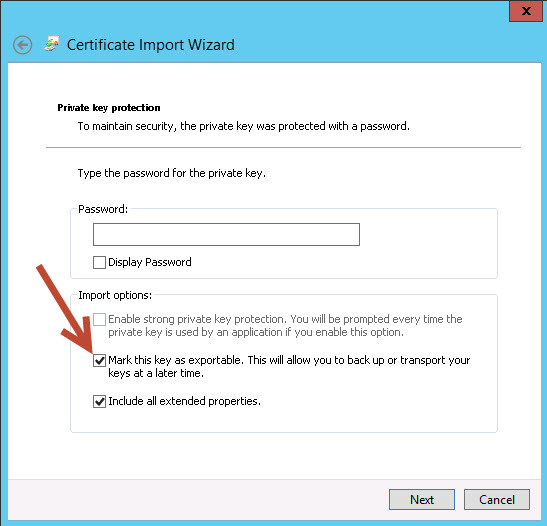
To make the private key exportable in Azure Cloud Services or any Windows-based platform, you need to configure the certificate correctly during its import. Certificates with non-exportable private keys are typically imported with that restriction due to security considerations. However, you can address this in a few ways:
1. Use an Exportable Key When Importing the Certificate
When importing a certificate into Azure or your local machine, you can specify that the private key should be exportable:
- Use the
certutilcommand-line tool:
Add thecertutil -importpfx MyCertificate.pfx AT_KEYEXCHANGE-privatekey:exportableflag to ensure the private key is exportable:certutil -importpfx MyCertificate.pfx AT_KEYEXCHANGE -privatekey:exportable - Programmatically via PowerShell:
$password = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "YourPassword" -Force -AsPlainText Import-PfxCertificate -FilePath "C:\Path\To\Certificate.pfx" -CertStoreLocation Cert:\LocalMachine\My -Password $password -Exportable
2. Export and Re-Import the Certificate with an Exportable Key
If you have the original certificate .pfx file:
- Export it from its original location as an exportable
.pfx. - Re-import it with the
Exportableflag enabled.
3. Check Key Permissions
If the private key isn't explicitly set to be non-exportable, the error might also arise from insufficient permissions. Grant the appropriate user account permissions to access the private key:
- Open
certlm.msc(Local Computer Certificates Store). - Find your certificate under
Personal > Certificates. - Right-click the certificate and choose
All Tasks > Manage Private Keys. - Add the user account running your application with appropriate permissions (Read and Full Control).
4. Generate the Certificate Programmatically with Exportable Key
If you are generating the certificate programmatically in Azure or locally, ensure you create it with the private key exportable:
- Using PowerShell:
New-SelfSignedCertificate -DnsName "YourDomain" -CertStoreLocation "Cert:\LocalMachine\My" -KeyExportPolicy Exportable
5. Use Key Vault for Certificate Management
Azure Key Vault provides secure storage for certificates and allows you to access the private key when needed:
- Import the certificate into Azure Key Vault, ensuring the private key is included.
- Access the private key using the Azure Key Vault SDK or API.
Example in C#:
var keyClient = new KeyClient(new Uri(keyVaultUrl), new DefaultAzureCredential());
var key = await keyClient.GetKeyAsync(certificateName);
var rsa = key.ToRSA();