Firewall rules in Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server
APPLIES TO:  Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
Azure Database for PostgreSQL - Flexible Server
When you're running Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server, you have two main networking options. The options are private access (virtual network integration) and public access (allowed IP addresses).
With public access, the Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance is accessed through a public endpoint. By default, the firewall blocks all access to the server. To specify which IP hosts can access the server, you create server-level firewall rules. Firewall rules specify allowed public IP address ranges. The firewall grants access to the server based on the originating IP address of each request. With private access no public endpoint is available and only hosts located on the same network can access Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server.
You can create firewall rules by using the Azure portal or by using Azure CLI commands. You must be the subscription owner or a subscription contributor.
Server-level firewall rules apply to all databases on the same Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance. The rules don't affect access to the Azure portal website.
The following diagram shows how connection attempts from the internet and Azure must pass through the firewall before they can reach Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server databases:
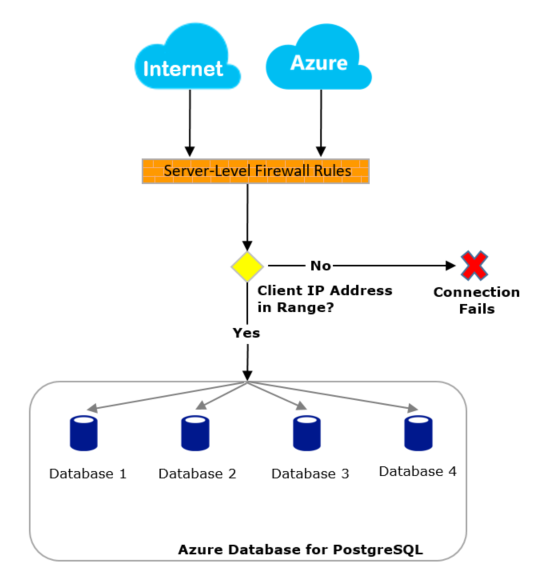
Connect from the internet
If the source IP address of the request is within one of the ranges specified in the server-level firewall rules, the connection is granted. Otherwise, it's rejected.
For example, if your application connects with a Java Database Connectivity (JDBC) driver for Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server, you might encounter this error because the firewall is blocking the connection:
java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException: java.lang.RuntimeException: org.postgresql.util.PSQLException: FATAL: no pg_hba.conf entry for host "123.45.67.890", user "adminuser", database "postgresql", SSL
Note
To access Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server from your local computer, ensure that the firewall on your network and local computer allow outgoing communication on TCP port 5432.
Connect from Azure
We recommend that you find the outgoing IP address of any application or service and explicitly allow access to those individual IP addresses or ranges. For example, you can find the outgoing IP address of an Azure App Service app, or use a public IP address that's tied to a virtual machine.
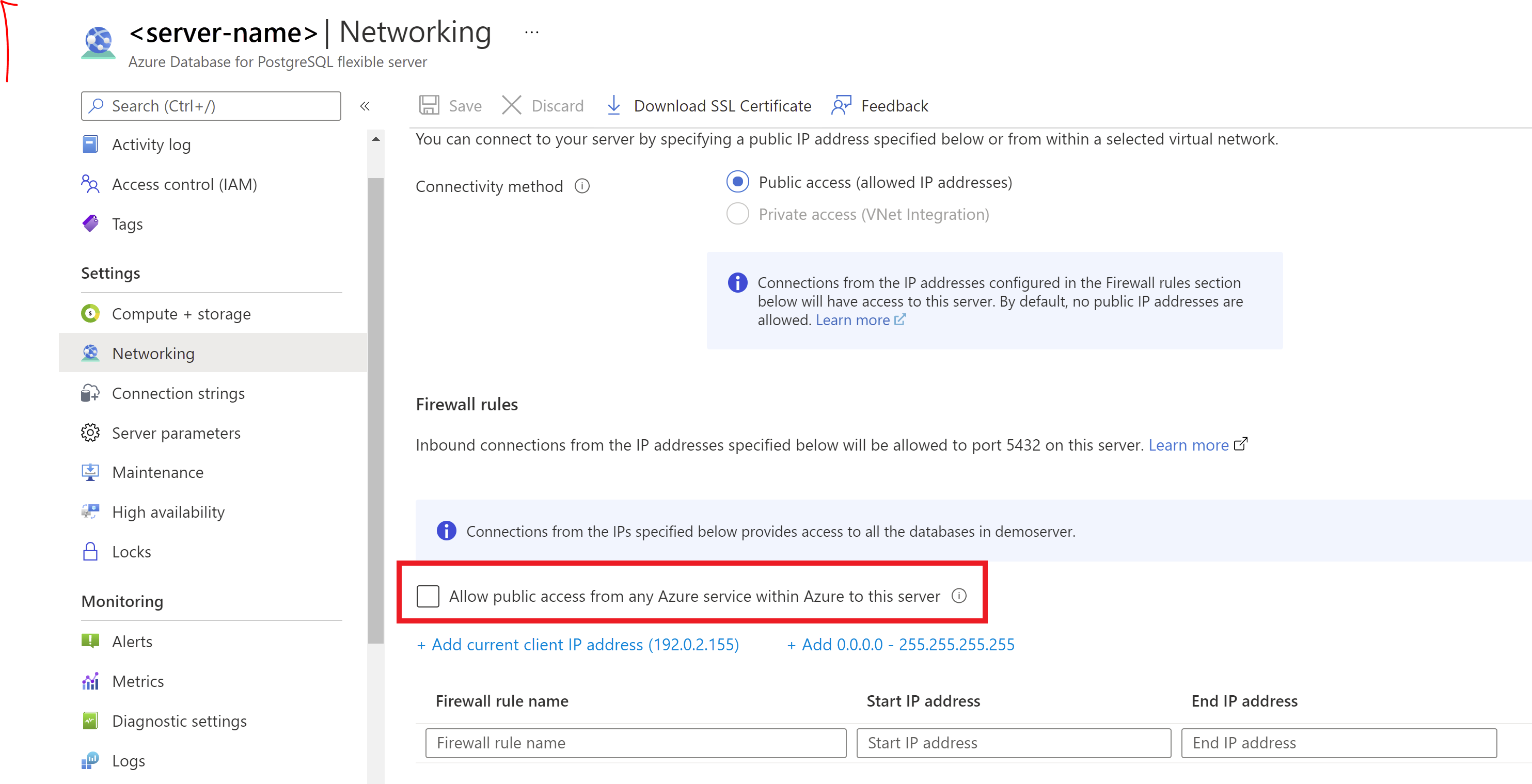
If a fixed outgoing IP address isn't available for your Azure service, consider enabling connections from all IP addresses for Azure datacenters:
- In the Azure portal, on the Networking pane, select the Allow public access from any Azure service within Azure to this server checkbox.
- Select Save.
Important
The Allow public access from any Azure service within Azure to this server option configures the firewall to allow all connections from Azure, including connections from the subscriptions of other customers. When you're using this option, make sure your sign-in and user permissions limit access to only authorized users.
Programmatically manage firewall rules
In addition to using the Azure portal, you can manage firewall rules programmatically by using the Azure CLI.
From the Azure CLI, a firewall rule setting with a starting and ending address equal to 0.0.0.0 does the equivalent of the Allow public access from any Azure service within Azure to this server option in the portal. If firewall rules reject the connection attempt, the app won't reach the Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance.
Troubleshoot firewall problems
Consider the following possibilities when access to an Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance doesn't behave as you expect:
Changes to the allowlist haven't taken effect yet: Changes to the firewall configuration of an Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance might take up to five minutes.
The sign-in isn't authorized, or an incorrect password was used: If a sign-in doesn't have permissions on the Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance or the password is incorrect, the connection to the server is denied. Creating a firewall setting only provides clients with an opportunity to try connecting to your server. Each client must still provide the necessary security credentials.
For example, the following error might appear if authentication fails for a JDBC client:
java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException: java.lang.RuntimeException: org.postgresql.util.PSQLException: FATAL: password authentication failed for user "yourusername"
The firewall isn't allowing dynamic IP addresses: If you have an internet connection with dynamic IP addressing and you're having trouble getting through the firewall, try one of the following solutions:
Ask your internet service provider (ISP) for the IP address range assigned to your client computers that access the Azure Database for PostgreSQL flexible server instance. Then add the IP address range as a firewall rule.
Get static IP addresses instead for your client computers, and then add the static IP addresses as a firewall rule.
Firewall rules aren't available for IPv6 format: The firewall rules must be in IPv4 format. If you specify firewall rules in IPv6 format, you'll get a validation error.