Use Microsoft Entra ID for authentication with Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
APPLIES TO:  Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
In this article, you configure Microsoft Entra ID access for authentication with Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server. You'll also learn how to use a Microsoft Entra token with Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server.
You can configure Microsoft Entra authentication for Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server either during server provisioning or later. Only Microsoft Entra administrator users can create or enable users for Microsoft Entra ID-based authentication. We recommend not using the Microsoft Entra administrator for regular database operations because that role has elevated user permissions (for example, CREATEDB).
You can have multiple Microsoft Entra admin users with Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server. Microsoft Entra admin users can be a user, a group, or service principal.
Prerequisites
- You need an Azure account with an active subscription. Create an account for free.
Configure network requirements
Microsoft Entra ID is a multitenant application. It requires outbound connectivity to perform certain operations, like adding Microsoft Entra admin groups. Additionally, you need network rules for Microsoft Entra connectivity to work, depending on your network topology:
- Public access (allowed IP addresses): No extra network rules are required.
- Private access (virtual network integration):
- You need an outbound network security group (NSG) rule to allow virtual network traffic to only reach the
AzureActiveDirectoryservice tag. - If you're using a route table, you need to create a rule with the destination service tag
AzureActiveDirectoryand next hopInternet. - Optionally, if you're using a proxy, you can add a new firewall rule to allow HTTP/S traffic to reach only the
AzureActiveDirectoryservice tag.
- You need an outbound network security group (NSG) rule to allow virtual network traffic to only reach the
- Custom DNS: There are additional considerations if you are using custom DNS in your Virtual Network (VNET). In such cases, it is crucial to ensure that the following endpoints resolve to their corresponding IP addresses: login.microsoftonline.com: This endpoint is used for authentication purposes. Verify that your custom DNS setup enables resolving login.microsoftonline.com to its correct IP addresses graph.microsoft.com: This endpoint is used to access the Microsoft Graph API. Ensure your custom DNS setup allows the resolution of graph.microsoft.com to the correct IP addresses.
To set the Microsoft Entra admin during server provisioning, follow these steps:
- In the Azure portal, during server provisioning, select either PostgreSQL and Microsoft Entra authentication or Microsoft Entra authentication only as the authentication method.
- On the Set admin tab, select a valid Microsoft Entra user, group, service principal, or managed identity in the customer tenant to be the Microsoft Entra administrator.
You can optionally add a local PostgreSQL admin account if you prefer using the PostgreSQL and Microsoft Entra authentication method.
Note
You can add only one Azure admin user during server provisioning. You can add multiple Microsoft Entra admin users after the Server is created.
![Screenshot that shows selections for setting a Microsoft Entra admin during server provisioning.].](media/how-to-configure-sign-in-azure-ad-authentication/set-azure-ad-admin-server-creation.png)
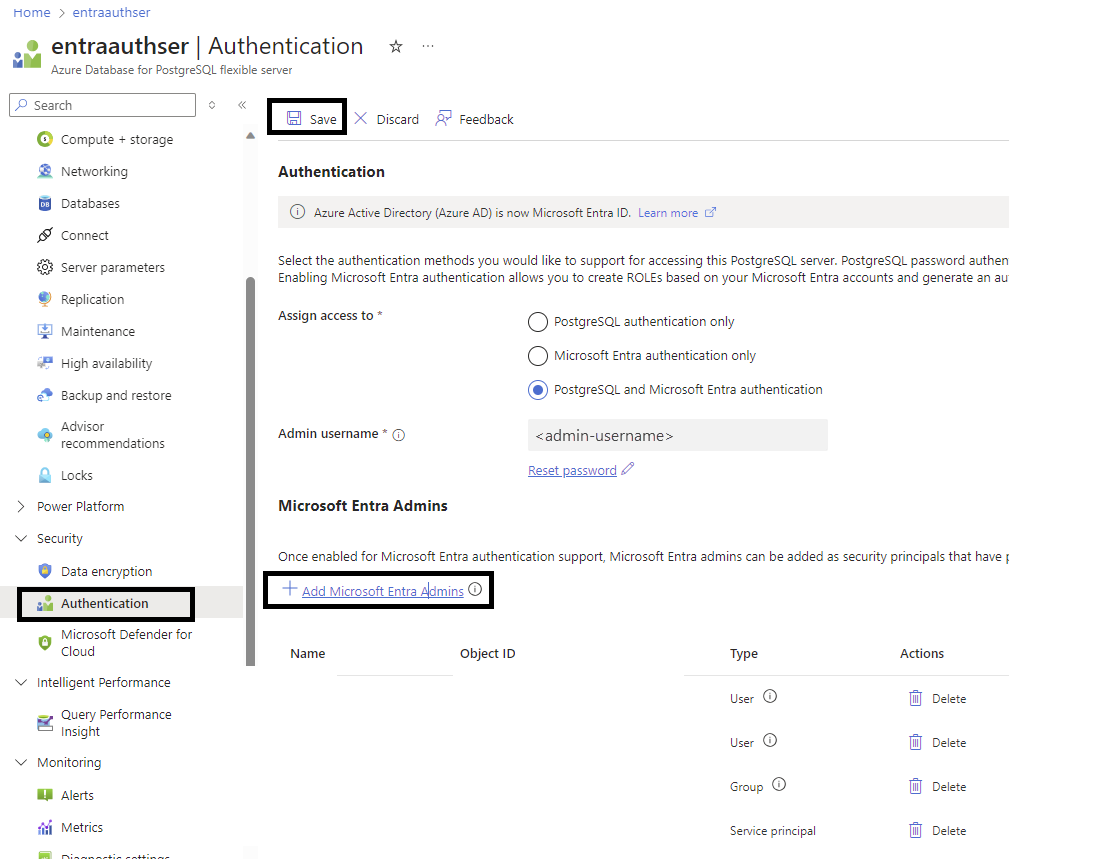
To set the Microsoft Entra administrator after server creation, follow these steps:
- In the Azure portal, select the instance of Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server that you want to enable for Microsoft Entra ID.
- Under Security, select Authentication. Then choose either PostgreSQL and Microsoft Entra authentication or Microsoft Entra authentication only as the authentication method, based on your requirements.
- Select Add Microsoft Entra Admins. Then select a valid Microsoft Entra user, group, service principal, or managed identity in the customer tenant to be a Microsoft Entra administrator.
- Select Save.
Important
When setting the administrator, a new user is added to Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server with full administrator permissions.
Connect to Azure Database for PostgreSQL by using Microsoft Entra ID
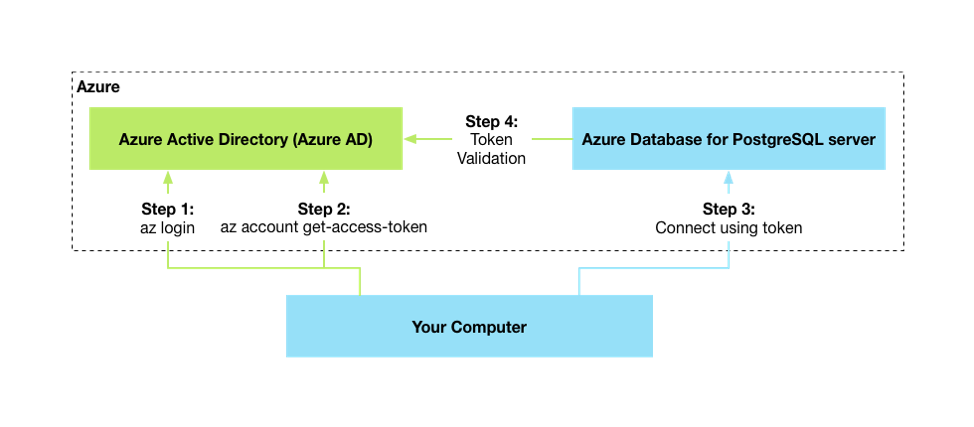
The following high-level diagram summarizes the workflow of using Microsoft Entra authentication with Azure Database for PostgreSQL:
Microsoft Entra integration works with standard PostgreSQL tools like psql, which aren't Microsoft Entra aware and support only specifying the username and password when you're connecting to PostgreSQL. As shown in the preceding diagram, the Microsoft Entra token is passed as the password.
We've tested the following clients:
- psql command line: Use the
PGPASSWORDvariable to pass the token. - Azure Data Studio: Use the PostgreSQL extension.
- Other libpq-based clients: Examples include common application frameworks and object-relational mappers (ORMs).
- PgAdmin: Clear Connect now at server creation.
Authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID
Use the following procedures to authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID as an Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server user. You can follow along in Azure Cloud Shell, on an Azure virtual machine, or on your local machine.
Sign in to the user's Azure subscription
Start by authenticating with Microsoft Entra ID by using the Azure CLI. This step isn't required in Azure Cloud Shell.
az login
The command opens a browser window to the Microsoft Entra authentication page. It requires you to give your Microsoft Entra user ID and password.
Retrieve the Microsoft Entra access token
Use the Azure CLI to acquire an access token for the Microsoft Entra authenticated user to access Azure Database for PostgreSQL. Here's an example of the public cloud:
az account get-access-token --resource https://ossrdbms-aad.database.windows.net
The preceding resource value must be specified as shown. For other clouds, you can look up the resource value by using the following command:
az cloud show
For Azure CLI version 2.0.71 and later, you can specify the command in the following convenient version for all clouds:
az account get-access-token --resource-type oss-rdbms
After authentication is successful, Microsoft Entra ID returns an access token:
{
"accessToken": "TOKEN",
"expiresOn": "...",
"subscription": "...",
"tenant": "...",
"tokenType": "Bearer"
}
The token is a Base64 string. It encodes all the information about the authenticated user and is targeted to the Azure Database for PostgreSQL service.
Use a token as a password for signing in with client psql
When connecting, it's best to use the access token as the PostgreSQL user password.
While using the psql command-line client, the access token needs to be passed through the PGPASSWORD environment variable. The reason is that the access token exceeds the password length that psql can accept directly.
Here's a Windows example:
set PGPASSWORD=<copy/pasted TOKEN value from step 2>
$env:PGPASSWORD='<copy/pasted TOKEN value from step 2>'
Here's a Linux/macOS example:
export PGPASSWORD=<copy/pasted TOKEN value from step 2>
You can also combine step 2 and step 3 together using command substitution. The token retrieval can be encapsulated into a variable and passed directly as a value for PGPASSWORD environment variable:
export PGPASSWORD=$(az account get-access-token --resource-type oss-rdbms --query "[accessToken]" -o tsv)
Now you can initiate a connection with Azure Database for PostgreSQL as you usually would:
psql "host=mydb.postgres... user=user@tenant.onmicrosoft.com dbname=postgres sslmode=require"
Use a token as a password for signing in with PgAdmin
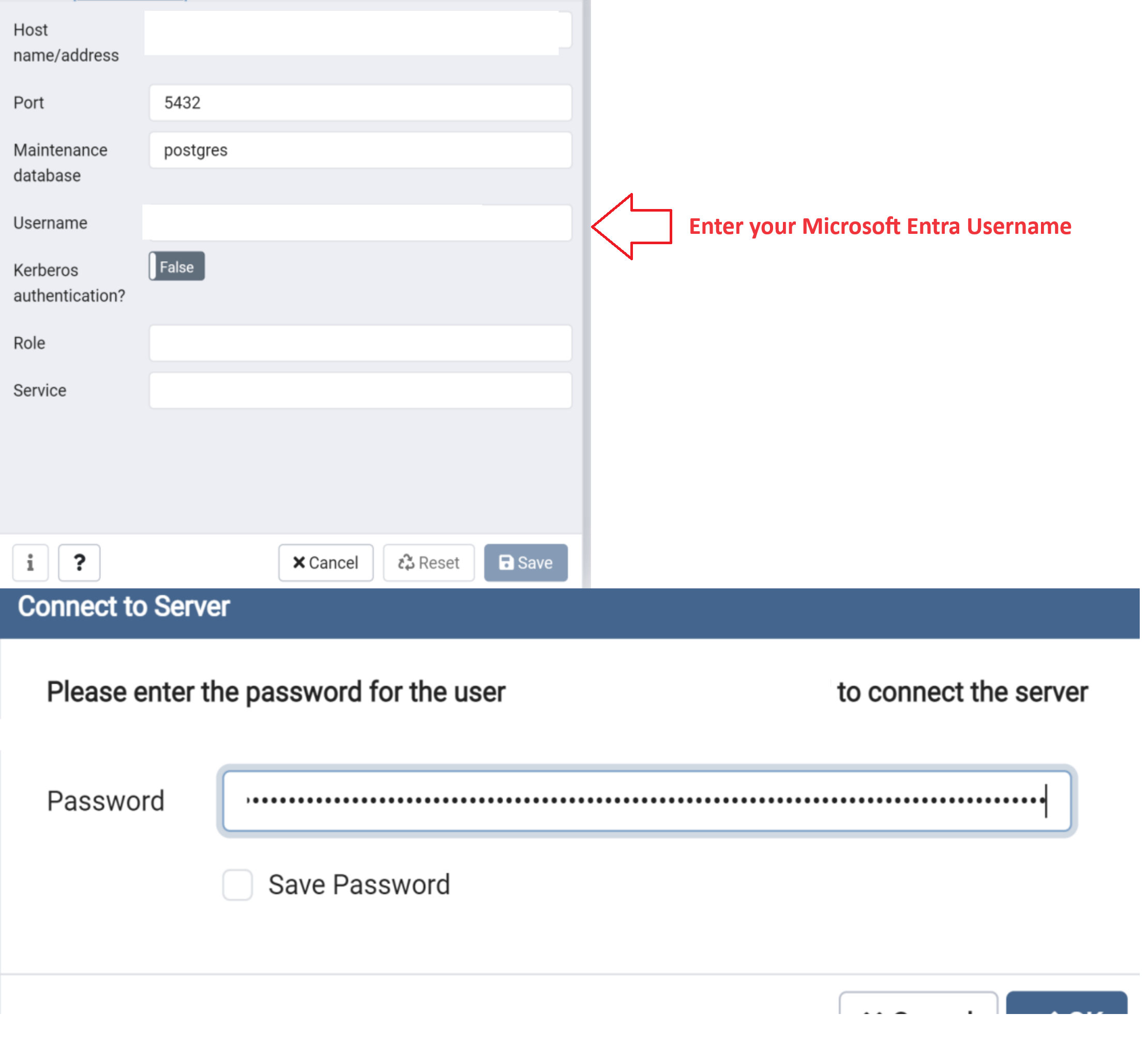
To connect by using a Microsoft Entra token with PgAdmin, follow these steps:
- Open Pgadmin and select Register from left hand menu and select Server
- In General Tab provide a connection name and clear the Connect now option.
- Select the Connection tab and provide your Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance details for Hostname/address and username and save. username is your Microsoft Entra ID or email
- From the browser menu, select your Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server connection and select Connect Server
- Enter your Active Directory token password when prompted.
Here are some essential considerations when you're connecting:
user@tenant.onmicrosoft.comis the userPrincipalName of the Microsoft Entra user.Be sure to use the exact way the Azure user is spelled. Microsoft Entra user and group names are case-sensitive.
If the name contains spaces, use a backslash (
\) before each space to escape it. You can use the Azure CLI to get the signed in user and set the value forPGUGSERenvironment variable:export PGUSER=$(az ad signed-in-user show --query "[userPrincipalName]" -o tsv | sed 's/ /\\ /g')The access token's validity is 5 minutes to 60 minutes. You should get the access token before initiating the sign-in to Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
You're now authenticated to your Azure Database for PostgreSQL server through Microsoft Entra authentication.
Authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID as a group member
Create Microsoft Entra groups in Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server
To enable a Microsoft Entra group to access your database, use the same mechanism you used for users, but specify the group name instead. For example:
select * from pgaadauth_create_principal('Prod DB Readonly', false, false).
When group members sign in, they use their access tokens but specify the group name as the username.
Note
Azure Database for PostgreSQL Flexible Server supports managed identities and service principals as group members.
Sign in to the user's Azure subscription
Authenticate with Microsoft Entra ID by using the Azure CLI. This step isn't required in Azure Cloud Shell. The user needs to be a member of the Microsoft Entra group.
az login
Retrieve the Microsoft Entra access token
Use the Azure CLI to acquire an access token for the Microsoft Entra authenticated user to access Azure Database for PostgreSQL. Here's an example of the public cloud:
az account get-access-token --resource https://ossrdbms-aad.database.windows.net
You must specify the initial resource value exactly as shown. For other clouds, you can look up the resource value by using the following command:
az cloud show
For Azure CLI version 2.0.71 and later, you can specify the command in the following convenient version for all clouds:
az account get-access-token --resource-type oss-rdbms
After authentication is successful, Microsoft Entra ID returns an access token:
{
"accessToken": "TOKEN",
"expiresOn": "...",
"subscription": "...",
"tenant": "...",
"tokenType": "Bearer"
}
Use a token as a password for signing in with psql or PgAdmin
These considerations are essential when you're connecting as a group member:
- The group name is the name of the Microsoft Entra group that you're trying to connect.
- Be sure to use the exact way the Microsoft Entra group name is spelled. Microsoft Entra user and group names are case-sensitive.
- When you're connecting as a group, use only the group name and not the alias of a group member.
- If the name contains spaces, use a backslash (
\) before each space to escape it. - The access token's validity is 5 minutes to 60 minutes. We recommend you get the access token before initiating the sign-in to Azure Database for PostgreSQL.
You're now authenticated to your PostgreSQL server through Microsoft Entra authentication.