be used to connect to the data store. Learn more from Prerequisites section. If not specified, the default Azure Integration Runtime is used. | No |
Tip
If you get an error, "ORA-01025: UPI parameter out of range", and your Oracle version is 8i, add WireProtocolMode=1 to your connection string. Then try again.
If you have multiple Oracle instances for failover scenario, you can create Oracle linked service and fill in the primary host, port, user name, password, etc., and add a new "Additional connection properties" with property name as AlternateServers and value as (HostName=<secondary host>:PortNumber=<secondary port>:ServiceName=<secondary service name>) - do not miss the brackets and pay attention to the colons (:) as separator. As an example, the following value of alternate servers defines two alternate database servers for connection failover:
(HostName=AccountingOracleServer:PortNumber=1521:SID=Accounting,HostName=255.201.11.24:PortNumber=1522:ServiceName=ABackup.NA.MyCompany).
More connection properties you can set in connection string per your case:
| Property | Description | Allowed values |
|---|---|---|
| ArraySize | The number of bytes the connector can fetch in a single network round trip. E.g., ArraySize=10485760.Larger values increase throughput by reducing the number of times to fetch data across the network. Smaller values increase response time, as there is less of a delay waiting for the server to transmit data. |
An integer from 1 to 4294967296 (4 GB). Default value is 60000. The value 1 does not define the number of bytes, but indicates allocating space for exactly one row of data. |
To enable encryption on Oracle connection, you have two options:
To use Triple-DES Encryption (3DES) and Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), on the Oracle server side, go to Oracle Advanced Security (OAS) and configure the encryption settings. For details, see this Oracle documentation. The Oracle Application Development Framework (ADF) connector automatically negotiates the encryption method to use the one you configure in OAS when establishing a connection to Oracle.
To use TLS, set up
truststorefor SSL server authentication by applying one of the following three methods:Method 1 (recommended):
Install the TLS/SSL certificate by importing it into the local certificate store. The built-in Oracle driver is able to load the needed certificate from the certificate store.
In the service, configure the Oracle connection string with
EncryptionMethod=1.
Method 2:
Get the TLS/SSL certificate information. Get the Distinguished Encoding Rules (DER)-encoded or Privacy Enhanced Mail (PEM)-encoded certificate information of your TLS/SSL cert.
openssl x509 -inform (DER|PEM) -in [Full Path to the DER/PEM Certificate including the name of the DER/PEM Certificate] -textIn the service, configure the Oracle connection string with
EncryptionMethod=1and the correspondingTrustStorevalue. For example,Host=<host>;Port=<port>;Sid=<sid>;User Id=<username>;Password=<password>;EncryptionMethod=1;TrustStore= data:// -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----<certificate content>-----END CERTIFICATE-----Note
- The value of the
TrustStorefield should be prefixed withdata://. - When specifying content for multiple certificates, specify the content of each certificate between
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----and-----END CERTIFICATE-----. The number of dashes (-----) should be the same before and after bothBEGIN CERTIFICATEandEND CERTIFICATE. For example:
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----<certificate content 1>-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----<certificate content 2>-----END CERTIFICATE-----
-----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----<certificate content 3>-----END CERTIFICATE----- - The
TrustStorefield supports content up to 8192 characters in length.
- The value of the
Method 3:
Create the
truststorefile with strong ciphers like AES256.openssl pkcs12 -in [Full Path to the DER/PEM Certificate including the name of the DER/PEM Certificate] -out [Path and name of TrustStore] -passout pass:[Keystore PWD] -keypbe AES-256-CBC -certpbe AES-256-CBC -nokeys -exportPlace the
truststorefile on the self-hosted integration runtime machine. For example, place the file atC:\MyTrustStoreFile.In the service, configure the Oracle connection string with
EncryptionMethod=1and the correspondingTrustStore/TrustStorePasswordvalue. For example,Host=<host>;Port=<port>;Sid=<sid>;User Id=<username>;Password=<password>;EncryptionMethod=1;TrustStore=C:\\MyTrustStoreFile;TrustStorePassword=<trust_store_password>.
Example:
{
"name": "OracleLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "Oracle",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "Host=<host>;Port=<port>;Sid=<sid>;User Id=<username>;Password=<password>;"
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Example: store password in Azure Key Vault
{
"name": "OracleLinkedService",
"properties": {
"type": "Oracle",
"typeProperties": {
"connectionString": "Host=<host>;Port=<port>;Sid=<sid>;User Id=<username>;",
"password": {
"type": "AzureKeyVaultSecret",
"store": {
"referenceName": "<Azure Key Vault linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
},
"secretName": "<secretName>"
}
},
"connectVia": {
"referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>",
"type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference"
}
}
}
Dataset properties
This section provides a list of properties supported by the Oracle dataset. For a full list of sections and properties available for defining datasets, see Datasets.
To copy data from and to Oracle, set the type property of the dataset to OracleTable. The following properties are supported.
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the dataset must be set to OracleTable. |
Yes |
| schema | Name of the schema. | No for source, Yes for sink |
| table | Name of the table/view. | No for source, Yes for sink |
| tableName | Name of the table/view with schema. This property is supported for backward compatibility. For new workload, use schema and table. |
No for source, Yes for sink |
Example:
{
"name": "OracleDataset",
"properties":
{
"type": "OracleTable",
"schema": [],
"typeProperties": {
"schema": "<schema_name>",
"table": "<table_name>"
},
"linkedServiceName": {
"referenceName": "<Oracle linked service name>",
"type": "LinkedServiceReference"
}
}
}
Copy activity properties
This section provides a list of properties supported by the Oracle source and sink. For a full list of sections and properties available for defining activities, see Pipelines.
Oracle as source
Tip
To load data from Oracle efficiently by using data partitioning, learn more from Parallel copy from Oracle.
To copy data from Oracle, set the source type in the copy activity to OracleSource. The following properties are supported in the copy activity source section.
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the copy activity source must be set to OracleSource. |
Yes |
| oracleReaderQuery | Use the custom SQL query to read data. An example is "SELECT * FROM MyTable".When you enable partitioned load, you need to hook any corresponding built-in partition parameters in your query. For examples, see the Parallel copy from Oracle section. |
No |
| convertDecimalToInteger | Oracle NUMBER type with zero or unspecified scale will be converted to corresponding integer. Allowed values are true and false (default). If you are using Oracle version 2.0, this property will only be allowed to be set when supportV1DataTypes is true. |
No |
| partitionOptions | Specifies the data partitioning options used to load data from Oracle. Allowed values are: None (default), PhysicalPartitionsOfTable, and DynamicRange. When a partition option is enabled (that is, not None), the degree of parallelism to concurrently load data from an Oracle database is controlled by the parallelCopies setting on the copy activity. |
No |
| partitionSettings | Specify the group of the settings for data partitioning. Apply when the partition option isn't None. |
No |
| partitionNames | The list of physical partitions that needs to be copied. Apply when the partition option is PhysicalPartitionsOfTable. If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook ?AdfTabularPartitionName in the WHERE clause. For an example, see the Parallel copy from Oracle section. |
No |
| partitionColumnName | Specify the name of the source column in integer type that will be used by range partitioning for parallel copy. If not specified, the primary key of the table is auto-detected and used as the partition column. Apply when the partition option is DynamicRange. If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook ?AdfRangePartitionColumnName in the WHERE clause. For an example, see the Parallel copy from Oracle section. |
No |
| partitionUpperBound | The maximum value of the partition column to copy data out. Apply when the partition option is DynamicRange. If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook ?AdfRangePartitionUpbound in the WHERE clause. For an example, see the Parallel copy from Oracle section. |
No |
| partitionLowerBound | The minimum value of the partition column to copy data out. Apply when the partition option is DynamicRange. If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook ?AdfRangePartitionLowbound in the WHERE clause. For an example, see the Parallel copy from Oracle section. |
No |
Example: copy data by using a basic query without partition
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyFromOracle",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<Oracle input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "OracleSource",
"convertDecimalToInteger": false,
"oracleReaderQuery": "SELECT * FROM MyTable"
},
"sink": {
"type": "<sink type>"
}
}
}
]
Oracle as sink
To copy data to Oracle, set the sink type in the copy activity to OracleSink. The following properties are supported in the copy activity sink section.
| Property | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|
| type | The type property of the copy activity sink must be set to OracleSink. |
Yes |
| writeBatchSize | Inserts data into the SQL table when the buffer size reaches writeBatchSize.Allowed values are Integer (number of rows). |
No (default is 10,000) |
| writeBatchTimeout | The wait time for the batch insert operation to complete before it times out. Allowed values are Timespan. An example is 00:30:00 (30 minutes). |
No |
| preCopyScript | Specify a SQL query for the copy activity to run before writing data into Oracle in each run. You can use this property to clean up the preloaded data. | No |
| maxConcurrentConnections | The upper limit of concurrent connections established to the data store during the activity run. Specify a value only when you want to limit concurrent connections. | No |
Example:
"activities":[
{
"name": "CopyToOracle",
"type": "Copy",
"inputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<input dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"outputs": [
{
"referenceName": "<Oracle output dataset name>",
"type": "DatasetReference"
}
],
"typeProperties": {
"source": {
"type": "<source type>"
},
"sink": {
"type": "OracleSink"
}
}
}
]
Parallel copy from Oracle
The Oracle connector provides built-in data partitioning to copy data from Oracle in parallel. You can find data partitioning options on the Source tab of the copy activity.
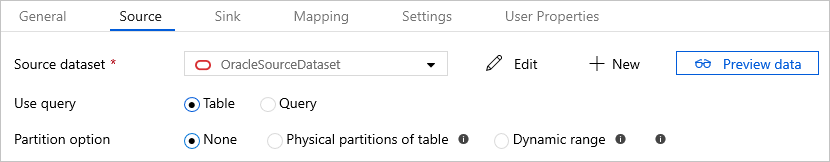
When you enable partitioned copy, the service runs parallel queries against your Oracle source to load data by partitions. The parallel degree is controlled by the parallelCopies setting on the copy activity. For example, if you set parallelCopies to four, the service concurrently generates and runs four queries based on your specified partition option and settings, and each query retrieves a portion of data from your Oracle database.
You are suggested to enable parallel copy with data partitioning especially when you load large amount of data from your Oracle database. The following are suggested configurations for different scenarios. When copying data into file-based data store, it's recommended to write to a folder as multiple files (only specify folder name), in which case the performance is better than writing to a single file.
| Scenario | Suggested settings |
|---|---|
| Full load from large table, with physical partitions. | Partition option: Physical partitions of table. During execution, the service automatically detects the physical partitions, and copies data by partitions. |
| Full load from large table, without physical partitions, while with an integer column for data partitioning. | Partition options: Dynamic range partition. Partition column: Specify the column used to partition data. If not specified, the primary key column is used. |
| Load a large amount of data by using a custom query, with physical partitions. | Partition option: Physical partitions of table. Query: SELECT * FROM <TABLENAME> PARTITION("?AdfTabularPartitionName") WHERE <your_additional_where_clause>.Partition name: Specify the partition name(s) to copy data from. If not specified, the service automatically detects the physical partitions on the table you specified in the Oracle dataset. During execution, the service replaces ?AdfTabularPartitionName with the actual partition name, and sends to Oracle. |
| Load a large amount of data by using a custom query, without physical partitions, while with an integer column for data partitioning. | Partition options: Dynamic range partition. Query: SELECT * FROM <TABLENAME> WHERE ?AdfRangePartitionColumnName <= ?AdfRangePartitionUpbound AND ?AdfRangePartitionColumnName >= ?AdfRangePartitionLowbound AND <your_additional_where_clause>.Partition column: Specify the column used to partition data. You can partition against the column with integer data type. Partition upper bound and partition lower bound: Specify if you want to filter against partition column to retrieve data only between the lower and upper range. During execution, the service replaces ?AdfRangePartitionColumnName, ?AdfRangePartitionUpbound, and ?AdfRangePartitionLowbound with the actual column name and value ranges for each partition, and sends to Oracle. For example, if your partition column "ID" is set with the lower bound as 1 and the upper bound as 80, with parallel copy set as 4, the service retrieves data by 4 partitions. Their IDs are between [1,20], [21, 40], [41, 60], and [61, 80], respectively. |
Tip
When copying data from a non-partitioned table, you can use "Dynamic range" partition option to partition against an integer column. If your source data doesn't have such type of column, you can leverage ORA_HASH function in source query to generate a column and use it as partition column.
Example: query with physical partition
"source": {
"type": "OracleSource",
"query": "SELECT * FROM <TABLENAME> PARTITION(\"?AdfTabularPartitionName\") WHERE <your_additional_where_clause>",
"partitionOption": "PhysicalPartitionsOfTable",
"partitionSettings": {
"partitionNames": [
"<partitionA_name>",
"<partitionB_name>"
]
}
}
Example: query with dynamic range partition
"source": {
"type": "OracleSource",
"query": "SELECT * FROM <TABLENAME> WHERE ?AdfRangePartitionColumnName <= ?AdfRangePartitionUpbound AND ?AdfRangePartitionColumnName >= ?AdfRangePartitionLowbound AND <your_additional_where_clause>",
"partitionOption": "DynamicRange",
"partitionSettings": {
"partitionColumnName": "<partition_column_name>",
"partitionUpperBound": "<upper_value_of_partition_column>",
"partitionLowerBound": "<lower_value_of_partition_column>"
}
}
Data type mapping for Oracle
When you copy data from and to Oracle, the following interim data type mappings are used within the service. To learn about how the copy activity maps the source schema and data type to the sink, see Schema and data type mappings.
| Oracle data type | Interim service data type (for version 2.0) | Interim service data type (for version 1.0) |
|---|---|---|
| BFILE | Byte[] | Byte[] |
| BINARY_FLOAT | Single | Single |
| BINARY_DOUBLE | Double | Double |
| BLOB | Byte[] | Byte[] |
| CHAR | String | String |
| CLOB | String | String |
| DATE | DateTime | DateTime |
| FLOAT (P < 16) | Double | Double |
| FLOAT (P >= 16) | Decimal | Double |
| INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH | Int64 | String |
| INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND | TimeSpan | String |
| LONG | String | String |
| LONG RAW | Byte[] | Byte[] |
| NCHAR | String | String |
| NCLOB | String | String |
| NUMBER (p,s) | Int16, Int32, Int64, Double, Single, Decimal | Decimal, String (if p > 28) |
| NUMBER without precision and scale | Decimal | Double |
| NVARCHAR2 | String | String |
| RAW | Byte[] | Byte[] |
| TIMESTAMP | DateTime | DateTime |
| TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE | DateTime | DateTime |
| TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE | DateTimeOffset | DateTime |
| VARCHAR2 | String | String |
| XMLTYPE | String | String |
Note
NUMBER(p,s) is mapped to the appropriate interim service data type depending on the precision (p) and scale (s).
Lookup activity properties
To learn details about the properties, check Lookup activity.
Upgrade the Oracle connector
Here are steps that help you upgrade the Oracle connector:
In Edit linked service page, select 2.0 (Preview) under Version and configure the linked service by referring to Linked service properties version 2.0.
For the authentication related properties including username and password, specify the original values in the corresponding fields in version 2.0. Other connection properties such as host, port, and Oracle Service Name/Oracle SID in version 1.0 are now parameters of the
serverproperty in version 2.0.For example, if you configure the version 1.0 linked service as shown below:
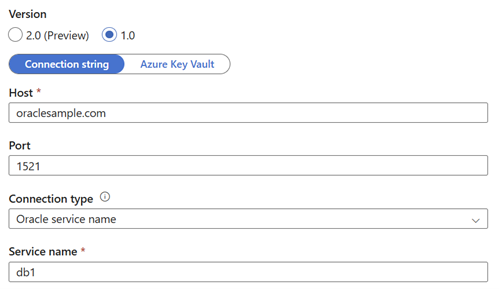
{ "name": "OracleLinkedService", "properties": { "type": "Oracle", "typeProperties": { "connectionString": "host=oraclesample.com;port=1521;servicename=db1" }, "connectVia": { "referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>", "type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference" } } }The identical version 2.0 linked service configuration using Easy Connect (Plus) Naming is:

{ "name": "OracleLinkedService", "properties": { "type": "Oracle", "version": "2.0", "typeProperties": { "server": "oraclesample.com:1521/db1", "username": "<user name>", "password": "<password>", "authenticationType": "<authentication type>" }, "connectVia": { "referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>", "type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference" } } }The identical version 2.0 linked service configuration using Connector Descriptor is:

{ "name": "OracleLinkedService", "properties": { "type": "Oracle", "version": "2.0", "typeProperties": { "server": "(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST= oraclesample.com)(PORT=1521))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=db1)))", "username": "<user name>", "password": "<password>", "authenticationType": "<authentication type>" }, "connectVia": { "referenceName": "<name of Integration Runtime>", "type": "IntegrationRuntimeReference" } } }Tip
Azure Key Vault is supported for the
serverproperty. You can edit the linked service JSON to add the Azure Key Vault reference, as shown below:
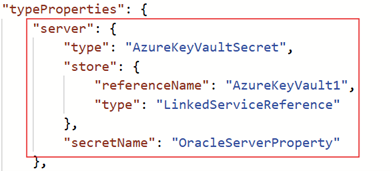
Note that:
If you use Oracle Service Name in version 1.0, you can use Easy Connect (Plus) Naming or Connector Descriptor as the server format in version 2.0.
If you use Oracle SID in version 1.0, you need to use Connector Descriptor as the server format in version 2.0.
For some additional connection properties in version 1.0, we provide alternative properties or parameters in the
serverproperty in version 2.0. You can refer to the table below to upgrade the version 1.0 properties.Version 1.0 Version 2.0 encryptionmethod PROTOCOL (parameter in server)tnsnamesfile TNS_ADMIN (environment variable supported on the self-hosted integration runtime) servername server enablebulkload
Value: 1, 0enableBulkLoad
Value: true, falsefetchtswtzastimestamp
Value: 1, 0fetchTswtzAsTimestamp
Value: true, falsealternateservers DESCRIPTION_LIST (parameter in server)arraysize fetchSize cachedcursorlimit statementCacheSize connectionretrycount RETRY_COUNT (parameter in server)initializationstring initializationString logintimeout CONNECT_TIMEOUT (parameter in server)cryptoprotocolversion SSL_VERSION (parameter in server)truststore WALLET_LOCATION (parameter in server)For example, if you use
alternateserversin version 1.0, you can set theDESCRIPTION_LISTparameter in the server property in version 2.0:Version 1.0 linked service using
alternateservers:{ "name": "OracleV1", "properties": { "type": "Oracle", "typeProperties": { "connectionString": "host=oraclesample.com;port=1521;servicename=db1;alternateservers=(HostName= oraclesample2.com:PortNumber=1521:SID=db2,HostName=255.201.11.24:PortNumber=1522:ServiceName=db3)" } } }Identical version 2.0 linked service using
DESCRIPTION_LISTparameter in Connector Descriptor:{ "name": "OracleV2", "properties": { "type": "Oracle", "version": "2.0", "typeProperties": { "server": "(DESCRIPTION_LIST=(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=oraclesample.com)(PORT=1521))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=db1)))(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=oraclesample2.com)(PORT=1521))(CONNECT_DATA=(SID=db2)))(DESCRIPTION=(ADDRESS=(PROTOCOL=tcp)(HOST=255.201.11.24)(PORT=1522))(CONNECT_DATA=(SERVICE_NAME=db3))))", "username": "<user name>", "password": "<password>", "authenticationType": "<authentication type>" } } }
The data type mapping for the Oracle linked service version 2.0 is different from that for the version 1.0. To learn the latest data type mapping, see Data type mapping for Oracle.
An additional connection property
supportV1DataTypesin version 2.0 can reduce upgrade difficulties caused by data type changes. Setting this property totrueensures that the data type in version 2.0 remains consistent with version 1.0.
Differences between Oracle version 2.0 and version 1.0
The Oracle connector version 2.0 offers new functionalities and is compatible with most features of version 1.0. The following table shows the feature differences between version 2.0 and version 1.0.
| Version 2.0 | Version 1.0 |
|---|---|
| The following mappings are used from Oracle data types to interim service data types used by the service internally. NUMBER(p,s) -> Int16, Int32, Int64, Double, Single, Decimal FLOAT(p)-> Double or Decimal based on its precision NUMBER -> Decimal TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE -> DateTimeOffset INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH -> Int64 INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND -> TimeSpan |
The following mappings are used from Oracle data types to interim service data types used by the service internally. NUMBER(p,s) -> Decimal or String based on its precision FLOAT(p)-> Double NUMBER -> Double TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE -> DateTime INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH -> String INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND -> String |
Support convertDecimalToInteger in copy source when supportV1DataTypes is set to true. |
Support convertDecimalToInteger in copy source. |
Using ? as a placeholder for script activity query parameters is not support. You can use the named parameter (such as :paramA) or the positional parameter (such as :1) as a replacement. |
Support using ? as a placeholder for script activity query parameters. |