Overview of Azure Files identity-based authentication for SMB access
This article explains how you can use identity-based authentication, either on-premises or in Azure, to enable identity-based access to Azure file shares over SMB. Just like Windows file servers, you can grant permissions to an identity at the share, directory, or file level. There's no additional service charge to enable identity-based authentication on your storage account.
Identity-based authentication isn't currently supported with Network File System (NFS) shares. However, it's available over SMB for both Windows and Linux clients.
For security reasons, using identity-based authentication to access file shares is recommended over using the storage account key.
Important
Never share your storage account keys. Use identity-based authentication instead.
How it works
Azure file shares use the Kerberos protocol to authenticate with an identity source. When an identity associated with a user or application running on a client attempts to access data in Azure file shares, the request is sent to the identity source to authenticate the identity. If authentication is successful, the identity source returns a Kerberos ticket. The client then sends a request that includes the Kerberos ticket, and Azure Files uses that ticket to authorize the request. The Azure Files service only receives the Kerberos ticket, not the user's access credentials.
Common use cases
Identity-based authentication with SMB Azure file shares can be useful in a variety of scenarios:
Replace on-premises file servers
Replacing scattered on-premises file servers is a challenge every organization faces during their IT modernization journey. Using identity-based authentication with Azure Files provides a seamless migration experience, allowing end users to continue to access their data with the same credentials.
Lift and shift applications to Azure
When you lift and shift applications to the cloud, you'll likely want to keep the same authentication model for file share access. Identity-based authentication eliminates the need to change your directory service, expediting cloud adoption.
Backup and disaster recovery (DR)
If you're keeping your primary file storage on-premises, Azure Files is an ideal solution for backup and DR to improve business continuity. You can use Azure file shares to back up your file servers while preserving Windows discretionary access control lists (DACLs). For DR scenarios, you can configure an authentication option to support proper access control enforcement at failover.
Choose an identity source for your storage account
Before you enable identity-based authentication on your storage account, you need to know what identity source you're going to use. It's likely that you already have one, as most companies and organizations have some type of domain environment configured. Consult your Active Directory (AD) or IT admin to be sure. If you don't already have an identity source, you'll need to configure one before you can enable identity-based authentication.
Supported authentication scenarios
You can enable identity-based authentication over SMB using one of three identity sources: On-premises Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS), Microsoft Entra Domain Services, or Microsoft Entra Kerberos (hybrid identities only). You can only use one identity source for file access authentication per storage account, and it applies to all file shares in the account.
On-premises AD DS: On-premises AD DS clients and virtual machines (VMs) can access Azure file shares with on-premises Active Directory credentials. The on-premises AD DS environment must be synced to Microsoft Entra ID using either the on-premises Microsoft Entra Connect application or Microsoft Entra Connect cloud sync, a lightweight agent that can be installed from the Microsoft Entra Admin Center. To use this authentication method, your client must be domain-joined or have unimpeded network connectivity to your AD DS. See the full list of prerequisites.
Microsoft Entra Kerberos for hybrid identities: You can use Microsoft Entra ID to authenticate hybrid user identities, allowing end users to access Azure file shares without requiring network connectivity to domain controllers. This option requires an existing AD DS deployment, which is then synced to your Microsoft Entra tenant so that Microsoft Entra ID can authenticate your hybrid identities. Cloud-only identities aren't currently supported using this method. See the full list of prerequisites.
Microsoft Entra Domain Services: Cloud-based VMs that are joined to Microsoft Entra Domain Services can access Azure file shares with Microsoft Entra credentials. In this solution, Microsoft Entra ID runs a traditional Windows Server AD domain that is a child of the customer's Microsoft Entra tenant. Microsoft Entra Domain Services is currently the only option for authenticating cloud-only identities. See the full list of prerequisites.
Use the following guidelines to determine which identity source you should choose.
If your organization already has an on-premises AD and isn't ready to move identities to the cloud, and if your clients, VMs, and applications are domain-joined or have unimpeded network connectivity to those domain controllers, choose AD DS.
If some or all of the clients don't have unimpeded network connectivity to your AD DS, or if you're storing FSLogix profiles on Azure file shares for Microsoft Entra joined VMs, choose Microsoft Entra Kerberos.
If you have an existing on-premises AD but are planning to move applications to the cloud and you want your identities to exist both on-premises and in the cloud, choose Microsoft Entra Kerberos.
If you don't have an existing identity source, if you need to authenticate cloud-only identities, or if you already use Microsoft Entra Domain Services, choose Microsoft Entra Domain Services. If you don't already have a domain service deployed in Azure, you'll notice a new charge on your Azure bill for this service.
Enable an identity source
Once you've chosen an identity source, you must enable it on your storage account.
AD DS
For AD DS authentication, you must domain-join your client machines or VMs. You can host your AD domain controllers on Azure VMs or on-premises. Either way, your domain-joined clients must have unimpeded network connectivity to the domain controller, so they must be within the corporate network or virtual network (VNET) of your domain service.
The following diagram depicts on-premises AD DS authentication to Azure file shares over SMB. The on-premises AD DS must be synced to Microsoft Entra ID using Microsoft Entra Connect Sync or Microsoft Entra Connect cloud sync. Only hybrid user identities that exist in both on-premises AD DS and Microsoft Entra ID can be authenticated and authorized for Azure file share access. This is because the share-level permission is configured against the identity represented in Microsoft Entra ID, whereas the directory/file-level permission is enforced with that in AD DS. Make sure that you configure the permissions correctly against the same hybrid user.
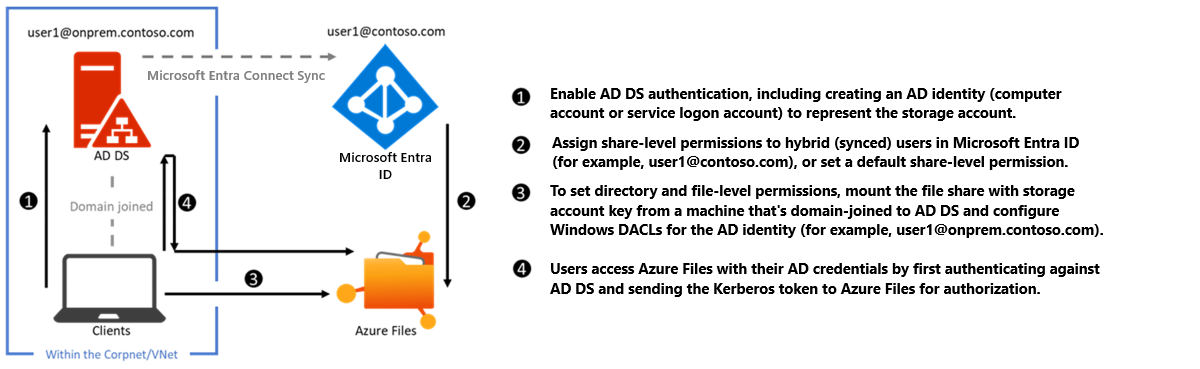
To enable AD DS authentication, first read Overview - on-premises Active Directory Domain Services authentication over SMB for Azure file shares and then see Enable AD DS authentication for Azure file shares.
Microsoft Entra Kerberos for hybrid identities
Enabling and configuring Microsoft Entra ID for authenticating hybrid user identities allows Microsoft Entra users to access Azure file shares using Kerberos authentication. This configuration uses Microsoft Entra ID to issue the Kerberos tickets to access the file share with the industry-standard SMB protocol. This means end users can access Azure file shares without requiring network connectivity to domain controllers from Microsoft Entra hybrid joined and Microsoft Entra joined VMs. However, configuring directory and file-level permissions for users and groups requires unimpeded network connectivity to the on-premises domain controller.
Important
Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication only supports hybrid user identities; it doesn't support cloud-only identities. A traditional AD DS deployment is required, and it must be synced to Microsoft Entra ID using Microsoft Entra Connect Sync or Microsoft Entra Connect cloud sync. Clients must be Microsoft Entra joined or Microsoft Entra hybrid joined. Microsoft Entra Kerberos isn't supported on clients joined to Microsoft Entra Domain Services or joined to AD only.
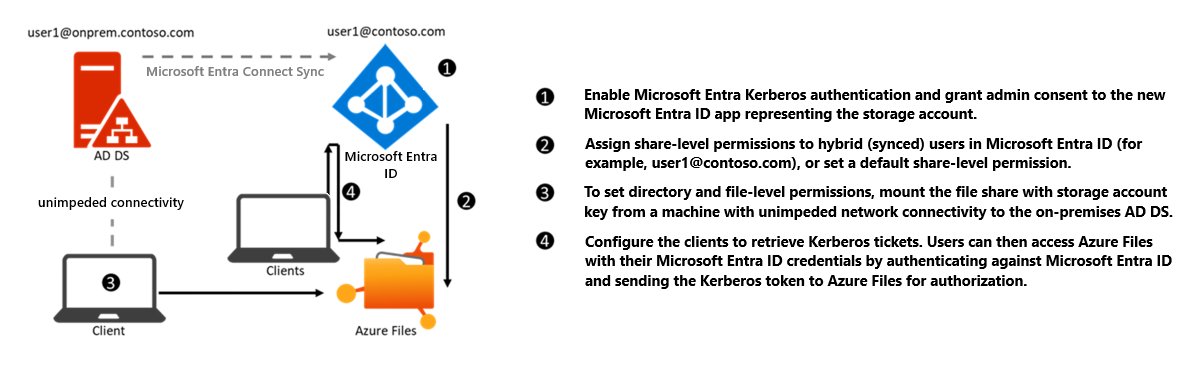
To enable Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication for hybrid identities, see Enable Microsoft Entra Kerberos authentication for hybrid identities on Azure Files.
You can also use this feature to store FSLogix profiles on Azure file shares for Microsoft Entra joined VMs. For more information, see Create a profile container with Azure Files and Microsoft Entra ID.
Microsoft Entra Domain Services
For Microsoft Entra Domain Services authentication, you must enable Microsoft Entra Domain Services and domain-join the VMs you plan to access file data from. Your domain-joined VM must reside in the same VNET as your Microsoft Entra Domain Services hosted domain.
The following diagram represents the workflow for Microsoft Entra Domain Services authentication to Azure file shares over SMB. It follows a similar pattern to on-premises AD DS authentication, but there are two major differences:
You don't need to create an identity in Microsoft Entra Domain Services to represent the storage account. This is performed by the enablement process in the background.
All users that exist in Microsoft Entra ID can be authenticated and authorized. Users can be cloud-only or hybrid. The sync from Microsoft Entra ID to Microsoft Entra Domain Services is managed by the platform without requiring any user configuration. However, the client must be joined to the Microsoft Entra Domain Services hosted domain. It can't be Microsoft Entra joined or registered. Microsoft Entra Domain Services doesn't support non-Azure clients (i.e. user laptops, workstations, VMs in other clouds, etc.) being domain-joined to the Microsoft Entra Domain Services hosted domain. However, it's possible to mount a file share from a non-domain-joined client by providing explicit credentials such as DOMAINNAME\username or using the fully qualified domain name (username@FQDN).

To enable Microsoft Entra Domain Services authentication, see Enable Microsoft Entra Domain Services authentication on Azure Files.
Glossary
It's helpful to understand some key terms relating to identity-based authentication for Azure file shares:
Kerberos authentication
Kerberos is an authentication protocol that's used to verify the identity of a user or host. For more information on Kerberos, see Kerberos Authentication Overview.
Server Message Block (SMB) protocol
SMB is an industry-standard network file-sharing protocol. For more information on SMB, see Microsoft SMB Protocol and CIFS Protocol Overview.
Microsoft Entra ID
Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) is Microsoft's multitenant cloud-based directory and identity management service. Microsoft Entra ID combines core directory services, application access management, and identity protection into a single solution.
Microsoft Entra Domain Services
Microsoft Entra Domain Services provides managed domain services such as domain join, group policies, LDAP, and Kerberos/NTLM authentication. These services are fully compatible with Active Directory Domain Services. For more information, see Microsoft Entra Domain Services.
On-premises Active Directory Domain Services (AD DS)
AD DS is commonly adopted by enterprises in on-premises environments or on cloud-hosted VMs, and AD DS credentials are used for access control. For more information, see Active Directory Domain Services Overview.
Hybrid identities
Hybrid user identities are identities in AD DS that are synced to Microsoft Entra ID using either the on-premises Microsoft Entra Connect Sync application or Microsoft Entra Connect cloud sync, a lightweight agent that can be installed from the Microsoft Entra Admin Center.