Detect, explore, and validate functional dependencies in your data, using semantic link
Functional dependencies are relationships between columns in a table, where the values in one column are used to determine the values in another column. Understanding these dependencies can help you uncover patterns and relationships in your data, which in turn can help with feature engineering, data cleaning, and model building tasks. Functional dependencies act as an effective invariant that allows you to find and fix data quality issues that might be hard to detect otherwise.
In this article, you use semantic link to:
- Find dependencies between columns of a FabricDataFrame
- Visualize dependencies
- Identify data quality issues
- Visualize data quality issues
- Enforce functional constraints between columns in a dataset
Prerequisites
Get a Microsoft Fabric subscription. Or, sign up for a free Microsoft Fabric trial.
Sign in to Microsoft Fabric.
Use the experience switcher on the bottom left side of your home page to switch to Fabric.

- Go to the Data Science experience found in Microsoft Fabric.
- Create a new notebook to copy/paste code into cells.
- For Spark 3.4 and above, Semantic link is available in the default runtime when using Fabric, and there's no need to install it. If you're using Spark 3.3 or below, or if you want to update to the most recent version of Semantic Link, you can run the command:
python %pip install -U semantic-link - Add a Lakehouse to your notebook.
For Spark 3.4 and above, Semantic link is available in the default runtime when using Fabric, and there's no need to install it. If you use Spark 3.3 or below, or if you want to update to the most recent version of Semantic Link, run this command:
%pip install -U semantic-link
```
## Find functional dependencies in data
The SemPy `find_dependencies` function detects functional dependencies between the columns of a FabricDataFrame. The function uses a threshold on conditional entropy to discover approximate functional dependencies, where low conditional entropy indicates strong dependence between columns. To make the `find_dependencies` function more selective, you can set a lower threshold on conditional entropy. The lower threshold means that only stronger dependencies will be detected.
This Python code snippet demonstrates how to use `find_dependencies`:
```python
from sempy.fabric import FabricDataFrame
from sempy.dependencies import plot_dependency_metadata
import pandas as pd
df = FabricDataFrame(pd.read_csv("your_data.csv"))
deps = df.find_dependencies()
The find_dependencies function returns a FabricDataFrame with detected dependencies between columns.
A list represents columns that have a 1:1 mapping. The function also removes transitive edges, to try to prune the potential dependencies.
When you specify the dropna=True option, rows that have a NaN value in either column are eliminated from evaluation. This can result in nontransitive dependencies, as shown in this example:
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | NaN | 9 |
| 2 | NaN | 2 |
| 2 | 2 | 2 |
In some cases, the dependency chain can form cycles when you specify the dropna=True option, as shown in this example:
| A | B | C |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | NaN |
| 2 | 1 | NaN |
| NaN | 1 | 1 |
| NaN | 2 | 1 |
| 1 | NaN | 1 |
| 1 | NaN | 2 |
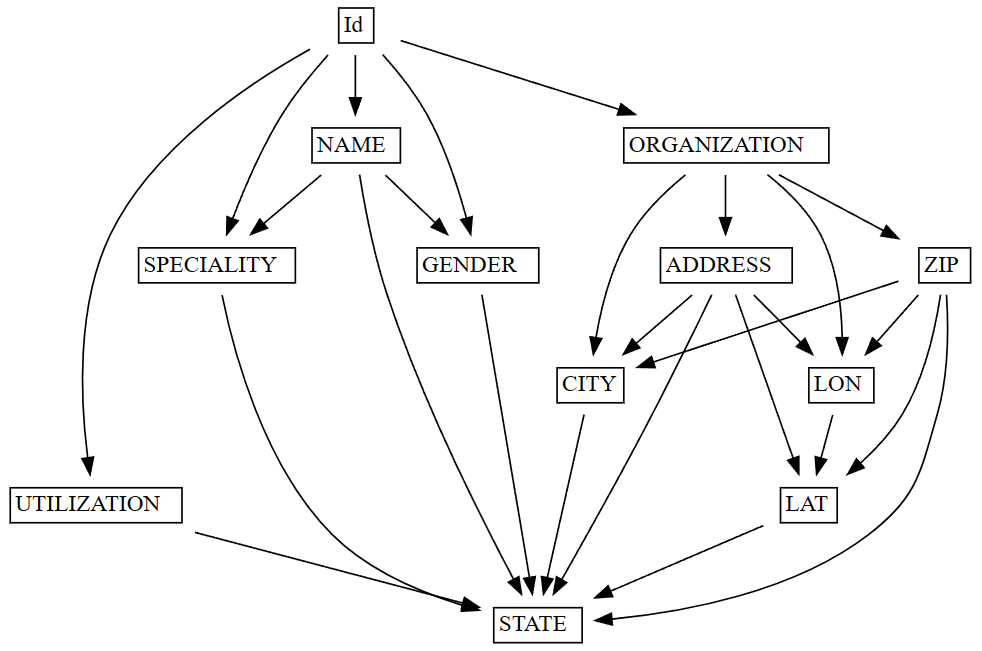
Visualize dependencies in data
After you find functional dependencies in a dataset (using find_dependencies), you can visualize the dependencies with the plot_dependency_metadata function. This function takes the resulting FabricDataFrame from find_dependencies and creates a visual representation of the dependencies between columns and groups of columns.
This Python code snippet shows how to use plot_dependencies:
from sempy.fabric import FabricDataFrame
from sempy.dependencies import plot_dependency_metadata
from sempy.samples import download_synthea
download_synthea(which='small')
df = FabricDataFrame(pd.read_csv("synthea/csv/providers.csv"))
deps = df.find_dependencies()
plot_dependency_metadata(deps)
The plot_dependency_metadata function generates a visualization that shows the 1:1 groupings of columns.
Columns that belong to a single group are placed in a single cell. If no suitable candidates are found, an empty FabricDataFrame is returned.
Identify data quality issues
Data quality issues can have various forms - for example, missing values, inconsistencies, or inaccuracies. Identifying and addressing these issues is important to ensure the reliability and validity of any analysis or model built on the data. One way to detect data quality issues is to examine violations of functional dependencies between columns in a dataset.
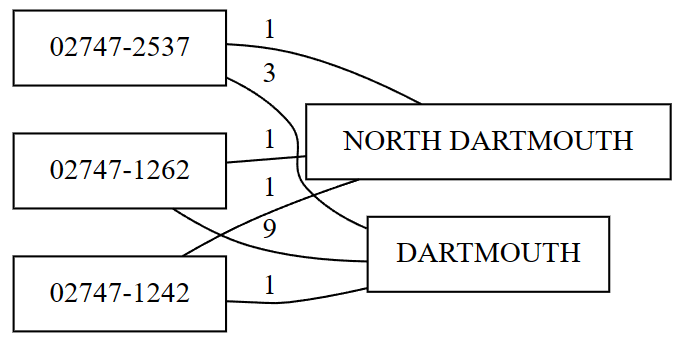
The list_dependency_violations function can help identify violations of functional dependencies between dataset columns. Given a determinant column and a dependent column, this function shows values that violate the functional dependency, along with the count of their respective occurrences. This can help inspect approximate dependencies and identify data quality issues.
This code snippet shows how to use the list_dependency_violations function:
from sempy.fabric import FabricDataFrame
from sempy.samples import download_synthea
download_synthea(which='small')
df = FabricDataFrame(pd.read_csv("synthea/csv/providers.csv"))
violations = df.list_dependency_violations(determinant_col="ZIP", dependent_col="CITY")
In this example, the function assumes a functional dependency between the ZIP (determinant) and CITY (dependent) columns. If the dataset has data quality issues - for example, the same ZIP Code assigned to multiple cities - the function outputs the data with the problems:
| ZIP | CITY | count |
|---|---|---|
| 12345 | Boston | 2 |
| 12345 | Seattle | 1 |
This output indicates that two different cities (Boston and Seattle) have the same ZIP Code value (12345). This suggests a data quality issue within the dataset.
The list_dependency_violations function provides more options that can handle missing values, show values mapped to violating values, limit the number of violations returned, and sort the results by count or determinant column.
The list_dependency_violations output can help identify dataset data quality issues. However, you should carefully examine the results and consider the context of your data, to determine the most appropriate course of action to address the identified issues. This approach might involve more data cleaning, validation, or exploration to ensure the reliability and validity of your analysis or model.
Visualize data quality issues
Data quality issues can damage the reliability and validity of any analysis or model built on that data. Identifying and addressing these issues is important to ensure the accuracy of your results. To detect data quality issues, you can examine violations of functional dependencies between columns in a dataset. Visualizing these violations can show the problems more clearly, and help you address them more effectively.
The plot_dependency_violations function can help visualize violations of functional dependencies between columns in a dataset. Given a determinant column and a dependent column, this function shows the violating values in a graphical format, to make it easier to understand the nature and extent of the data quality issues.
This code snippet shows how to use the plot_dependency_violations function:
from sempy.fabric import FabricDataFrame
from sempy.dependencies import plot_dependency_violations
from sempy.samples import download_synthea
download_synthea(which='small')
df = FabricDataFrame(pd.read_csv("synthea/csv/providers.csv"))
df.plot_dependency_violations(determinant_col="ZIP", dependent_col="CITY")
In this example, the function assumes an existing functional dependency between the ZIP (determinant) and CITY (dependent) columns. If the dataset has data quality issues - for example, the same ZIP code assigned to multiple cities - the function generates a graph of the violating values.
The plot_dependency_violations function provides more options that can handle missing values, show values mapped to violating values, limit the number of violations returned, and sort the results by count or determinant column.
The plot_dependency_violations function generates a visualization that can help identify dataset data quality issues. However, you should carefully examine the results and consider the context of your data, to determine the most appropriate course of action to address the identified issues. This approach might involve more data cleaning, validation, or exploration to ensure the reliability and validity of your analysis or model.
Enforce functional constraints
Data quality is crucial for ensuring the reliability and validity of any analysis or model built on a dataset. Enforcement of functional constraints between columns in a dataset can help improve data quality. Functional constraints can help ensure that the relationships between columns have accuracy and consistency, which can lead to more accurate analysis or model results.
The drop_dependency_violations function can help enforce functional constraints between columns in a dataset. It drops rows that violate a given constraint. Given a determinant column and a dependent column, this function removes rows with values that don't conform to the functional constraint between the two columns.
This code snippet shows how to use the drop_dependency_violations function:
from sempy.fabric import FabricDataFrame
from sempy.samples import download_synthea
download_synthea(which='small')
df = FabricDataFrame(pd.read_csv("synthea/csv/providers.csv"))
cleaned_df = df.drop_dependency_violations(determinant_col="ZIP", dependent_col="CITY")
Here, the function enforces a functional constraint between the ZIP (determinant) and CITY (dependent) columns. For each value of the determinant, the most common value of the dependent is picked, and all rows with other values are dropped. For example, given this dataset, the row with CITY=Seattle would be dropped, and the functional dependency ZIP -> CITY holds in the output:
| ZIP | CITY |
|---|---|
| 12345 | Seattle |
| 12345 | Boston |
| 12345 | Boston |
| 98765 | Baltimore |
| 00000 | San Francisco |
The drop_dependency_violations function provides the verbose option to control the output verbosity. By setting verbose=1, you can see the number of dropped rows. A verbose=2 value shows the entire row content of the dropped rows.
The drop_dependency_violations function can enforce functional constraints between columns in your dataset, which can help improve data quality and lead to more accurate results in your analysis or model. However, you must carefully consider the context of your data and the functional constraints you choose to enforce, to ensure that you don't accidentally remove valuable information from your dataset.