Mount SMB Azure file share on macOS
Azure Files is Microsoft's easy-to-use cloud file system. Azure file shares can be mounted with the industry standard SMB 3 protocol by macOS High Sierra 10.13+. This article shows two different ways to mount an Azure file share on macOS: with the Finder UI and using the Terminal.
Warning
Mounting a file share using storage account keys carries inherent security risks. For information on how to protect and manage your keys, see Manage storage account access keys. Azure Files doesn't currently support using identity-based authentication to mount a file share on macOS.
Applies to
| File share type | SMB | NFS |
|---|---|---|
| Standard file shares (GPv2), LRS/ZRS | ||
| Standard file shares (GPv2), GRS/GZRS | ||
| Premium file shares (FileStorage), LRS/ZRS |
Prerequisites for mounting an Azure file share on macOS
Storage account name: To mount an Azure file share, you'll need the name of the storage account.
Storage account key: To mount an Azure file share, you'll need the primary (or secondary) storage account key. SAS tokens aren't currently supported for mounting Azure file shares.
Ensure port 445 is open: SMB communicates over TCP port 445. On your client machine (the Mac), check to make sure your firewall isn't blocking TCP port 445. If your organization or ISP is blocking port 445, you might need to set up a VPN from on-premises to your Azure storage account with Azure Files exposed on your internal network using private endpoints. With this configuration, traffic will go through a secure tunnel as opposed to over the internet. For more information, see Networking considerations for direct Azure file share access. To see a summary of ISPs that allow or disallow access from port 445, go to TechNet.
Mount an Azure file share via Finder
Open Finder: Finder is open on macOS by default, but you can ensure that it's the currently selected application by clicking the macOS face icon on the dock:

Select "Connect to Server" from the "Go" Menu: Using the UNC path, convert the beginning double backslash (
\\) tosmb://and all other backslashes (\) to forward slashes (/). Your link should look like the following: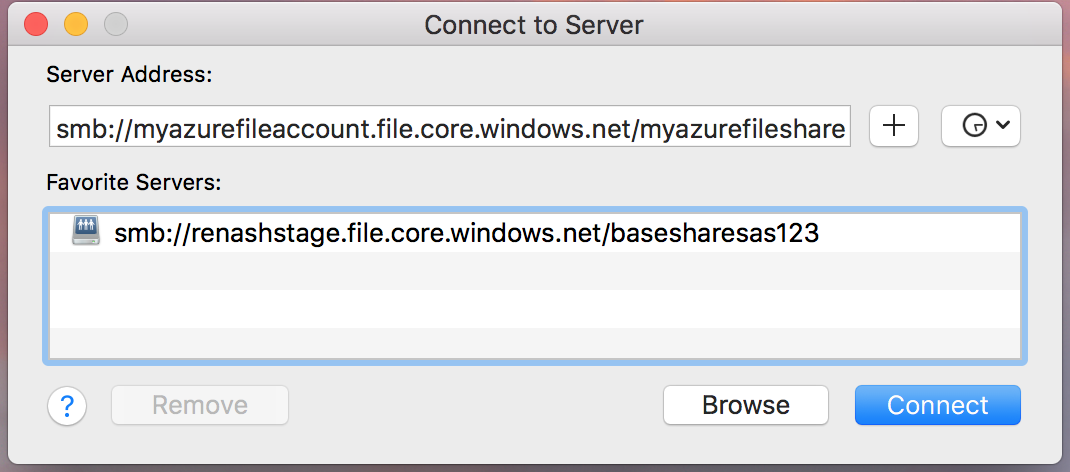
Use the storage account name and storage account key when prompted for a username and password: When you select Connect on the Connect to Server dialog, you'll be prompted for the username and password (this will be autopopulated with your macOS username). You have the option of placing the storage account name/storage account key in your macOS Keychain.
Use the Azure file share as desired: After substituting the share name and storage account key for the username and password, the share will be mounted. You may use this as you would normally use a local folder/file share, including dragging and dropping files into the file share:
Mount an Azure file share via Terminal
Replace
<storage-account-name>,<storage-account-key>, and<share-name>with the appropriate values for your environment.open smb://<storage-account-name>:<storage-account-key>@<storage-account-name>.file.core.windows.net/<share-name>Use the Azure file share as desired: The Azure file share will be mounted at the mount point specified by the previous command.