Managed HSM logging
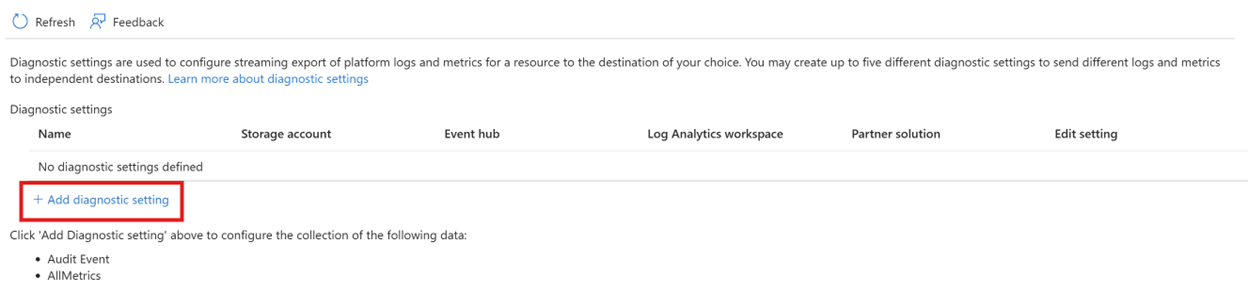
After you create one or more Managed HSMs, you'll likely want to monitor how and when your HSMs are accessed, and by who. You can do this by enabling logging, which saves information in an Azure storage account that you provide. A new container named insights-logs-auditevent is automatically created for your specified storage account. You can use this same storage account for collecting logs for multiple Managed HSMs. You can also choose to send your logs to a log analytics workspace, which can then be used to enable Microsoft Sentinel to detect suspicious activity automatically.
You can access your logging information 10 minutes (at most) after the Managed HSM operation. In most cases, it is sooner. It's up to you to manage your logs in your storage account:
- Use standard Azure access control methods to secure your logs by restricting who can access them.
- Delete logs that you no longer want to keep in your storage account.
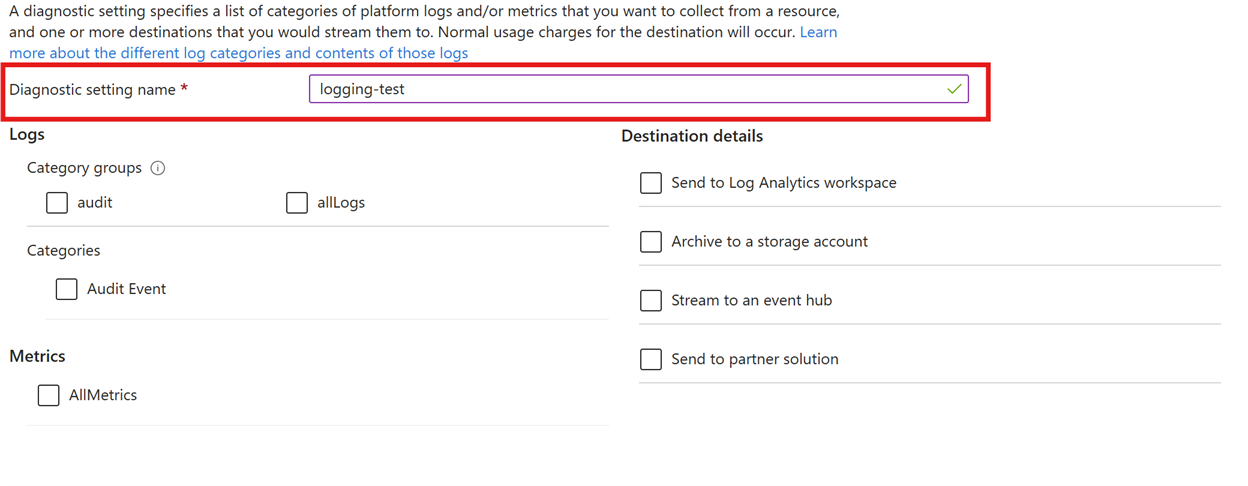
Use this tutorial to help you get started with Managed HSM logging. You should have a storage account or log analytics workspace already created before you enable logging and interpret the collected log information.
Prerequisites
To complete the steps in this article, you must have the following items:
- A subscription to Microsoft Azure. If you don't have one, you can sign up for a free trial.
- The Azure CLI version 2.25.0 or later. Run
az --versionto find the version. If you need to install or upgrade, see Install the Azure CLI. - A managed HSM in your subscription. See Quickstart: Provision and activate a managed HSM using Azure CLI to provision and activate a managed HSM.
- An Azure storage account and/or a Log Analytics workspace. If you do not have one or both, you can create them using the Azure portal:
Azure Cloud Shell
Azure hosts Azure Cloud Shell, an interactive shell environment that you can use through your browser. You can use either Bash or PowerShell with Cloud Shell to work with Azure services. You can use the Cloud Shell preinstalled commands to run the code in this article, without having to install anything on your local environment.
To start Azure Cloud Shell:
| Option | Example/Link |
|---|---|
| Select Try It in the upper-right corner of a code or command block. Selecting Try It doesn't automatically copy the code or command to Cloud Shell. |  |
| Go to https://shell.azure.com, or select the Launch Cloud Shell button to open Cloud Shell in your browser. |  |
| Select the Cloud Shell button on the menu bar at the upper right in the Azure portal. |  |
To use Azure Cloud Shell:
Start Cloud Shell.
Select the Copy button on a code block (or command block) to copy the code or command.
Paste the code or command into the Cloud Shell session by selecting Ctrl+Shift+V on Windows and Linux, or by selecting Cmd+Shift+V on macOS.
Select Enter to run the code or command.
Connect to your Azure subscription
Sign in to your Azure subscription by using the Azure CLI az login command:
az login
For more information on login options via the CLI, take a look at sign in with Azure CLI
Identify the managed HSM, storage account, and log analytics workspace
The first step in setting up key logging is to find the Managed HSM that you want to log.
Use the Azure CLI az keyvault show command to find the Managed HSM that you want to log.
You can also use the Azure CLI az storage account show command to find the storage account that you want to use for logging, and/or the Azure CLI az monitor log-analytics workspace show command to find the log analytics workspace that you want to use for logging.
hsmresource=$(az keyvault show --hsm-name ContosoMHSM --query id -o tsv)
storageresource=$(az storage account show --name ContosoMHSMLogs --query id -o tsv)
loganalyticsresource=$(az monitor log-analytics workspace show --resource-group ContosoResourceGroup --workspace-name ContosoLogs --query id -o tsv)
Enable logging
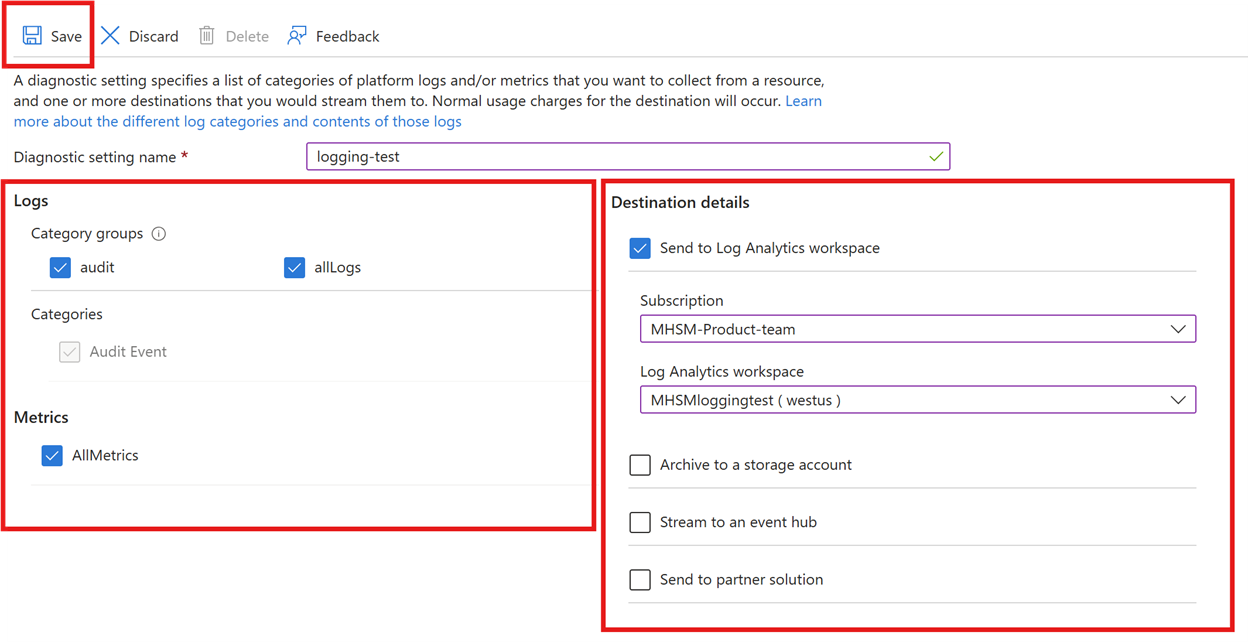
To enable logging for Managed HSM, use the Azure CLI az monitor diagnostic-settings create command, together with the variables from the previous commands. We will also set the -Enabled flag to "true" and set the category to "AuditEvent" (the only category for Managed HSM logging).
To send the logs to a storage account:
az monitor diagnostic-settings create --name ContosoMHSM-Diagnostics --resource $hsmresource --logs '[{"category": "AuditEvent","enabled": true}]' --storage-account $storageresource
To send the logs to a Log Analytics workspace:
az monitor diagnostic-settings create --name "ContosoMHSM-Diagnostics" --resource $hsmresource --logs '[{"category": "AuditEvent","enabled": true}]' --workspace $loganalyticsresource
What's logged
The following types of operations and events are logged for Managed HSM:
- All authenticated REST API requests, including failed requests as a result of access permissions, system errors, firewall blocks, or bad requests.
- Managed plane operations on the Managed HSM resource itself, including creation, deletion, and updating attributes such as tags.
- Security Domain related operations such as initialize & download, initialize recovery, upload
- Full HSM backup, restore, and selective restore operations
- Role management operations such as create/view/delete role assignments and create/view/delete custom role definitions
- Operations on keys, including:
- Creating, modifying, or deleting the keys.
- Signing, verifying, encrypting, decrypting, wrapping and unwrapping keys, listing keys.
- Key backup, restore, purge
- Key release
- Invalid paths that result in a 404 response.
Access your logs
Storage account
Managed HSM logs are stored in the insights-logs-auditevent container in the storage account that you provided. To view the logs, you have to download blobs. For information on Azure Storage, see Create, download, and list blobs with Azure CLI.
Individual blobs are stored as text, formatted as a JSON. Let's look at an example log entry. This example shows the log entry when a request to create a full backup is sent to the managed HSM.
[
{
"TenantId": "{tenant-id}",
"time": "2020-08-31T19:52:39.763Z",
"resourceId": "/SUBSCRIPTIONS/{subscription-id}/RESOURCEGROUPS/CONTOSORESOURCEGROUP/PROVIDERS/MICROSOFT.KEYVAULT/MANAGEDHSMS/CONTOSOMHSM",
"operationName": "BackupCreate",
"operationVersion": "7.0",
"category": "AuditEvent",
"resultType": "Success",
"properties": {
"PoolType": "M-HSM",
"sku_Family": "B",
"sku_Name": "Standard_B1"
},
"durationMs": 488,
"callerIpAddress": "X.X.X.X",
"identity": "{\"claim\":{\"appid\":\"{application-id}\",\"http_schemas_microsoft_com_identity\":{\"claims\":{\"objectidentifier\":\"{object-id}\"}},\"http_schemas_xmlsoap_org_ws_2005_05_identity\":{\"claims\":{\"upn\":\"admin@contoso.com\"}}}}",
"clientInfo": "azsdk-python-core/1.7.0 Python/3.8.2 (Linux-4.19.84-microsoft-standard-x86_64-with-glibc2.29) azsdk-python-azure-keyvault/7.2",
"correlationId": "aaaa0000-bb11-2222-33cc-444444dddddd",
"subnetId": "(unknown)",
"httpStatusCode": 202,
"PoolName": "mhsmdemo",
"requestUri": "https://ContosoMHSM.managedhsm.azure.net/backup",
"resourceGroup": "ContosoResourceGroup",
"resourceProvider": "MICROSOFT.KEYVAULT",
"resource": "ContosoMHSM",
"resourceType": "managedHSMs"
}
]
Log Analytics workspace
Managed HSM logs are stored in the Log Analytics workspace that you provided. You can use the Azure portal to query the logs. For more information, see Log Analytics tutorial.
Use Azure Monitor logs
You can use the Key Vault solution in Azure Monitor logs to review Managed HSM AuditEvent logs. In Azure Monitor logs, you use log queries to analyze data and get the information you need. For more information, including how to set it up, see Monitor Azure Managed HSM.
For learn how to analyze logs, see Sample Kusto log queries.
If you are sending your logs to a log analytics workspace, you can use Microsoft Sentinel to automatically detect suspicious activity. See Microsoft Sentinel for Azure Managed HSM.
Next steps
- Learn about best practices to provision and use a managed HSM
- Learn about how to Backup and Restore a Managed HSM