Generative AI solutions for developers
Generative AI, enabled by large language models (LLMs), opens exciting new possibilities for software developers and organizations. Services like Azure OpenAI Service make AI development accessible with easy-to-use APIs. Developers at all skill levels can integrate advanced AI functionality into their applications without specialized knowledge or hardware investment.
As an application developer, you might want to understand what role you can play and where you fit in. For example, perhaps you wonder on what level in the "AI stack" to focus your learning. Or you might wonder what you are capable of building given existing technologies.
To answer these questions, it's important that you first develop a mental model that maps how new terminology and technologies fit into what you already understand. Developing a mental model helps you design and build generative AI features into your applications.
In a series of articles, we show you how your current software development experience applies to generative AI. The articles also set a basis of keywords and concepts to build on as you begin to develop your first generative AI solutions.
How businesses benefit from using generative AI
To understand how your current software development experience applies to generative AI, it's important to understand how businesses intend to benefit from using generative AI.
Businesses view generative AI as a means to improve customer engagement, increase operational efficiency, and enhance problem-solving and creativity. Integrating generative AI into existing systems opens opportunities for businesses to enhance their software ecosystems. It can complement traditional software functionalities with advanced AI capabilities, such as personalized recommendations for users or an intelligent agent that can answer specific questions about an organization or its products or services.
Here are a few common scenarios where generative AI can help businesses:
Content generation:
- Generate text, code, images, and sound. This scenario can be useful for marketing, sales, IT, internal communications, and more.
Natural language processing:
- Compose or improve business communications through suggestions or complete generation of messages.
- Use "chat with your data." That is, enable a user to ask questions in a chat experience by using data that's stored in the organization's databases or documents as the basis for answers.
- Summarization, organization, and simplification of large bodies of content to make content more accessible.
- Use semantic search. That is, allowing users to search documents and data without using exact keyword matches.
- Translate language to increase the reach and accessibility of content.
Data analysis:
- Analyze markets and identify trends in data.
- Model "what if" scenarios to help companies plan for possible changes or challenges in every area of the business.
- Analyze code to suggest improvements, fix bugs, and generate documentation.
A software developer has an opportunity to dramatically increase their impact by integrating generative AI applications and functionality into the software their organization relies on.
How to build generative AI applications
Although the LLM does the heavy lifting, you build systems that integrate, orchestrate, and monitor the results. There's much to learn, but you can apply the skills you already have, including how to:
- Make calls to APIs by using REST, JSON, or language-specific software development kits (SDKs)
- Orchestrate calls to APIs and perform business logic
- Store to and retrieve from data stores
- Integrate input and results into the user experience
- Create APIs that can be called from LLMs
Developing generative AI solutions build on your existing skills.
Developer tools and services
Microsoft invests in developing tools, services, APIs, samples, and learning resources to help you as you begin your generative AI development journey. Each highlights a major concern or responsibility that is needed to construct a generative AI solution. To use a given service, API, or resource effectively, the challenge is to make sure that you:
- Understand the typical functions, roles, and responsibilities in a given type of generative AI feature. For example, as we discuss at length in conceptual articles that describe retrieval-augmented generation (RAG)-based chat systems, there are many architectural responsibilities in the system. It's important that you understand the problem domain and constraints intimately before you design a system that addresses the problem.
- Understand the APIs, services, and tools that exist for a given function, role, or responsibility. Now that you understand the problem domain and constraints, you can choose to build that aspect of the system yourself by using custom code or existing low-code/no-code tools, or you can call into APIs for existing services.
- Understand the options, including code-centric and no-code/low-code solutions. You can build everything yourself, but is that an efficient use of your time and skills? Depending on your requirements, you can usually stitch together a combination of technologies and approaches (code, no-code, low-code, tools).
There's no single right way to build generative AI features into your applications. You can choose from many tools and approaches. It's important to evaluate the trade-offs of each of them.
Start with the application layer
You don't need to understand everything about how generative AI works to get started and be productive. As stated earlier, you likely already know enough. You can use APIs and apply existing skills to get started.
For example, you don't need to train your own LLM from scratch. Training an LLM requires time and resources that most companies are unwilling to invest. Instead, build on top of existing pretrained foundational models like GPT-4 by making API calls into existing hosted services like the Azure OpenAI API. Adding generative AI features to an existing application is no different than adding any other functionality based on an API call.
Researching how LLMs are trained or how they work might satisfy your intellectual curiosity, but fully understanding how an LLM works requires a deep understanding of data science and the math background that supports it. Gaining this understanding might include graduate-level courses on statistics, probabilities, and information theory.
If you have a computer science background, you can appreciate that most application development happens at a higher layer in "the stack" of research and technologies. You might have some understanding of each layer, but you likely specialize in the application development layer, with a focus on a specific programming language and platform, like available APIs, tooling, and patterns.
The same is true for the field of AI. You can understand and appreciate the theory that goes into building on top of LLMs, but you likely will focus your attention on the application layer or help implement patterns or processes to enable a generative AI effort in your company.
Here's an oversimplified representation of the layers of knowledge that are required to implement generative AI features in a new or existing application:
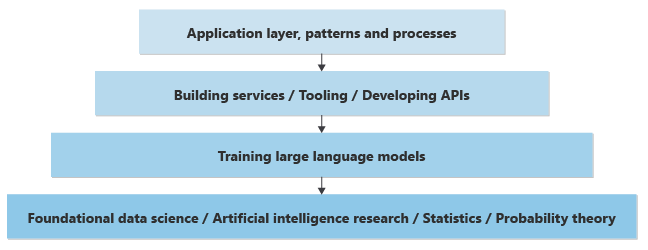
At the lowest level, data scientists are doing data science research to solve or improve AI based on a deep mathematical understanding of statistics, probability theory, and so on.
One layer up, based on the lowest foundational layer, data scientists implement theoretical concepts in LLMs, building the neural networks and training the weights and biases to provide a practical piece of software that can accept inputs (prompts) and generate results (completions). The computational process of composing completions based on prompts is called inference. Data scientists determine how the neurons of the neural network predict the next word or pixel to be generated.
Given the amount of processing power required to train models and generate results based on an input, models often are trained and hosted in large datacenters. It's possible to train or host a model on a local computer, but the results are often slow. Speed and efficiency come with dedicated GPU video cards that help handle the compute that's required to generate results.
When hosted in large datacenters, programmatic access to these models is provided through REST APIs. The APIs are sometimes "wrapped" by SDKs and are available to application developers for ease of use. Other tools can help improve the developer experience, providing observability or other utilities.
Application developers can make calls to these APIs to implement business functionality.
Beyond prompting the models programmatically, patterns and processes are emerging to help organizations build reliable business functionality based on generative AI. For example, patterns are emerging that help businesses ensure that the generated text, code, images, and sound comply with ethical and safety standards and with commitments to privacy of customer data.
In this stack of concerns or layers, if you're an application developer who is responsible for building business functionality, it's possible for you to push beyond the application layer into developing and training your own LLM. But this level of understanding requires a new set of skills that often is developed only through advanced education.
If you can't commit to developing competence in data science academically to help build the next layer down in the stack, you can focus on developing your knowledge of application layer topics:
- APIs and SDKs: What is available, and what the various endpoints produce.
- Related tools and services to help you build all the features that are required for a production-ready generative AI solution.
- Prompt engineering: How to achieve the best results by asking or rephrasing questions.
- Where bottlenecks emerge and how to scale a solution. This area includes understanding what is involved in logging or obtaining telemetry without violating customer privacy concerns.
- The characteristics of the various LLMs: Their strengths, use cases, benchmarks and what they measure, and key differentiations between vendors and models produced by each vendor. This information helps you choose the right model for the needs of your organization.
- The latest patterns, workflows, and processes that you can use to build effective and resilient generative AI features in your applications.
Tools and services from Microsoft
You can use low-code and no-code generative AI tools and services from Microsoft to help you build some or all of your solution. Various Azure services can play pivotal roles. Each contributes to the efficiency, scalability, and robustness of the solution.
API and SDKs for a code-centric approach
At the heart of every generative AI solution is an LLM model. Azure OpenAI provides access to all the features that are available in models like GPT-4.
| Product | Description |
|---|---|
| Azure OpenAI | A hosted service that provides access to powerful language models like GPT-4. You can use several APIs to perform all the typical functions of an LLM, including creating embeddings and creating a chat experience. You have full access to settings and customizations to get the results you want. |
Execution environments
Because you're building business logic, presentation logic, or APIs to integrate generative AI into your organization's applications, you need a service to host and execute that logic.
| Product | Description |
|---|---|
| Azure App Service (or one of several container-based cloud services) | This platform can host the web interfaces or APIs through which users interact with the RAG chat system. It supports rapid development, deployment, and scaling of web applications, so it's easier to manage the front-end components of the system. |
| Azure Functions | Use serverless compute to handle event-driven tasks within the RAG chat system. For example, use it to trigger data retrieval processes, process user queries, or handle background tasks like data synchronization and cleanup. It allows a more modular, scalable approach to building the system's back end. |
Low-code and no-code solutions
Some of the logic that you need to implement your generative AI vision can be built quickly and be hosted reliably by using a low-code or no-code solution.
| Product | Description |
|---|---|
| Azure AI Foundry | You can use Azure AI Foundry to train, test, and deploy custom machine learning models to enhance a RAG chat system. For example, use Azure AI Foundry to customize response generation or to improve the relevance of retrieved information. |
Vector database
Some generative AI solutions might require storage and retrieval of data used to augment generation. An example is a RAG-based chat system that allows users to chat with your organization's data. In this use case, you need a vector data store.
| Product | Description |
|---|---|
| Azure AI Search | You can use this service to efficiently search through large datasets to find relevant information that informs the responses generated by the language model. It's useful for the retrieval component of a RAG system, so the generated responses are as informative and contextually relevant as possible. |
| Azure Cosmos DB | This globally distributed, multi-model database service can store the vast amounts of structured and unstructured data that the RAG chat system needs to access. Its fast read and write capabilities make it ideal for serving real-time data to the language model and for storing user interactions for further analysis. |
| Azure Cache for Redis | This fully managed in-memory data store can be used for caching frequently accessed information, reducing latency and improving the performance of the RAG chat system. It's especially useful for storing session data, user preferences, and common queries. |
| Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server | This managed database service can store application data, including logs, user profiles, and historical chat data. Its flexibility and scalability support the dynamic needs of a RAG chat system so that data is consistently available and secure. |
Each of these Azure services contributes to creating a comprehensive, scalable, and efficient architecture for a generative AI solution. They help developers access and use the best of Azure cloud capabilities and AI technologies.
Code-centric generative AI development by using the Azure OpenAI API
In this section, we focus on the Azure OpenAI API. As stated earlier, you access LLM functionality programmatically through a RESTful web API. You can use literally any modern programming language to call into these APIs. In many cases, language-specific or platform-specific SDKs operate as wrappers around the REST API calls to make the experience more idiomatic.
Here's the list of Azure OpenAI REST API wrappers:
- Azure OpenAI client library for .NET
- Azure OpenAI client library for Java
- Azure OpenAI client library for JavaScript
- Azure OpenAI client module for Go
- Use the OpenAI Python package and change several options. Python doesn't offer an Azure-specific client library.
If a language or platform SDK is unavailable, the worst-case scenario is that you must make REST calls directly to the web APIs:
Most developers are familiar with how to call web APIs.
Azure OpenAI offers a range of APIs that are designed to facilitate different types of AI-powered tasks, so developers can integrate advanced AI functionalities into their applications. Here's an overview of the key APIs available from OpenAI:
- Chat Completions API: This API is focused on text-generation scenarios, including conversational capabilities to support creating chatbots and virtual assistants that can engage in natural, human-like dialogue. It's optimized for interactive use cases, including customer support, personal assistants, and interactive learning environments. However, it's used for all text-generation scenarios, including summarization, autocompletion, writing documents, analyzing text, and translation. It's the entry point for vision capabilities that are currently in preview (that is, to upload an image and ask questions about it).
- Moderation API: This API is designed to help developers identify and filter out potentially harmful content within text. It's a tool that helps ensure safer user interactions by automatically detecting offensive, unsafe, or otherwise inappropriate material.
- Embeddings API: The Embeddings API generates vector representations of text inputs. It converts words, sentences, or paragraphs into high-dimensional vectors. These embeddings can be used for semantic search, clustering, content similarity analysis, and more. It captures the underlying meaning and semantic relationships in the text.
- Image Generation API: Use this API to generate original, high-quality images and art from textual descriptions. It's based on OpenAI's DALL·E model, which can create images that match a wide variety of styles and subjects based on the prompts it receives.
- Audio API: This API provides access to OpenAI's audio model and is designed for automatic speech recognition. It can transcribe spoken language into text, or text into speech, supporting various languages and dialects. It's useful for applications that require voice commands, audio content transcription, and more.
Although you can use generative AI to work with many different media modalities, in the rest of this article, we focus on text-based generative AI solutions. These solutions include scenarios like chat and summarization.
Get started developing with generative AI
Software developers who are new to an unfamiliar language, API, or technology usually begin to learn it by following tutorials or training modules that demonstrate how to build small applications. Some software developers prefer to take a self-guided approach and build small experimental applications. Both approaches are valid and useful.
As you get started, it's best to start small, promise little, iterate, and build your understanding and skill. Developing applications by using generative AI has unique challenges. For example, in traditional software development, you can rely on deterministic output. That is, for any set of inputs, you can expect the exact same output every time. But generative AI is nondeterministic. You never get the exact same answer twice for a given prompt, which is at the root of many new challenges.
As you get started, consider these tips.
Tip 1: Be clear about what you want to achieve
- Be specific about the problem you're trying to solve: Generative AI can solve a wide range of problems, but success comes from clearly defining the specific problem you aim to solve. Are you trying to generate text, images, code, or something else? The more specific you are, the better you can tailor the AI to meet your needs.
- Understand your audience: Knowing your audience helps tailor the AI's output to match their expectations, whether it's casual users or experts in a particular field.
Tip 2: Use the strengths of LLMs
- Understand the limitations and biases of LLMs: Although LLMs are powerful, they have limitations and inherent biases. Knowing the limitations and biases can help you design around them or incorporate mitigations.
- Understand where LLMs excel: LLMs excel at tasks like content creation, summarization, and language translation. Although their decision-making capabilities and discriminative capabilities are getting stronger with each new version, there might be other types of AI that are more appropriate for your scenario or use case. Choose the right tool for the job.
Tip 3: For good results, use good prompts
- Learn prompt engineering best practices: Crafting effective prompts is an art. Experiment with different prompts to see how they affect the output. Be concise but descriptive.
- Commit to iterative refinement: Often, the first prompt might not yield the desired result. It's a process of trial and error. Use outputs to further refine your prompts.
Build your first generative AI solution
If you want to start experimenting with building a generative AI solution immediately, we recommend that you take a look at Get started with chat by using your own data sample for Python. The tutorial is also available for .NET, Java, and JavaScript.
Final considerations for application design
Here's a short list of things to consider and other takeaways from this article that might affect your application design decisions:
- Define the problem space and audience clearly to align AI's capabilities with user expectations. Optimize the solution's effectiveness for the intended use case.
- Use low-code/no-code platforms for rapid prototyping and development if they meet your project's requirements. Evaluate the trade-off between development speed and customizability. Explore the possibilities of low-code and no-code solutions for parts of your application to speed up development and enable nontechnical team members to contribute to the project.