NVIDIA GPU Driver Extension for Windows
The NVIDIA GPU Driver Extension for Windows installs NVIDIA GPU drivers on Windows N-series virtual machines (VMs). Depending on the VM family, the extension installs CUDA or GRID drivers. When you install NVIDIA drivers by using this extension, you accept and agree to the terms of the NVIDIA End-User License Agreement. During the installation process, the VM might reboot to complete the driver setup.
The instructions for manual installation of the drivers, and the list of current supported versions are available for review. For more information, see Install NVIDIA GPU drivers on N-series VMs running Windows.
The NVIDIA GPU Driver Extension can also be deployed on Linux N-series VMs. For more information, see NVIDIA GPU Driver Extension for Linux.
Note
The GPU driver extensions do not automatically update the driver after the extension is installed. If you need to move to a newer driver version then either manually download and install the driver or remove and add the extension again.
Prerequisites
Confirm your virtual machine satisfies the prerequisites for using the NVIDIA GPU Driver Extension.
Operating system support
The NVIDIA GPU Driver Extension supports the following Windows versions:
| Distribution | Version |
|---|---|
| Windows 11 | Core |
| Windows 10 | Core |
| Windows Server 2022 | Core |
| Windows Server 2019 | Core |
| Windows Server 2016 | Core |
| Windows Server 2012 R2 | Core |
Internet connection required
The NVIDIA GPU Driver Extension requires that the target VM is connected to the internet and has access.
Review the extension schema
The following JSON snippet shows the schema for the extension:
{
"name": "<myExtensionName>",
"type": "extensions",
"apiVersion": "2015-06-15",
"location": "<location>",
"dependsOn": [
"[concat('Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/', <myVM>)]"
],
"properties": {
"publisher": "Microsoft.HpcCompute",
"type": "NvidiaGpuDriverWindows",
"typeHandlerVersion": "1.4",
"autoUpgradeMinorVersion": true,
"settings": {
}
}
}
Properties
The JSON schema includes values for the following parameters.
| Name | Value/Example | Data type |
|---|---|---|
apiVersion |
2015-06-15 | date |
publisher |
Microsoft.HpcCompute | string |
type |
NvidiaGpuDriverWindows | string |
typeHandlerVersion |
1.4 | int |
Deploy the extension
Azure VM extensions can be managed by using the Azure CLI, PowerShell, Azure Resource Manager (ARM) templates, and the Azure portal.
Note
Some of the following examples use <placeholder> parameter values in the commands. Before you run each command, make sure to replace any placeholder values with specific values for your configuration.
Azure portal
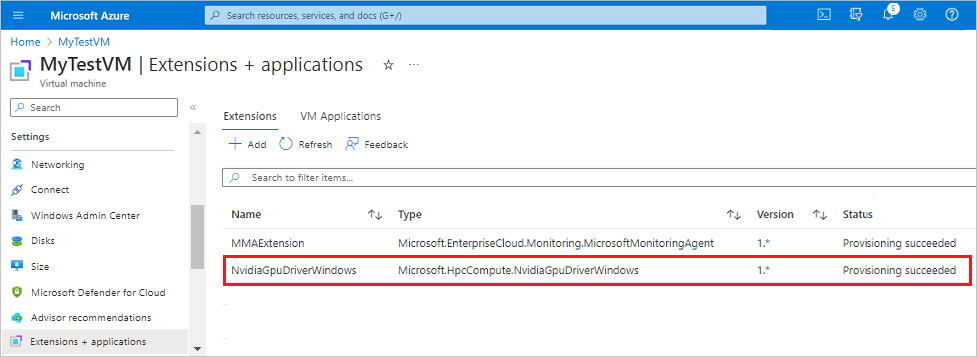
To install the NVIDIA GPU Driver Extension in the Azure portal, follow these steps:
In the Azure portal, go to the virtual machine on which you want to install the extension.
Under Settings, select Extensions + Applications.
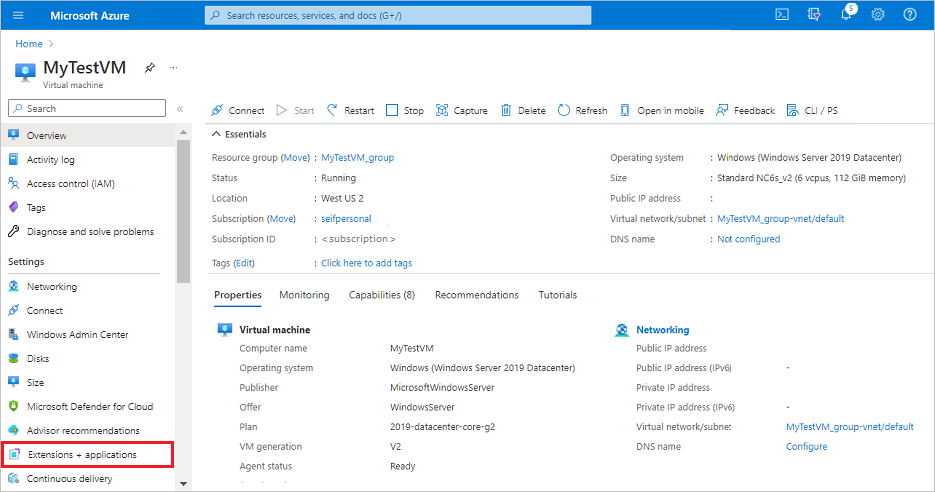
Under Extensions, select + Add.
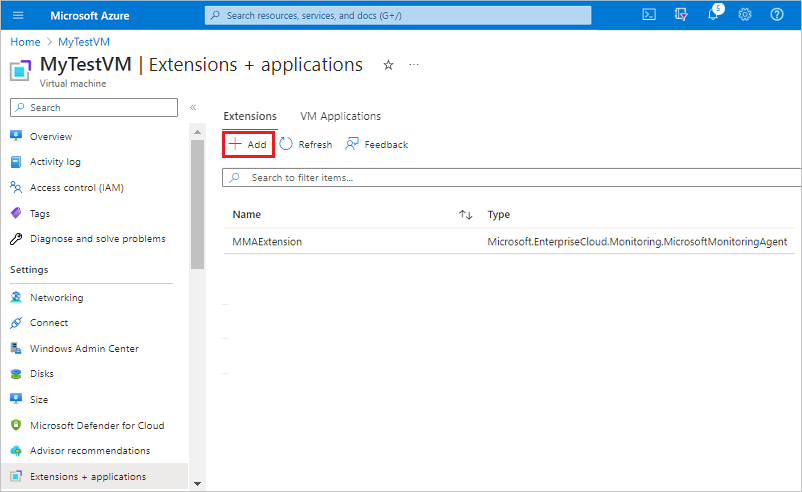
Locate and select NVIDIA GPU Driver Extension, then select Next.
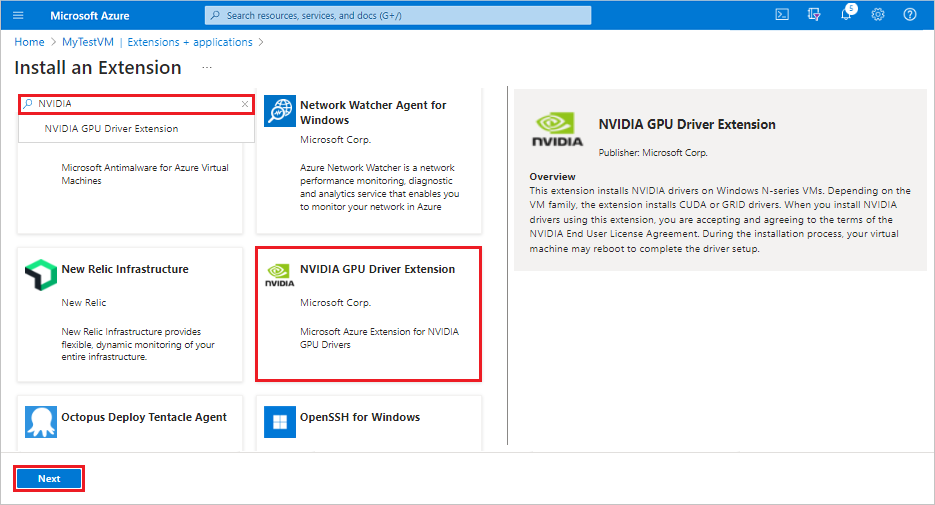
Select Review + create. Confirm the deployment action, and select Create.
Wait a few minutes for the extension to deploy.
Confirm the extension is listed as an installed extension for the virtual machine.
ARM template
ARM templates are ideal when you deploy one or more virtual machines that require post-deployment configuration.
The JSON configuration for a virtual machine extension can be nested inside the virtual machine resource or placed at the root or top level of a JSON ARM template. The placement of the JSON configuration affects the value of the resource name and type. For more information, see Set name and type for child resources.
The following example assumes the extension is nested inside the virtual machine resource. When the extension resource is nested, the JSON is placed in the "resources": [] object of the virtual machine.
{
"name": "<myExtensionName>",
"type": "extensions",
"location": "[<resourceGroup().location>]",
"apiVersion": "2015-06-15",
"dependsOn": [
"[concat('Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/', <myVM>)]"
],
"properties": {
"publisher": "Microsoft.HpcCompute",
"type": "NvidiaGpuDriverWindows",
"typeHandlerVersion": "1.4",
"autoUpgradeMinorVersion": true,
"settings": {
}
}
}
PowerShell
Use the following PowerShell command to deploy the NVIDIA GPU Driver Extension to a virtual machine.
Set-AzVMExtension
-ResourceGroupName "<myResourceGroup>" `
-VMName "<myVM>" `
-Location "<location>" `
-Publisher "Microsoft.HpcCompute" `
-ExtensionName "NvidiaGpuDriverWindows" `
-ExtensionType "NvidiaGpuDriverWindows" `
-TypeHandlerVersion 1.4 `
-SettingString '{ `
}'
Azure CLI
Run the following command in the Azure CLI to deploy the NVIDIA GPU Driver Extension to a virtual machine.
az vm extension set \
--resource-group <myResourceGroup> \
--vm-name <myVM> \
--name NvidiaGpuDriverWindows \
--publisher Microsoft.HpcCompute \
--version 1.4 \
--settings '{ \
}'
Troubleshoot issues
Here are some suggestions for how to troubleshoot deployment issues.
Check extension status
Check the status of your extension deployment in the Azure portal, or by using PowerShell or the Azure CLI.
To see the deployment state of extensions for a given VM, run the following commands:
Get-AzVMExtension -ResourceGroupName <myResourceGroup> -VMName <myVM> -Name <myExtensionName>
az vm extension list --resource-group <myResourceGroup> --vm-name <myVM> -o table
Review output logs
View output logs for the NVIDIA GPU Driver Extension deployment under
C:\WindowsAzure\Logs\Plugins\Microsoft.HpcCompute.NvidiaGpuDriverWindows\.
Respond to error codes
The following table lists common error codes for deployment and potential follow-up actions.
| Error | Description | Action |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Operation successful. | No required action. |
| 1 | Operation successful. | Reboot. |
| 100 | Operation not supported or couldn't be completed. | Check log files to determine cause of error, such as: - PowerShell version isn't supported. - VM size isn't an N-series VM. - Failure during data download. |
| 240, 840 | Operation timeout. | Retry operation. |
| -1 | Exception occurred. | Check log files to determine cause of exception. |
| -5x | Operation interrupted due to pending reboot. | Reboot the VM. Installation continues after reboot. Uninstall should be invoked manually. |
Known issues
GRID Driver version 17.x is incompatible on NVv3 (NVIDIA Tesla M60). GRID drivers up to version 16.5 are supported. NvidiaGpuDriverWindows installs the latest drivers which are incompatible on NVv3 SKU. Instead, use the following runtime settings to force the extension to install an older version of the driver. For more information on driver versions, see NVIDIA GPU resources.
az vm extension set --resource-group <rg-name> --vm-name <vm-name> --name NvidiaGpuDriverWindows --publisher Microsoft.HpcCompute --settings "{'driverVersion':'538.46'}"
{
"name": "NvidiaGpuDriverWindows",
"type": "extensions",
"apiVersion": "2015-06-15",
"location": "<location>",
"dependsOn": [
"[concat('Microsoft.Compute/virtualMachines/', <myVM>)]"
],
"properties": {
"publisher": "Microsoft.HpcCompute",
"type": "NvidiaGpuDriverWindows",
"typeHandlerVersion": "1.9",
"autoUpgradeMinorVersion": true,
"settings": {
"driverVersion": "538.46"
}
}
}
Get support
Here are some other options to help you resolve deployment issues:
For assistance, contact the Azure experts on the Q&A and Stack Overflow forums.
If you don't find an answer on the site, you can post a question for input from Microsoft or other members of the community.
You can also Contact Microsoft Support. For information about using Azure support, read the Azure support FAQ.
Next steps
- For more information about extensions, see Virtual machine extensions and features for Windows.
- For more information about N-series VMs, see GPU optimized virtual machine sizes.