Create and configure datasets in the .NET Framework using Visual Studio
Note
Datasets and related classes are legacy .NET Framework technologies from the early 2000s that enable applications to work with data in memory while the applications are disconnected from the database. The technologies are especially useful for applications that enable users to modify data and persist the changes back to the database. Although datasets have proven to be a very successful technology, we recommend that new .NET applications use Entity Framework Core. Entity Framework provides a more natural way to work with tabular data as object models, and it has a simpler programming interface.
A dataset is a set of objects that store data from a database in memory and support change tracking to enable create, read, update, and delete (CRUD) operations on that data without the need to be always connected to the database. To work with datasets, you should have a basic knowledge of database concepts.
You can create a typed DataSet class in Visual Studio at design time by using the Data Source Configuration Wizard. For information on creating datasets programmatically, see Create a dataset.
Prerequisites
Visual Studio with the .NET desktop development and Data storage and processing workloads installed. To install them, open Visual Studio Installer and choose Modify next to the version of Visual Studio you want to modify.
A .NET Framework project. Don't use .NET Core or .NET 5 or later.
SQL Server Express LocalDB. If you don't have SQL Server Express LocalDB, you can install it from the SQL Server download page.
Create a new dataset by using the Data Source Configuration Wizard
Open your project in Visual Studio, and then choose Project > Add New Data Source to start the Data Source Configuration Wizard.
Select Database as the type of data source, and then select Next.
Choose DataSet, and then select Next.
Choose one or more databases as the data connection for your dataset, and then select Next.
Choose the tables (or individual columns), views, stored procedures, and functions from the database that you want to be represented in the dataset.
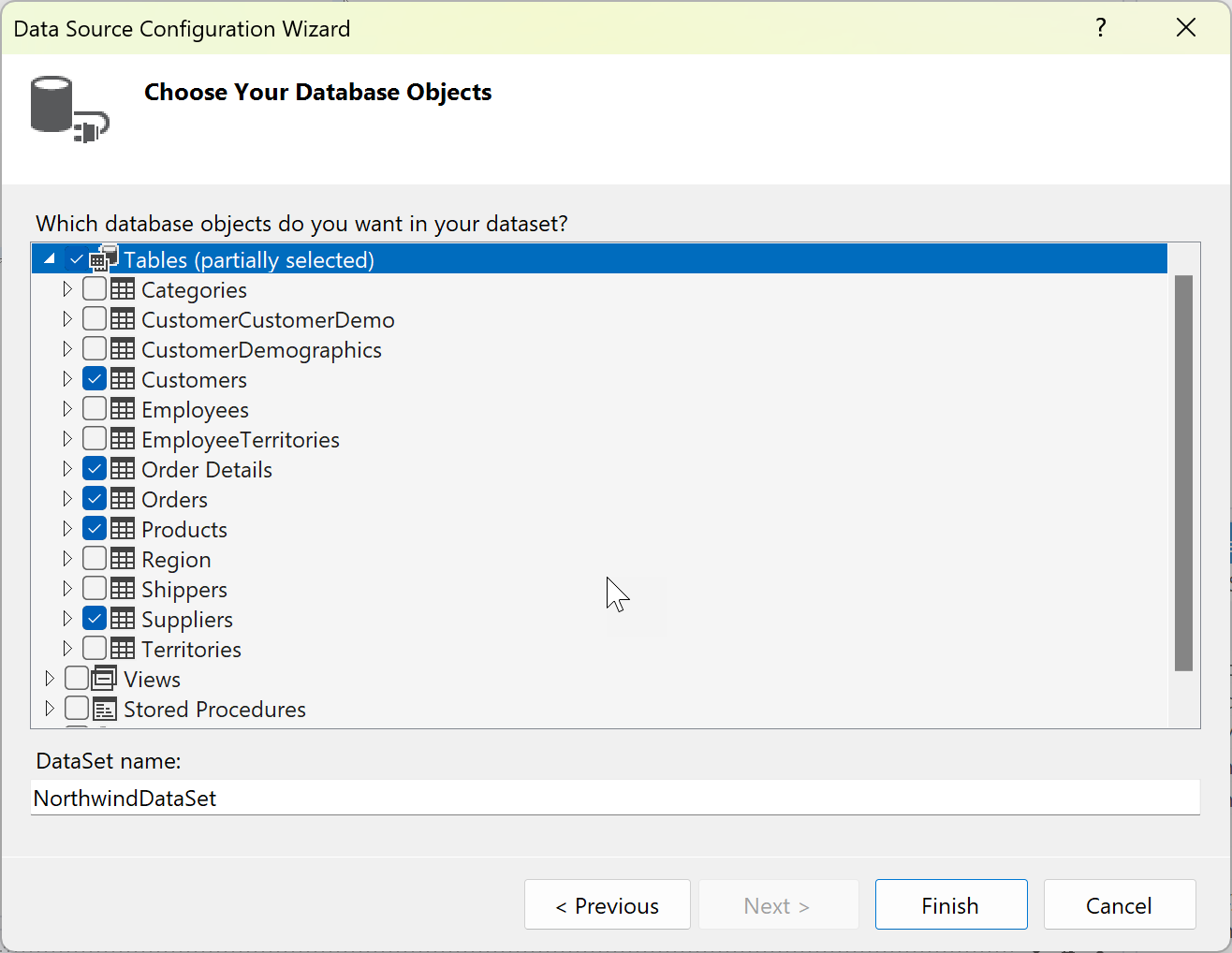
Select Finish.
The dataset appears as a node in Solution Explorer.
Double-click the dataset node in Solution Explorer.
The dataset opens in the Dataset Designer.
Each table in the dataset has an associated
TableAdapterobject, which is represented at the bottom of the table diagram. The table adapter is used to populate the dataset and optionally to send commands to the database.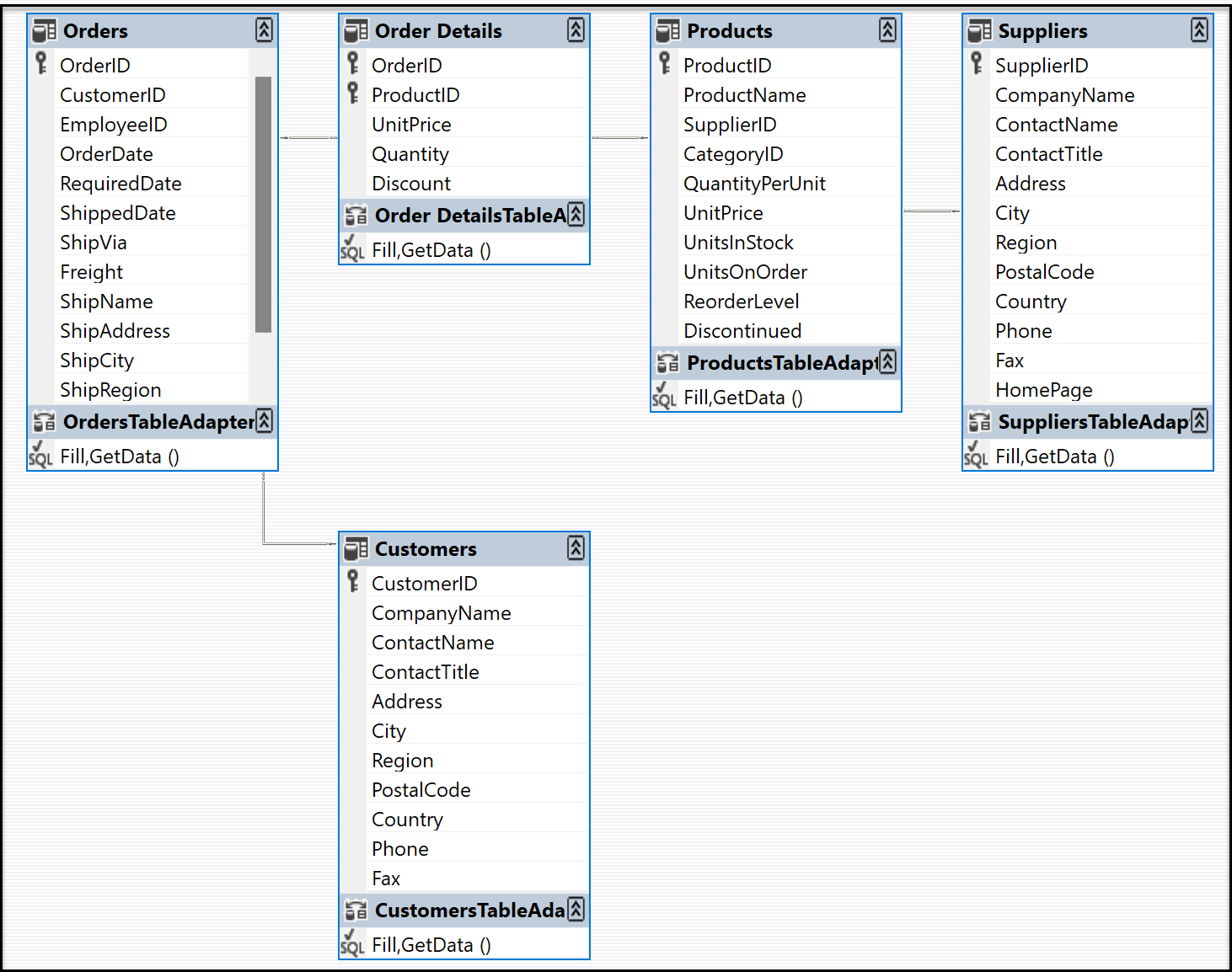
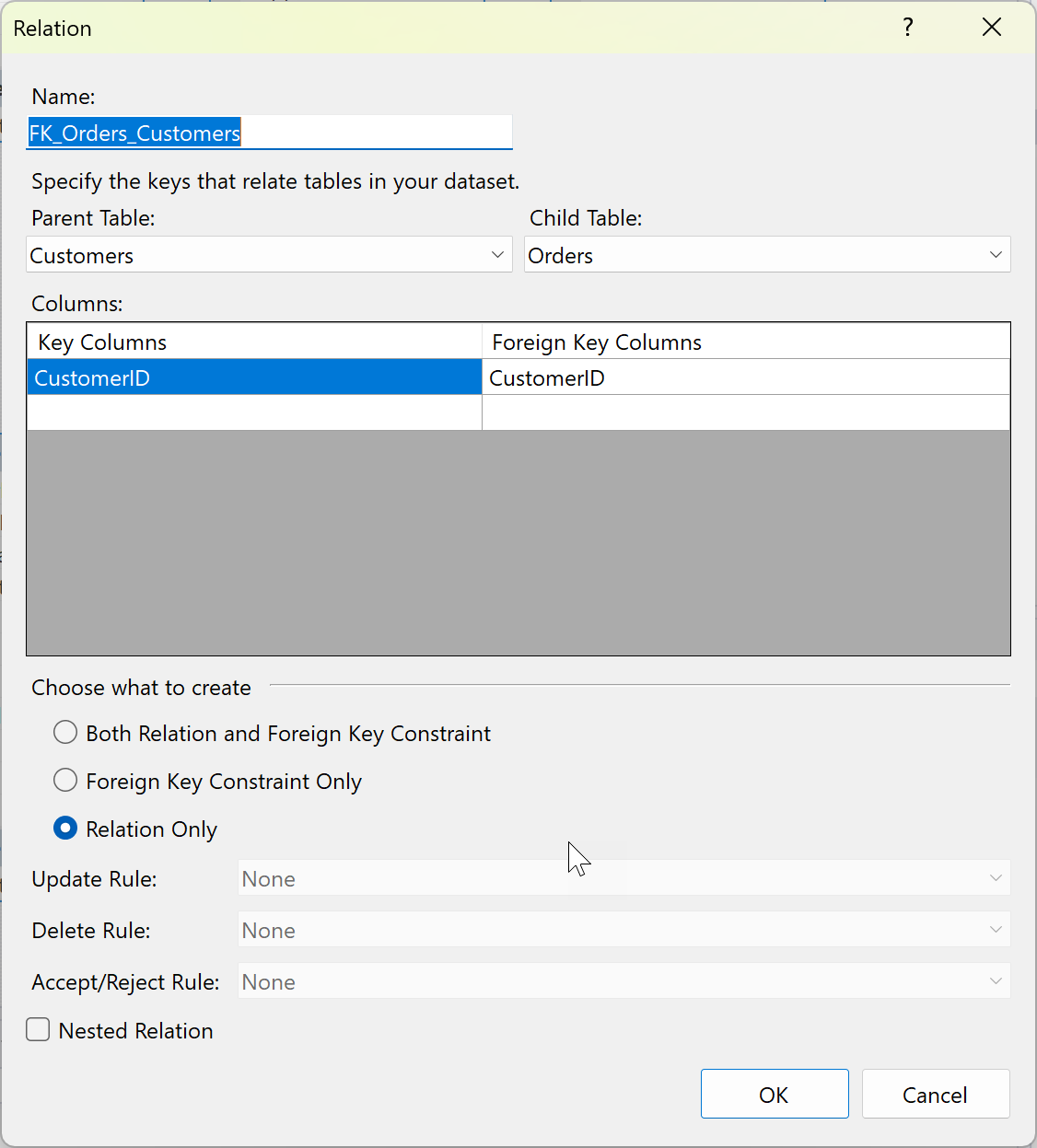
If you want to change the behavior of hierarchical updates, you can double-click a relation line between two tables to display the Relation dialog.
The relation lines that connect the tables represent table relationships, as defined in the database. By default, foreign-key constraints in a database are represented as a relation only, with the update and delete rules set to none, which is typically what you want. For more information, see Create relationships between datasets and Hierarchical update.
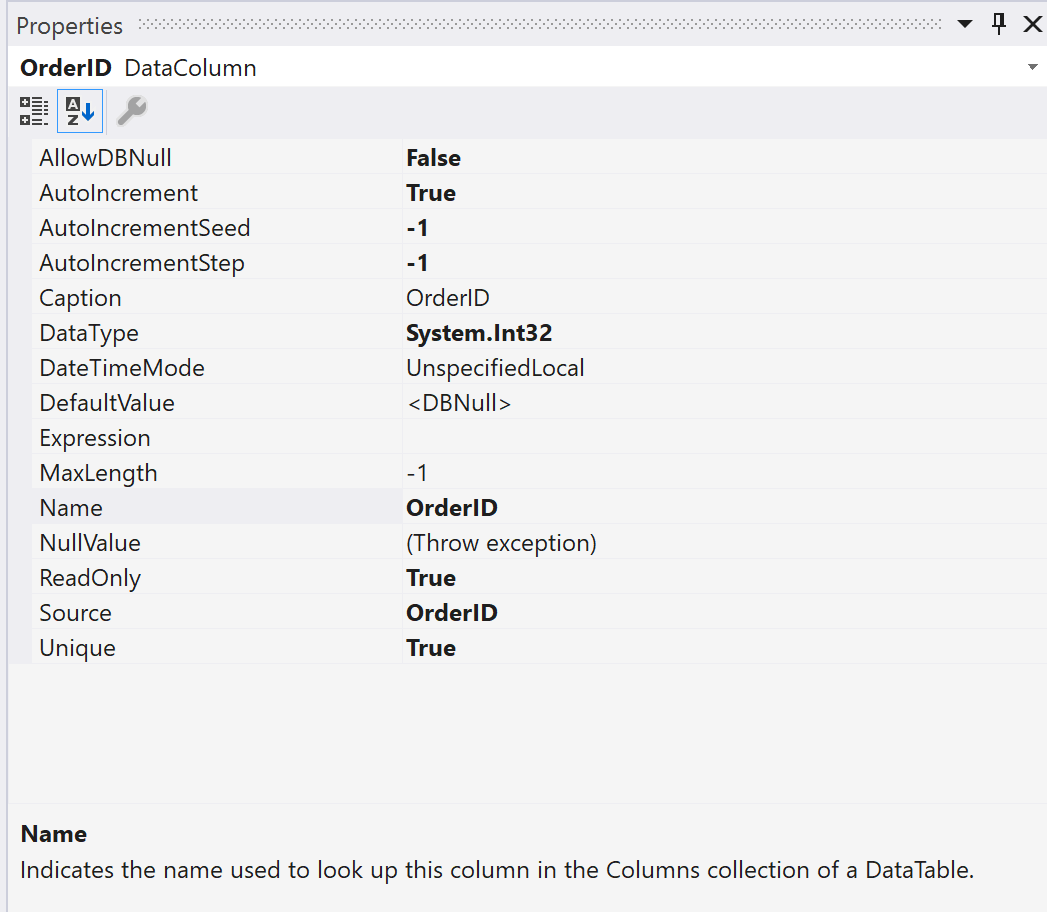
In the Dataset Designer, select a table, table adapter, or column name to see its properties in the Properties window. Although you can modify some of the values in the window, remember that you're modifying the dataset, not the source database.
You can add new tables or table adapters to the dataset, add new queries for existing table adapters, or specify new relations between tables by dragging those items from the left Toolbox tab. This tab appears when the Dataset Designer is in focus.
Optionally, you might want to specify how to populate the dataset with data. To do so, use the TableAdapter Configuration Wizard. For more information, see Fill datasets by using TableAdapters.
Add a database table or other object to an existing dataset
This procedure shows how to add a table from the same database that you used to first create the dataset:
Double-click the dataset node in Solution Explorer.
The dataset opens in the Dataset Designer.
Select the Data Sources tab in the left margin of Visual Studio, or enter data sources in the search box.
Right-click the dataset node and select Configure Data Source with Wizard.
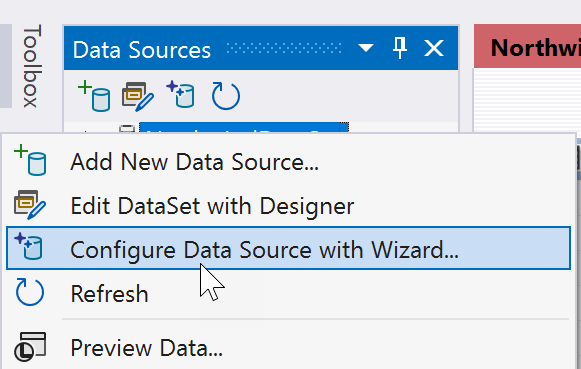
Use the Data Source Configuration Wizard to specify which additional tables, stored procedures, or other database objects to add to the dataset.
Add a stand-alone data table to a dataset
Open your dataset in the Dataset Designer.
Drag a DataTable class from the DataSet tab of the Toolbox onto the Dataset Designer.
Add columns to define your data table. Right-click the table and choose Add > Column. In the Properties window, set the data type of the column. If necessary, add a key by selecting Add > Key.
Stand-alone tables need to implement Fill logic so that you can fill them with data. For information about filling data tables, see Populate a DataSet from a DataAdapter.