Get started with Azure Maps Power BI visual
This article shows how to use the Microsoft Azure Maps Power BI visual.
APPLIES TO:  Power BI service for consumers
Power BI service for consumers  Power BI service for designers & developers
Power BI service for designers & developers  Power BI Desktop
Power BI Desktop  Requires Pro or Premium license
Requires Pro or Premium license
Note
This visual can be created and viewed in both Power BI Desktop and the Power BI service. The steps and illustrations in this article are from Power BI Desktop.
The Azure Maps Power BI visual provides a rich set of data visualizations for spatial data on top of a map. It's estimated that over 80% of business data has a location context. The Azure Maps Power BI visual can be used to gain insights into how this location context relates to and influences your business data.
Note
Power BI ensures that no Personal Identifiable Information (PII) is sent to Azure Maps. Additionally, IP addresses are truncated in the Power BI diagnostic logs.
What is sent to Azure?
The Azure Maps Power BI visual connects to cloud service hosted in Azure to retrieve location data such as map images and coordinates that are used to create the map visualization.
- Details about the area the map is focused on are sent to Azure to retrieve images needed to render the map canvas (also known as map tiles).
- Data in the Location, Latitude, and Longitude buckets may be sent to Azure to retrieve map coordinates (a process called geocoding).
- Telemetry data may be collected on the health of the visual (for example, crash reports), if the telemetry option in Power BI is enabled.
Other than the scenarios previously described, no other data overlaid on the map is sent to the Azure Maps servers. All rendering of data happens locally within the client.
Tip
If using the Azure Maps Geographic API endpoints, your firewall may need to be updated to allow access to the Azure Maps platform using either or all of the following URLs:
https://atlas.microsoft.comhttps://us.atlas.microsoft.comhttps://eu.atlas.microsoft.com
Important
The selection tool within the Azure Maps Power BI visual relies on TomTom data, consequently user data may not always remain within the user’s geographical boundary.
For more information about privacy and terms of use related to the Azure Maps Power BI visual, see Microsoft Azure Legal Information.
Use the Azure Maps Power BI visual
Once the Azure Maps Power BI visual is enabled, select the Azure Maps icon from the Visualizations pane.
Power BI creates an empty Azure Maps visual design canvas.
Take the following steps to load the Azure Maps visual:
Performing one of the two following actions in the Fields pane provides the minimal data needed to load the Azure Maps visual:
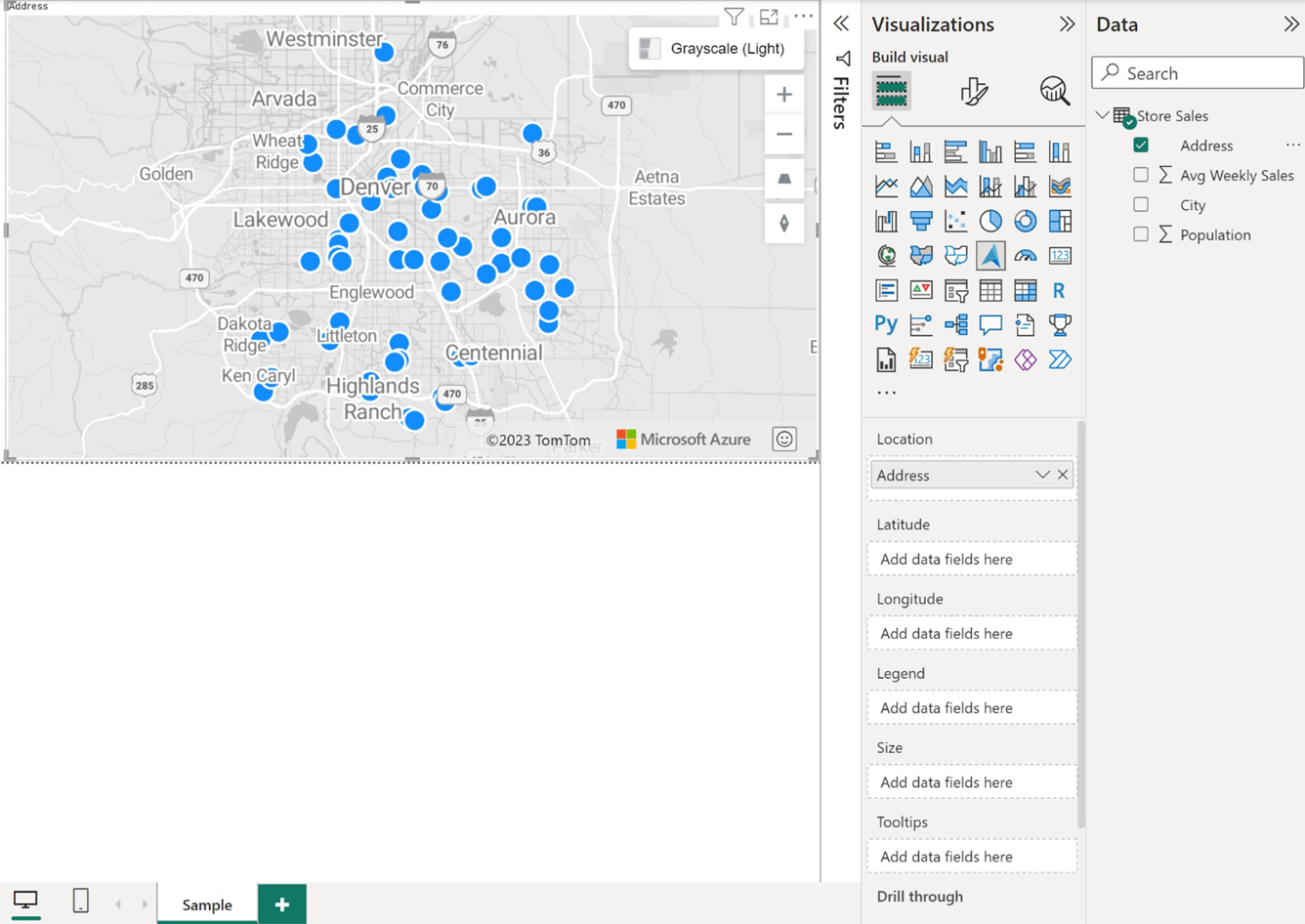
- Drag data fields containing latitude and longitude coordinate information into the Latitude and/or Longitude buckets.
- Drag data fields containing geospatial data to the Location bucket.
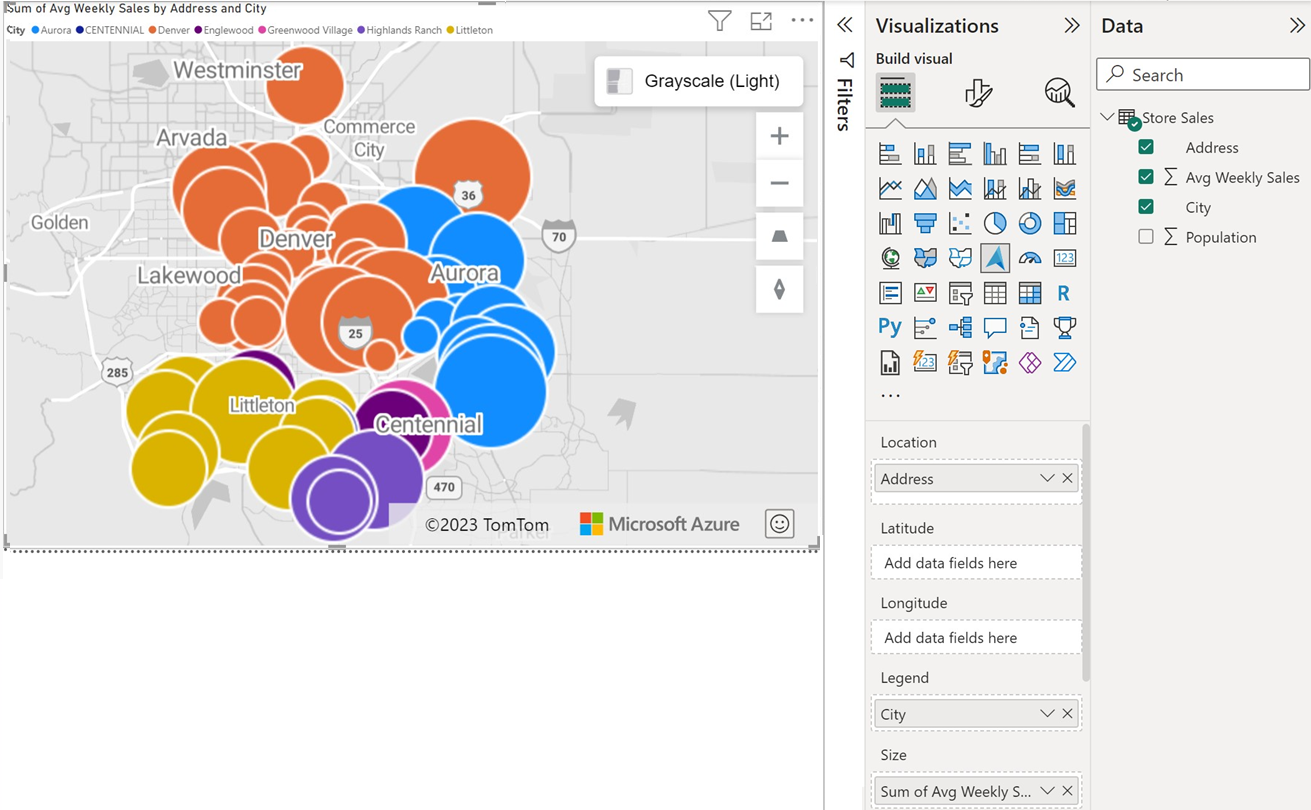
To color the data based on categorization, drag a categorical field into the Legend bucket of the Fields pane. In this example, we're using the BussinessName column.
To scale the data relatively, drag a measure into the Size bucket of the Fields pane. In this example, we're using Avg Weekly Sales column.
Note
Unlike the other screenshots in this section, this screenshot demonstrates Geocoding in Azure Maps Power BI Visual, using coordinate fields (lat/lon) instead of providing a physical address.
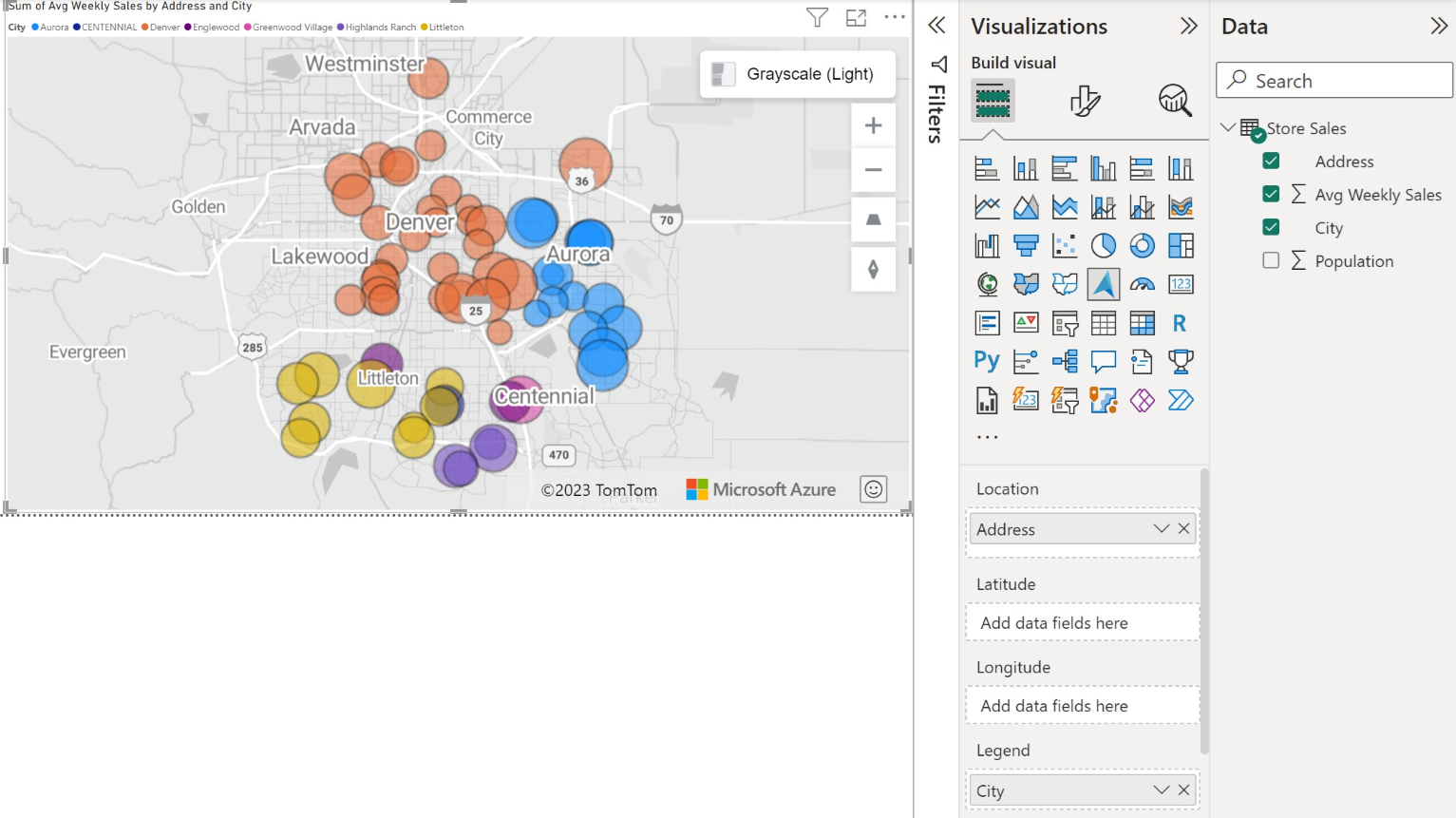
Use the options in the Format pane to customize how data is rendered. The following image is the same map as shown previously, but with the bubble layers fill transparency option set to 25%, smaller radius, and a black border.
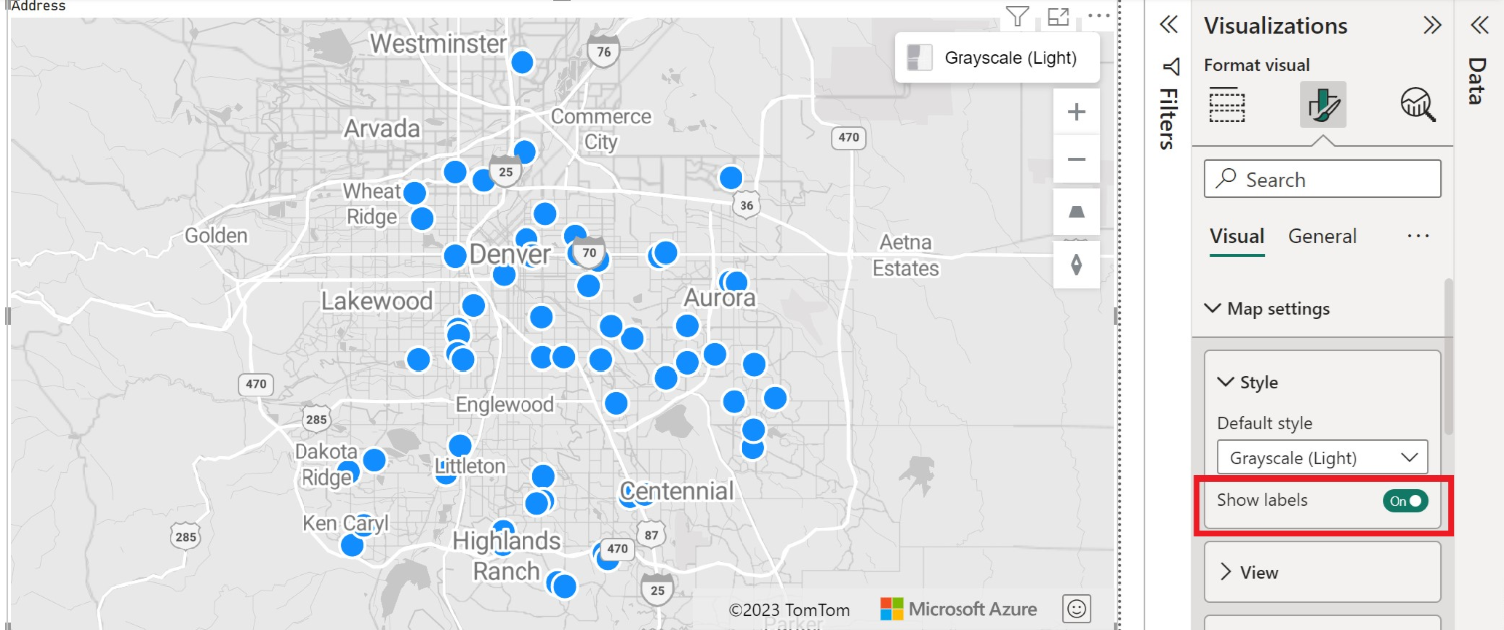
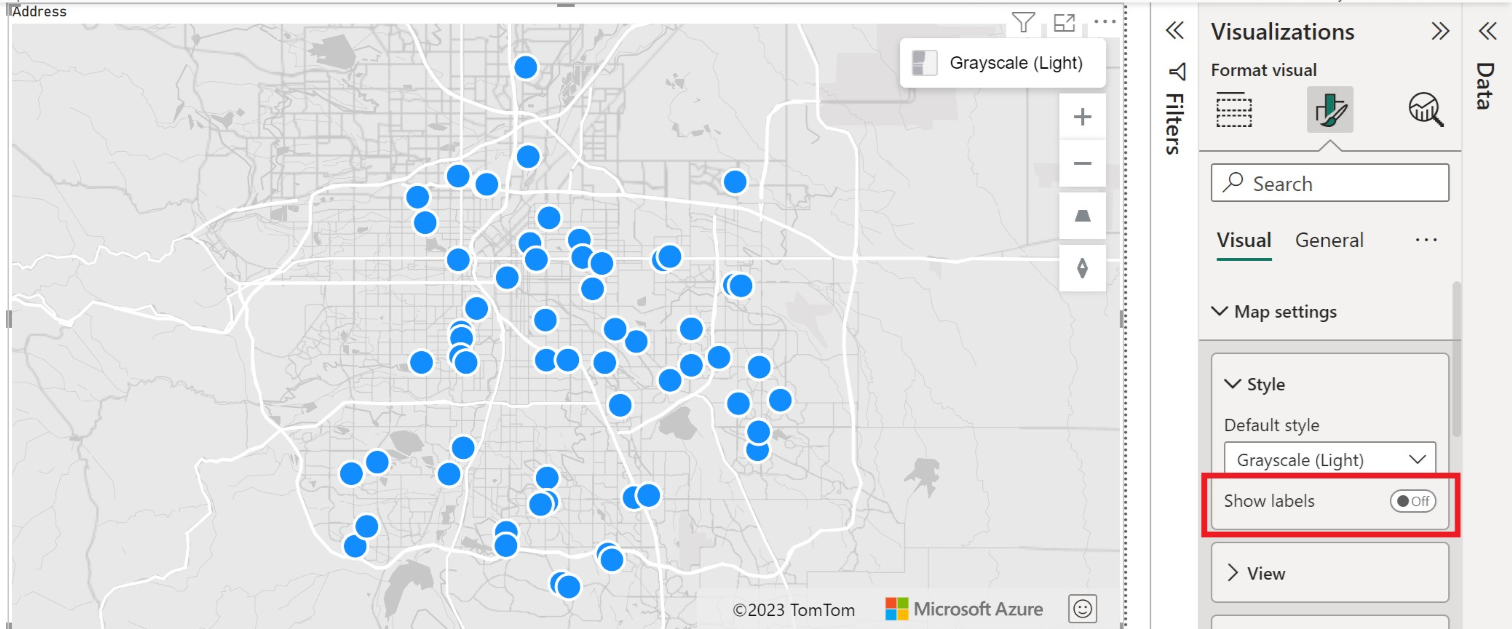
You can also show or hide labels in the Format pane. The following two images show maps with the Show labels setting turned on and off:
Fields pane buckets
The following data buckets are available in the Fields pane of the Azure Maps visual.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Location | Used to enter easily understandable geographical data such as country/region, state, and city. |
| Latitude | The field used to specify the latitude value of the data points. Latitude values should be between -90 and 90 in decimal degrees format. |
| Longitude | The field used to specify the longitude value of the data points. Longitude values should be between -180 and 180 in decimal degrees format. |
| Legend | The field used to categorize the data and assign a unique color for data points in each category. When this bucket is filled, a Data colors section appears in the Format pane that allows adjustments to the colors. |
| Size | The measure used for relative sizing of data points on the map. |
| Tooltips | Other data fields to display in tooltips when shapes are hovered. |
Map settings
The Map settings section of the Format pane provide options for customizing how the map is displayed and reacts to updates.
The Map settings section is divided into three subsections: style, view and controls.
Style
The following settings are available in the Style section:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Style | The style of the map. The dropdown list contains blank and blank accessible, grayscale dark, grayscale light, high contrast dark, high contrast light, night, road, road shaded relief, satellite and satellite road labels. |
| Show labels | A toggle switch that enables you to either show or hide map labels. For more information, see list item number five in the previous section. |
View
The following settings available in the View section enable the user to specify the default map view information when the Auto zoom setting is set to Off.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Auto zoom | Automatically zooms the map into the data loaded through the Fields pane of the visual. As the data changes, the map updates its position accordingly. When Auto zoom is set to Off, the remaining settings in this section become active that enable to user to define the default map view. |
| Zoom | The default zoom level of the map. Can be a number between 0 and 22. |
| Center latitude | The default latitude of the center of the map. |
| Center longitude | The default longitude of the center of the map. |
| Heading | The default orientation of the map in degrees, where 0 is north, 90 is east, 180 is south, and 270 is west. Can be any number between 0 and 360. |
| Pitch | The default tilt of the map in degrees between 0 and 60, where 0 is looking straight down at the map. |
Controls
The following settings are available in the Controls section:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| World wrap | Allows the user to pan the map horizontally infinitely. |
| Style picker | Adds a button to the map that allows the report readers to change the style of the map. |
| Navigation | Adds buttons to the map as another method to allow the report readers to zoom, rotate, and change the pitch of the map. See this document on Navigating the map for details on all the different ways users can navigate the map. |
| Selection | Adds a button that allows the user to choose between different modes to select data on the map; circle, rectangle, polygon (lasso), or travel time or distance. To complete drawing a polygon; select the first point, or double-click on the last point on the map, or press the c key. |
| Geocoding culture | The default, Auto, refers to the Western Address System. The only other option, JA, refers to the Japanese address system. In the western address system, you begin with the address details and then proceed to the larger categories such as city, state and postal code. In the Japanese address system, the larger categories are listed first and finish with the address details. |
Considerations and Limitations
The Azure Maps Power BI visual is available in the following services and applications:
| Service/App | Availability |
|---|---|
| Power BI Desktop | Yes |
| Power BI service (app.powerbi.com) | Yes |
| Power BI mobile applications | Yes |
| Power BI publish to web | Yes |
| Power BI Embedded | Yes |
| Power BI service embedding (PowerBI.com) | Yes |
| Power BI export | No |
| Power BI subscriptions | No |
Where is Azure Maps available?
At this time, Azure Maps is currently available in all countries and regions except:
- China
- South Korea
- Azure Government (GCC + GCC High)
For coverage details for the different Azure Maps services that power this visual, see Geographic coverage information.
Which web browsers are supported by the Azure Maps Power BI visual?
For a list of supported browsers, see Azure Maps Web SDK supported browsers.
How many data points can I visualize?
This visual supports up to 30,000 data points.
Can addresses or other location strings be used in this visual?
Yes, addresses and other location strings can be used in the Azure Maps Power BI visual. For more information on addresses and other location strings, see The location field in the Geocoding in Azure Maps Power BI Visual article.
Next steps
Learn more about the Azure Maps Power BI visual:
Customize the visual: