Service levels for Azure NetApp Files
Service levels are an attribute of a capacity pool. Service levels are defined and differentiated by the allowed maximum throughput for a volume in the capacity pool based on the quota that is assigned to the volume. Throughput is a combination of read and write speed.
Supported service levels
Azure NetApp Files supports four service levels: Standard, Premium, Ultra, and Flexible.
Standard storage:
The Standard service level provides up to 16 MiB/s of throughput per 1 TiB of capacity provisioned.Premium storage:
The Premium service level provides up to 64 MiB/s of throughput per 1 TiB of capacity provisioned.Ultra storage:
The Ultra service level provides up to 128 MiB/s of throughput per 1 TiB of capacity provisioned.-
The Flexible service level enables you to adjust throughput and size limits independently. This service level is designed for demanding applications such as Oracle or SAP HANA. You can also use the Flexible service level to create high-capacity volumes with (relatively) low throughput requirements or the reverse: low-capacity volumes with high throughput requirements. The minimum throughput to be assigned to a Flexible capacity pool is 128 MiB/second regardless of the pool quota. The first 128 MiB/s of throughput, known as the baseline, is included in the Flexible service level. The maximum throughput is 5 x 128 x the size of the capacity pool in TiB. For more information see Flexible service level throughput examples. You can assign throughput and capacity to volumes that are part of a Flexible capacity pool in the same way you do volumes that are part of a manual QoS capacity pool of any service level. Cool access isn't currently supported with the Flexible service level.
Important
The Flexible service level is only supported for new manual QoS capacity pools. For a list of regions that support the Flexible service level, see Create a capacity pool for Azure NetApp Files.
Storage with cool access:
Cool access storage is available with the Standard, Premium, and Ultra service levels. The throughput experience for any of these service levels with cool access is the same for cool access as it is for data in the hot tier. It may differ when data that resides in the cool tier is accessed. For more information, see Azure NetApp Files storage with cool access and Performance considerations for storage with cool access.
Throughput limits
The throughput limit for a volume is determined by the combination of the following factors:
- The service level of the capacity pool to which the volume belongs
- The quota assigned to the volume
- The QoS type (auto or manual) of the capacity pool
Throughput limit examples of volumes in an auto QoS capacity pool
The following diagram shows throughput limit examples of volumes in an auto QoS capacity pool:
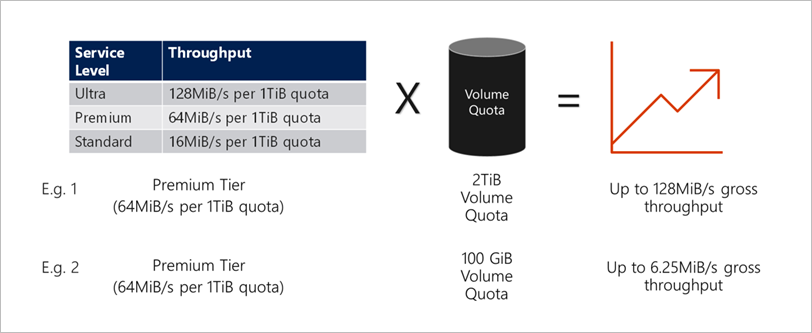
In Example 1, a volume from an auto QoS capacity pool with the Premium storage tier that is assigned 2 TiB of quota will be assigned a throughput limit of 128 MiB/s (2 TiB * 64 MiB/s). This scenario applies regardless of the capacity pool size or the actual volume consumption.
In Example 2, a volume from an auto QoS capacity pool with the Premium storage tier that is assigned 100 GiB of quota is assigned a throughput limit of 6.25 MiB/s (0.09765625 TiB * 64 MiB/s). This scenario applies regardless of the capacity pool size or the actual volume consumption.
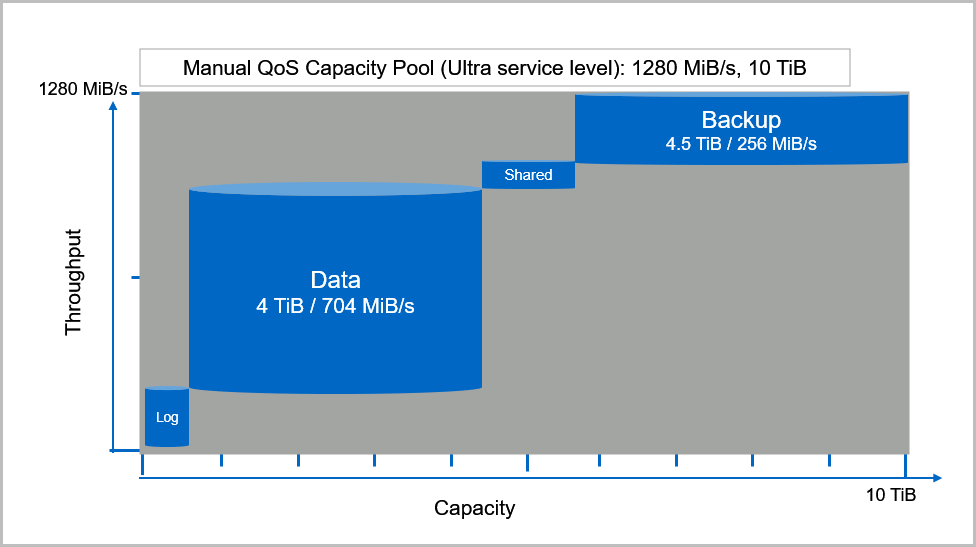
Throughput limit examples of volumes in a manual QoS capacity pool
If you use a manual QoS capacity pool, you can assign the capacity and throughput for a volume independently. When you create a volume in a manual QoS capacity pool, you can specify the throughput (MiB/S) value. The total throughput assigned to volumes in a manual QoS capacity pool depends on the size of the pool and the service level. Throughput limits for the Standard, Premium, and Ultra service levels are capped by a formula: capacity pool size in TiB x service level throughput/TiB. For instance, a 10-TiB capacity pool with the Ultra service level has a total throughput capacity of 1,280 MiB/s (10 TiB x 128 MiB/s/TiB) available for the volumes. For the Flexible service level, the formula is 5 x capacity pool size in TiB x minimum service level throughput (128 MiB/s/TiB). For examples, see Flexible service level throughput examples.
For example, for an SAP HANA system, this capacity pool can be used to create the following volumes. Each volume provides the individual size and throughput to meet your application requirements:
- SAP HANA data volume: Size 4 TiB with up to 704 MiB/s
- SAP HANA log volume: Size 0.5 TiB with up to 256 MiB/s
- SAP HANA shared volume: Size 1 TiB with up to 64 MiB/s
- SAP HANA backup volume: Size 4.5 TiB with up to 256 MiB/s
The following diagram illustrates the scenarios for the SAP HANA volumes:
The following diagram illustrates the scenarios for the SAP HANA volumes but with the Flexible service level and a baseline throughput of 128 MiB/S:
The example extends to the Flexible service level as well. A Flexible service level capacity pool can be used to create the following volumes. Each volume provides the individual size and throughput to meet your application requirements:
- SAP HANA data volume: Size 4 TiB with up to 704 MiB/s
- SAP HANA log volume: Size 0.5 TiB with up to 256 MiB/s
- SAP HANA shared volume: Size 1 TiB with up to 64 MiB/s
- SAP HANA backup volume: Size 4.5 TiB with up to 384 MiB/s
As illustrated in the diagram, the SAP HANA backup volume received the 128MiB/s additional baseline throughput.
Flexible service level throughput examples:
| Flexible pool size (TiB) | Allowable throughput minimum (MiB/s) | Allowable throughput maximum (MiB/s) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 128 | 5 * 128 * 1 = 640 |
| 2 | 128 | 5 * 128 * 2 = 1,280 |
| 10 | 128 | 5 * 128 * 10 = 6,400 |
| 50 | 128 | 5 * 128 * 50 = 32,000 |
| 100 | 128 | 5 * 128 * 100 = 64,000 |
| 1,024 | 128 | 5 * 128 * 1,024 = 655,360 |
Note
A baseline throughput of 128 MiB/s is provided for every pool, at no additional cost.
