R library management
Libraries provide reusable code that you might want to include in your programs or projects for Microsoft Fabric Spark.
Microsoft Fabric supports an R runtime with many popular open-source R packages, including TidyVerse, preinstalled. When a Spark instance starts, these libraries are included automatically and available to be used immediately in notebooks or Spark job definitions.
You might need to update your R libraries for various reasons. For example, one of your core dependencies released a new version, or your team has built a custom package that you need available in your Spark clusters.
There are two types of libraries you may want to include based on your scenario:
Feed libraries refer to the ones residing in public sources or repositories, such as CRAN or GitHub.
Custom libraries are the code built by you or your organization, .tar.gz can be managed through Library Management portals.
There are two levels of packages installed on Microsoft Fabric:
Environment: Manage libraries through an environment to reuse the same set of libraries across multiple notebooks or jobs.
Session : A session-level installation creates an environment for a specific notebook session. The change of session-level libraries isn't persisted between sessions.
Summarizing the current available R library management behaviors:
| Library Type | Environment installation | Session-level installation |
|---|---|---|
| R Feed (CRAN) | Not Supported | Supported |
| R Custom | Supported | Supported |
Prerequisites
Get a Microsoft Fabric subscription. Or, sign up for a free Microsoft Fabric trial.
Sign in to Microsoft Fabric.
Use the experience switcher on the bottom left side of your home page to switch to Fabric.

Session-level R libraries
When doing interactive data analysis or machine learning, you might try newer packages or you might need packages that are currently unavailable on your workspace. Instead of updating the workspace settings, you can use session-scoped packages to add, manage, and update session dependencies.
- When you install session-scoped libraries, only the current notebook has access to the specified libraries.
- These libraries don't impact other sessions or jobs using the same Spark pool.
- These libraries are installed on top of the base runtime and pool level libraries.
- Notebook libraries take the highest precedence.
- Session-scoped R libraries don't persist across sessions. These libraries are installed at the start of each session when the related installation commands are executed.
- Session-scoped R libraries are automatically installed across both the driver and worker nodes.
Note
The commands of managing R libraries are disabled when running pipeline jobs. If you want to install a package within a pipeline, you must use the library management capabilities at the workspace level.
Install R packages from CRAN
You can easily install an R library from CRAN.
# install a package from CRAN
install.packages(c("nycflights13", "Lahman"))
You can also use CRAN snapshots as the repository to ensure to download the same package version each time.
# install a package from CRAN snapsho
install.packages("highcharter", repos = "https://cran.microsoft.com/snapshot/2021-07-16/")
Install R packages using devtools
The devtools library simplifies package development to expedite common tasks. This library is installed within the default Microsoft Fabric runtime.
You can use devtools to specify a specific version of a library to install. These libraries are installed across all nodes within the cluster.
# Install a specific version.
install_version("caesar", version = "1.0.0")
Similarly, you can install a library directly from GitHub.
# Install a GitHub library.
install_github("jtilly/matchingR")
Currently, the following devtools functions are supported within Microsoft Fabric:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
| install_github() | Installs an R package from GitHub |
| install_gitlab() | Installs an R package from GitLab |
| install_bitbucket() | Installs an R package from BitBucket |
| install_url() | Installs an R package from an arbitrary URL |
| install_git() | Installs from an arbitrary git repository |
| install_local() | Installs from a local file on disk |
| install_version() | Installs from a specific version on CRAN |
Install R custom libraries
To use a session-level custom library, you must first upload it to an attached Lakehouse.
Open the notebook you want to use the custom library in.
On the left side, select Add to add an existing lakehouse or create a lakehouse.
Right click or select the "..." next to Files to upload your .tar.gz file.
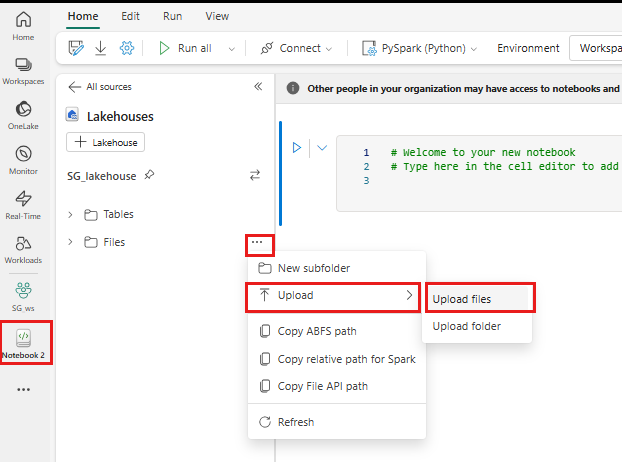
After uploading, go back to your notebook. Use the following command to install the custom library to your session:
install.packages("filepath/filename.tar.gz", repos = NULL, type = "source")
View installed libraries
Query all the libraries installed within your session using the library command.
# query all the libraries installed in current session
library()
Use the packageVersion function to check the version of the library:
# check the package version
packageVersion("caesar")
Remove an R package from a session
You can use the detach function to remove a library from the namespace. These libraries stay on disk until they're loaded again.
# detach a library
detach("package: caesar")
To remove a session-scoped package from a notebook, use the remove.packages() command. This library change has no impact on other sessions on the same cluster. Users can't uninstall or remove built-in libraries of the default Microsoft Fabric runtime.
Note
You can't remove core packages like SparkR, SparklyR, or R.
remove.packages("caesar")
Session-scoped R libraries and SparkR
Notebook-scoped libraries are available on SparkR workers.
install.packages("stringr")
library(SparkR)
str_length_function <- function(x) {
library(stringr)
str_length(x)
}
docs <- c("Wow, I really like the new light sabers!",
"That book was excellent.",
"R is a fantastic language.",
"The service in this restaurant was miserable.",
"This is neither positive or negative.")
spark.lapply(docs, str_length_function)
Session-scoped R libraries and sparklyr
With spark_apply() in sparklyr, you can use any R packages inside Spark. By default, in sparklyr::spark_apply(), the packages argument sets to FALSE. This copies libraries in the current libPaths to the workers, allowing you to import and use them on workers. For example, you can run the following to generate a caesar-encrypted message with sparklyr::spark_apply():
install.packages("caesar", repos = "https://cran.microsoft.com/snapshot/2021-07-16/")
spark_version <- sparkR.version()
config <- spark_config()
sc <- spark_connect(master = "yarn", version = spark_version, spark_home = "/opt/spark", config = config)
apply_cases <- function(x) {
library(caesar)
caesar("hello world")
}
sdf_len(sc, 5) %>%
spark_apply(apply_cases, packages=FALSE)
Related content
Learn more about the R functionalities: