Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Important
This feature is in preview.
Copilot for Data Science and Data Engineering is an AI assistant that helps analyze and visualize data. It works with Lakehouse tables and files, Power BI Datasets, and pandas/spark/fabric dataframes to provide answers and code snippets directly in a notebook. Connections to OneLake and default attached Lakehouses allow Copilot to provide contextualized code suggestions and natural language responses tailored to your data.
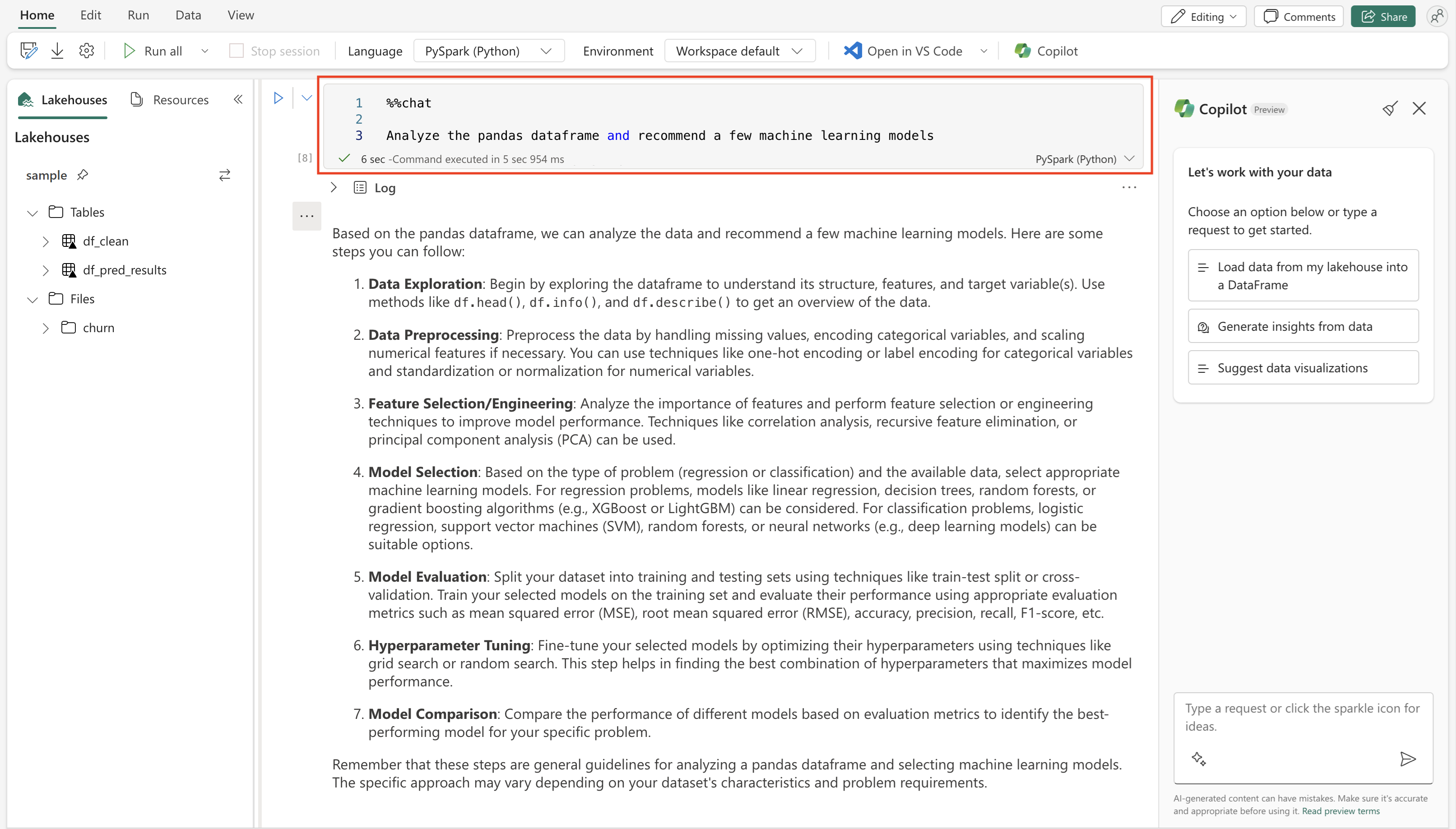
Copilot can help you understand your data better, and it can offer suggestions to begin your notebook, including generated code for the initial cells. After it identifies and adds data sources through the Fabric object explorer, Copilot Chat offers suggestions on model types to implement. You can copy these recommendations directly into your notebook to start development. If you're unsure of your next steps, you can invoke Copilot in-cell for model direction insights.
When you encounter errors, Copilot provides suggested fixes. For further help, you can chat with Copilot for more options, to avoid constant online searches.
You also benefit from automatic documentation, with a simple "Add Comments" feature that summarizes code and data changes. This makes cells clear for you and others. Throughout your workflow, you can consult Copilot at specific points, receiving real-time support and guidance to accelerate your development process.
Note
With Spark 3.4 and later versions in Microsoft Fabric, no installation cell is required to use Copilot in your notebook. Previous versions that required an installation cell (Spark 3.3 and earlier) are no longer supported.
Note
- Your administrator needs to enable the tenant switch before you start using Copilot. See the article Copilot tenant settings for details.
- Your F64 or P1 capacity needs to be in one of the regions listed in this article, Fabric region availability.
- If your tenant or capacity is outside the US or France, Copilot is disabled by default unless your Fabric tenant admin enables the Data sent to Azure OpenAI can be processed outside your tenant's geographic region, compliance boundary, or national cloud instance tenant setting in the Fabric Admin portal.
- Copilot in Microsoft Fabric isn't supported on trial SKUs. Only paid SKUs (F64 or higher, or P1 or higher) are supported.
- Copilot in Fabric is currently rolling out in public preview and is expected to be available for all customers by end of March 2024.
- See the article Overview of Copilot in Fabric and Power BI for more information.
Introduction to Copilot for Data Science and Data Engineering for Fabric Data Science
With Copilot for Data Science and Data Engineering, you can chat with an AI assistant that can help you handle your data analysis and visualization tasks. You can ask the Copilot questions about lakehouse tables, Power BI Datasets, or Pandas/Spark dataframes inside notebooks. Copilot answers in natural language or code snippets. Copilot can also generate data-specific code for you, depending on the task. For example, Copilot for Data Science and Data Engineering can generate code for:
- Chart creation
- Filtering data
- Applying transformations
- Machine learning models
First, select the Copilot icon in the notebooks ribbon. The Copilot chat panel opens, and a new cell appears at the top of your notebook. You might also select copilot at the top of your Fabric Notebooks cell as well.
To maximize Copilot effectiveness, load a table or dataset as a dataframe in your notebook. The AI can then access the data and understand its structure and content. Next, start chatting with the AI. Select the chat icon in the notebook toolbar, and type your question or request in the chat panel. For example, you can ask:
- "What is the average age of customers in this dataset?"
- "Show me a bar chart of sales by region"
- etc.
Copilot responds with the answer or the code, which you can copy and paste it your notebook. Copilot for Data Science and Data Engineering is a convenient, interactive way to explore and analyze your data.
Using the Copilot Chat panel to interact with your data
To chat with your data and get insights, select the chat icon in the notebook toolbar to open the Copilot chat panel. Type your questions or requests in the chat panel. For example, you can ask:
- "What is the average age of customers in this dataset?"
- "Show me a bar chart of sales by region"
- etc.
Copilot responds with the answer or the code, which you can copy and paste into your notebook. Additionally, Copilot can suggest what to do next with your data. Copilot provides suggestions and generates relevant code snippets to help you proceed with your data analysis and visualization tasks.
To interact with the Copilot chat panel in Microsoft Fabric notebooks, follow these steps:
Open the Copilot Chat Panel: To open the Copilot chat panel, select the chat icon in the notebook toolbar.
Ask Questions or Make Requests: Type your questions or requests in the chat panel. Here are some specific examples for data science and data engineering:
Data Exploration:
- "What is the distribution of the 'age' column in this dataset?"
- "Show me a histogram of the 'income' column."
Data Cleaning:
- "How can I handle missing values in this dataset?"
- "Generate code to remove duplicates from this dataframe."
Data Transformation:
- "How do I normalize the 'sales' column?"
- "Create a new column 'profit' by subtracting 'cost' from 'revenue'."
Visualization:
- "Plot a scatter plot of 'height' vs 'weight'."
- "Generate a box plot for the 'salary' column."
Machine Learning:
- "Train a decision tree classifier on this dataset."
- "Generate code for a k-means clustering algorithm with 3 clusters."
Model Evaluation:
- "How do I evaluate the accuracy of a logistic regression model?"
- "Generate a confusion matrix for the predictions."
Receive Responses: Copilot responds with natural language explanations or code snippets. You can copy and paste the code into your notebook to execute it.
Get Suggestions: If you don't know how to proceed, ask Copilot for suggestions:
- "What should I do next with this dataset?"
- "What are some recommended feature engineering techniques for this data?"
- Use Generated Code: Copy the generated code snippets from the chat panel, and paste them into your notebook cells to run them.
With these steps and the provided examples, you can effectively interact with the Copilot chat panel to enhance your data science and data engineering workflows in Microsoft Fabric notebooks.
Using the Copilot In-Cell Panel and Quick Actions
You can interact with Copilot directly within your notebook cells to generate code and perform quick actions on your code cells. Here's how to use the Copilot in-cell panel:
- Generate Code: To generate code for specific tasks, you can use the Copilot in-cell panel. For example, you can type your request in the text panel above the code cell:
Can you generate code for a logistic regression that fits this data?
Copilot provides the necessary code snippet directly in the cell below.
Fix Code: You can ask Copilot to fix errors in your code. Type your request in the text panel above the code cell, and Copilot suggests corrections.
Add Comments: To automatically document your code, use the "Add Comments" feature. Copilot generates comments that summarize the code and data changes, to make your notebook more readable.
Optimize Code: For performance improvements, you can ask Copilot to optimize your code. Copilot provides suggestions to enhance the efficiency of your code.
Explain Code: If you need clarification about a piece of code, ask Copilot for an explanation. Copilot provides a detailed explanation of the code's functionality.
Steps to Use Quick Actions
Invoke Copilot In-Cell: Select the Copilot icon in the notebook toolbar to start interacting with Copilot.
Type Your Request: Enter your request or question in the text panel above the code cell. For example:
Explain the following code snippet.
Receive Suggestions: Copilot responds with the relevant code, fixes, comments, optimizations, or explanations.
Apply Suggestions: Copy the generated code or suggestions from Copilot and paste them into your notebook cells to execute them.
With the Copilot in-cell panel, you can generate code, fix errors, add comments, optimize performance, and understand your code better, all within your Microsoft Fabric notebooks.
Copilot for Data Science and Data Engineering also has schema and metadata awareness of lakehouse tables. Copilot can provide relevant information in context of your data hosted in an attached lakehouse. For example, you can ask:
- "How many tables are in the lakehouse?"
- "What are the columns of the table customers?"
Copilot responds with the relevant information if you added the lakehouse to the notebook. Copilot also has awareness of the names of files added to any lakehouse attached to the notebook. You can refer to those files by name in your chat. For example, if you have a file named sales.csv in your lakehouse, you can ask Copilot to "Create a dataframe from sales.csv". Copilot generates the code and displays it in the chat panel. With Copilot for notebooks, you can easily access and query your data from different sources. You don't need the exact command syntax to do it.
Tips
- "Clear" your conversation in the Copilot chat panel with the broom located at the top of the chat panel. Copilot retains knowledge of any inputs or outputs during the session, but this helps if you find the current content distracting.
- Use the chat magics library to configure settings about Copilot, including privacy settings. The default sharing mode maximizes the context sharing Copilot can access. Therefore, limiting the information provided to copilot can directly and significantly affect the relevance of its responses.
- When Copilot first launches, it offers a set of helpful prompts that can help you get started. They can help kickstart your conversation with Copilot. To refer to prompts later, you can use the sparkle button at the bottom of the chat panel.
- You can "drag" the sidebar of the copilot chat to expand the chat panel, to view the code more clearly or to improve the readability of the outputs on your screen.
Limitations
Copilot features in the Data Science experience are currently scoped to notebooks. These features include the Copilot chat pane, IPython magic commands that can be used within a code cell, and automatic code suggestions as you type in a code cell. Copilot can also read Power BI semantic models using an integration of semantic link.
Copilot has two key intended uses:
- You can ask Copilot to examine and analyze data in your notebook (for example, by first loading a DataFrame and then asking Copilot about data inside the DataFrame).
- You can ask Copilot to generate a range of suggestions about your data analysis process - for example, what predictive models might be relevant, code to perform different types of data analysis, and documentation for a completed notebook.
Code generation with fast-moving or recently released libraries might include inaccuracies or fabrications.
Deletion and Export of data
Copilot in notebooks provides users with two essential commands to manage chat history within notebook cells: show_chat_history and clear_chat_history. The show_chat_history command exports the complete chat history for compliance purposes, to ensure that all necessary interactions are documented and accessible for review. For example, executing show_chat_history generates a comprehensive log of the chat history, which can then be reviewed or archived for compliance.
The clear_chat_history command removes all previous conversations from the notebook, so that the user can start fresh. This command clears out old interactions, to start a new conversation thread. For instance, executing clear_chat_history deletes all previous chat history, to leave the notebook free of any past conversations. These features enhance the overall functionality and user experience of Copilot in notebooks.