Tutorial: Use the Microsoft Purview Python SDK
This tutorial will introduce you to using the Microsoft Purview Python SDK. You can use the SDK to do all the most common Microsoft Purview operations programmatically, rather than through the Microsoft Purview governance portal.
In this tutorial, you'll learn how us the SDK to:
- Grant the required rights to work programmatically with Microsoft Purview
- Register a Blob Storage container as a data source in Microsoft Purview
- Define and run a scan
- Search the catalog
- Delete a data source
Prerequisites
For this tutorial, you'll need:
- Python 3.6 or higher
- An active Azure Subscription. If you don't have one, you can create one for free.
- A Microsoft Entra tenant associated with your subscription.
- An Azure Storage account. If you don't already have one, you can follow our quickstart guide to create one.
- A Microsoft Purview account. If you don't already have one, you can follow our quickstart guide to create one.
- A service principal with a client secret.
Important
For these scripts your endpoint value will be different depending on which Microsoft Purview portal you are using. Endpoint for the classic Microsoft Purview governance portal: purview.azure.com/ Endpoint for the New Microsoft Purview portal: purview.microsoft.com/
So if you're using the new portal, your endpoint value will be something like: "https://consotopurview.scan.purview.microsoft.com"
Give Microsoft Purview access to the Storage account
Before being able to scan the content of the Storage account, you need to give Microsoft Purview the right role.
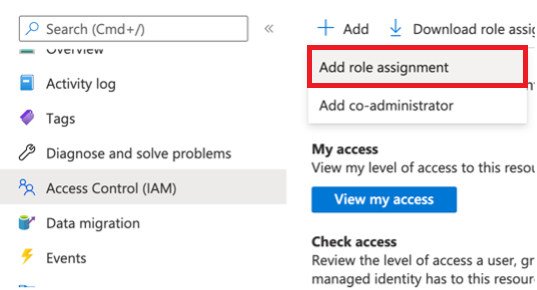
Go to your Storage Account through the Azure portal.
Select Access Control (IAM).
Select the Add button and select Add role assignment.
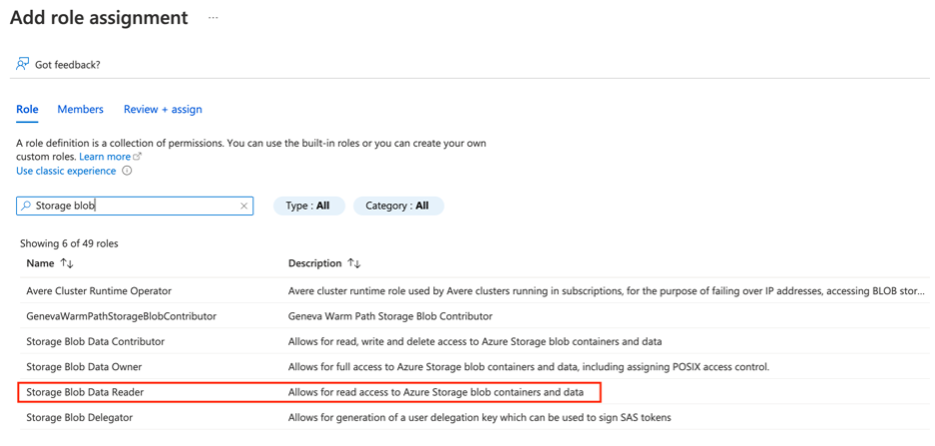
In the next window, search for the Storage blob Reader role and select it:
Then go on the Members tab and select Select members:
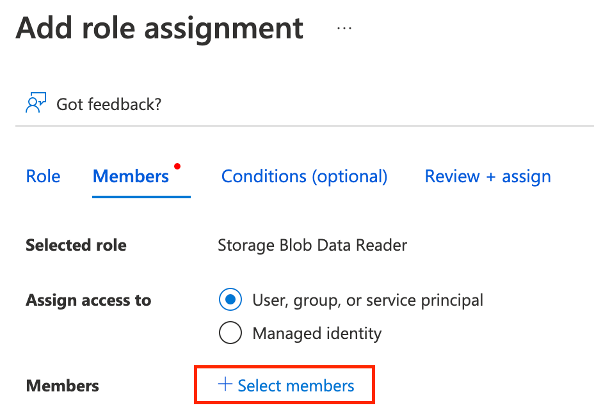
A new pane appears on the right. Search and select the name of your existing Microsoft Purview instance.
You can then select Review + Assign.
Microsoft Purview now has the required reading right to scan your Blob Storage.
Grant your application the access to your Microsoft Purview account
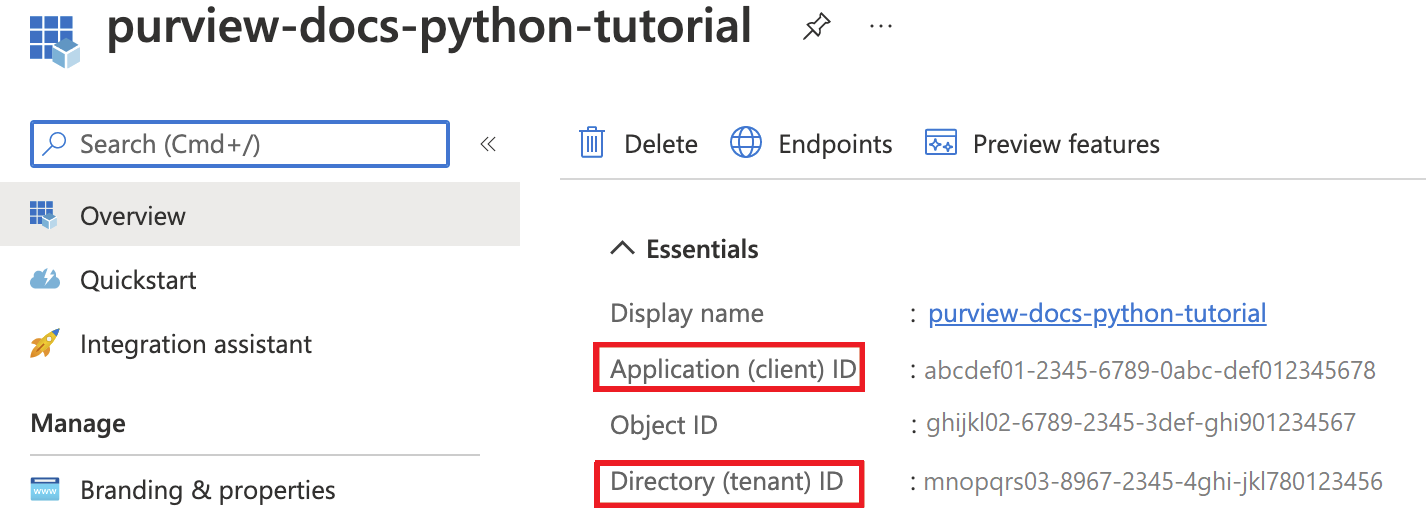
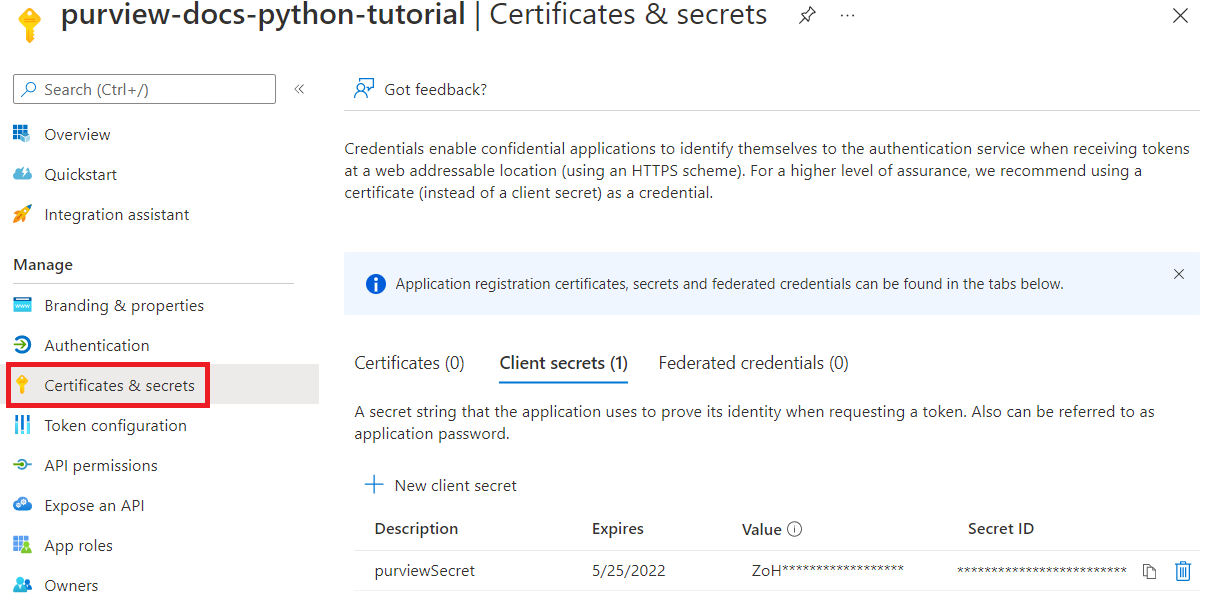
First, you'll need the Client ID, Tenant ID, and Client secret from your service principal. To find this information, select your Microsoft Entra ID.
Then, select App registrations.
Select your application and locate the required information:
Name
Client ID (or Application ID)
Tenant ID (or Directory ID)
-
You now need to give the relevant Microsoft Purview roles to your service principal. To do so, access your Microsoft Purview instance. Select Open Microsoft Purview governance portal or open the Microsoft Purview's governance portal directly and choose the instance that you deployed.
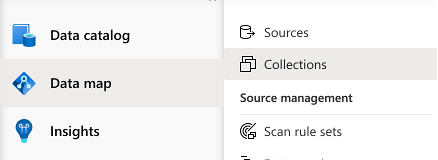
Inside the Microsoft Purview governance portal, select Data map, then Collections:
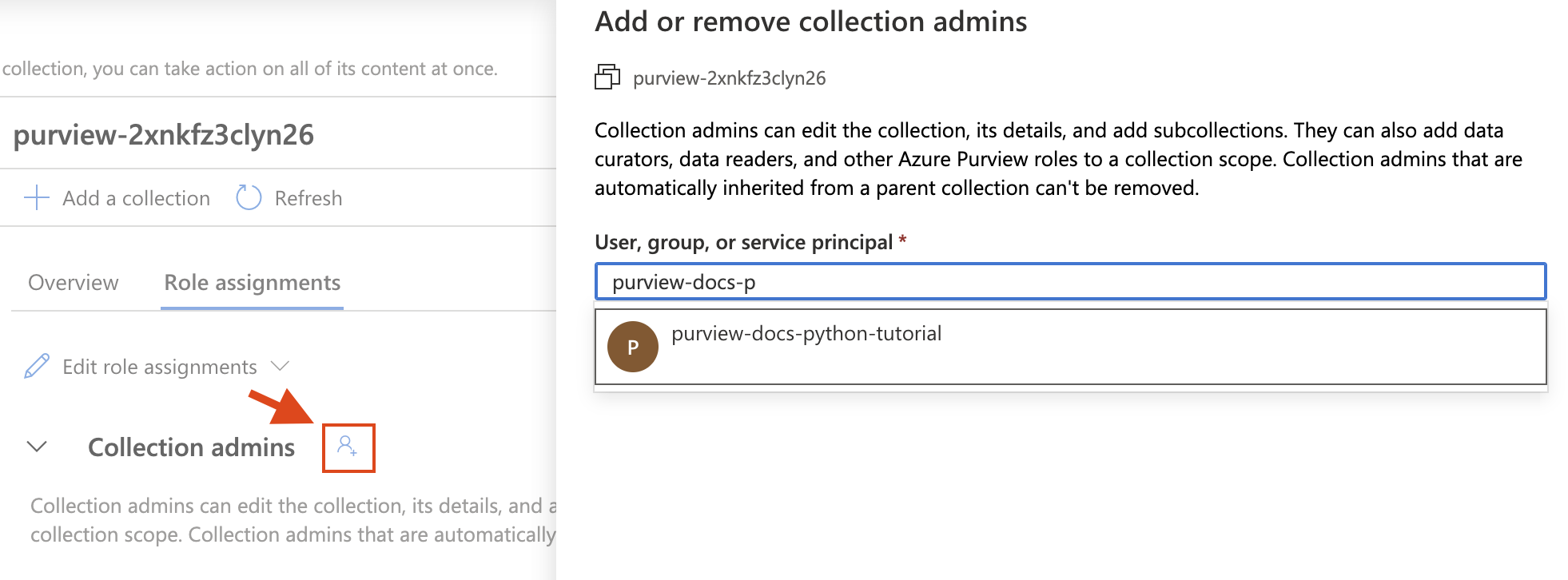
Select the collection you want to work with, and go on the Role assignments tab. Add the service principal in the following roles:
- Collection admins
- Data source admins
- Data curators
- Data readers
For each role, select the Edit role assignments button and select the role you want to add the service principal to. Or select the Add button next to each role, and add the service principal by searching its name or Client ID as shown below:
Install the Python packages
- Open a new command prompt or terminal
- Install the Azure identity package for authentication:
pip install azure-identity - Install the Microsoft Purview Scanning Client package:
pip install azure-purview-scanning - Install the Microsoft Purview Administration Client package:
pip install azure-purview-administration - Install the Microsoft Purview Client package:
pip install azure-purview-catalog - Install the Microsoft Purview Account package:
pip install azure-purview-account - Install the Azure Core package:
pip install azure-core
Create Python script file
Create a plain text file, and save it as a Python script with the suffix .py. For example: tutorial.py.
Instantiate a Scanning, Catalog, and Administration client
In this section, you learn how to instantiate:
- A scanning client useful to registering data sources, creating and managing scan rules, triggering a scan, etc.
- A catalog client useful to interact with the catalog through searching, browsing the discovered assets, identifying the sensitivity of your data, etc.
- An administration client is useful for interacting with the Microsoft Purview Data Map itself, for operations like listing collections.
First you need to authenticate to your Microsoft Entra ID. For this, you'll use the client secret you created.
Start with required import statements: our three clients, the credentials statement, and an Azure exceptions statement.
from azure.purview.scanning import PurviewScanningClient from azure.purview.catalog import PurviewCatalogClient from azure.purview.administration.account import PurviewAccountClient from azure.identity import ClientSecretCredential from azure.core.exceptions import HttpResponseErrorSpecify the following information in the code:
- Client ID (or Application ID)
- Tenant ID (or Directory ID)
- Client secret
client_id = "<your client id>" client_secret = "<your client secret>" tenant_id = "<your tenant id>"Specify your endpoint:
Important
Your endpoint value will be different depending on which Microsoft Purview portal you are using. Endpoint for the classic Microsoft Purview governance portal:
https://{your_purview_account_name}.purview.azure.com/Endpoint for the New Microsoft Purview portal:https://api.purview-service.microsoft.comScan endpoint for the classic Microsoft Purview governance portal:
https://{your_purview_account_name}.scan.purview.azure.com/Endpoint for the New Microsoft Purview portal:https://api.scan.purview-service.microsoft.compurview_endpoint = "<endpoint>" purview_scan_endpoint = "<scan endpoint>"You can now instantiate the three clients:
def get_credentials(): credentials = ClientSecretCredential(client_id=client_id, client_secret=client_secret, tenant_id=tenant_id) return credentials def get_purview_client(): credentials = get_credentials() client = PurviewScanningClient(endpoint=purview_scan_endpoint, credential=credentials, logging_enable=True) return client def get_catalog_client(): credentials = get_credentials() client = PurviewCatalogClient(endpoint=purview_endpoint, credential=credentials, logging_enable=True) return client def get_admin_client(): credentials = get_credentials() client = PurviewAccountClient(endpoint=purview_endpoint, credential=credentials, logging_enable=True) return client
Many of our scripts will start with these same steps, as we'll need these clients to interact with the account.
Register a data source
In this section, you'll register your Blob Storage.
Like we discussed in the previous section, first you'll import the clients you'll need to access your Microsoft Purview account. Also import the Azure error response package so you can troubleshoot, and the ClientSecretCredential to construct your Azure credentials.
from azure.purview.administration.account import PurviewAccountClient from azure.purview.scanning import PurviewScanningClient from azure.core.exceptions import HttpResponseError from azure.identity import ClientSecretCredentialGather the resource ID for your storage account by following this guide: get the resource ID for a storage account.
Then, in your Python file, define the following information to be able to register the Blob storage programmatically:
storage_name = "<name of your Storage Account>" storage_id = "<id of your Storage Account>" rg_name = "<name of your resource group>" rg_location = "<location of your resource group>" reference_name_purview = "<name of your Microsoft Purview account>"Provide the name of the collection where you'd like to register your blob storage. (It should be the same collection where you applied permissions earlier. If it isn't, first apply permissions to this collection.) If it's the root collection, use the same name as your Microsoft Purview instance.
collection_name = "<name of your collection>"Create a function to construct the credentials to access your Microsoft Purview account:
client_id = "<your client id>" client_secret = "<your client secret>" tenant_id = "<your tenant id>" def get_credentials(): credentials = ClientSecretCredential(client_id=client_id, client_secret=client_secret, tenant_id=tenant_id) return credentialsAll collections in the Microsoft Purview Data Map have a friendly name and a name.
- The friendly name name is the one you see on the collection. For example: Sales.
- The name for all collections (except the root collection) is a six-character name assigned by the data map.
Python needs this six-character name to reference any sub collections. To convert your friendly name automatically to the six-character collection name needed in your script, add this block of code:
Important
Your endpoint value will be different depending on which Microsoft Purview portal you are using. Endpoint for the classic Microsoft Purview governance portal: purview.azure.com/ Endpoint for the New Microsoft Purview portal: purview.microsoft.com/
So if you're using the new portal, your endpoint value will be something like: "https://consotopurview.scan.purview.microsoft.com"
def get_admin_client(): credentials = get_credentials() client = PurviewAccountClient(endpoint=purview_endpoint, credential=credentials, logging_enable=True) return client try: admin_client = get_admin_client() except ValueError as e: print(e) collection_list = client.collections.list_collections() for collection in collection_list: if collection["friendlyName"].lower() == collection_name.lower(): collection_name = collection["name"]For both clients, and depending on the operations, you also need to provide an input body. To register a source, you'll need to provide an input body for data source registration:
ds_name = "<friendly name for your data source>" body_input = { "kind": "AzureStorage", "properties": { "endpoint": f"https://{storage_name}.blob.core.windows.net/", "resourceGroup": rg_name, "location": rg_location, "resourceName": storage_name, "resourceId": storage_id, "collection": { "type": "CollectionReference", "referenceName": collection_name }, "dataUseGovernance": "Disabled" } }Now you can call your Microsoft Purview clients and register the data source.
Important
Your endpoint value will be different depending on which Microsoft Purview portal you are using. Endpoint for the classic Microsoft Purview governance portal:
https://{your_purview_account_name}.purview.azure.com/Endpoint for the New Microsoft Purview portal:https://api.purview-service.microsoft.comIf you're using the classic portal, your endpoint value will be:
https://{your_purview_account_name}.scan.purview.azure.comIf you're using the new portal, your endpoint value will be:https://scan.api.purview-service.microsoft.comdef get_purview_client(): credentials = get_credentials() client = PurviewScanningClient(endpoint={{ENDPOINT}}, credential=credentials, logging_enable=True) return client try: client = get_purview_client() except ValueError as e: print(e) try: response = client.data_sources.create_or_update(ds_name, body=body_input) print(response) print(f"Data source {ds_name} successfully created or updated") except HttpResponseError as e: print(e)
When the registration process succeeds, you can see an enriched body response from the client.
In the following sections, you'll scan the data source you registered and search the catalog. Each of these scripts will be similarly structured to this registration script.
Full code
from azure.purview.scanning import PurviewScanningClient
from azure.identity import ClientSecretCredential
from azure.core.exceptions import HttpResponseError
from azure.purview.administration.account import PurviewAccountClient
client_id = "<your client id>"
client_secret = "<your client secret>"
tenant_id = "<your tenant id>"
purview_endpoint = "<endpoint>"
purview_scan_endpoint = "<scan endpoint>"
storage_name = "<name of your Storage Account>"
storage_id = "<id of your Storage Account>"
rg_name = "<name of your resource group>"
rg_location = "<location of your resource group>"
collection_name = "<name of your collection>"
ds_name = "<friendly data source name>"
def get_credentials():
credentials = ClientSecretCredential(client_id=client_id, client_secret=client_secret, tenant_id=tenant_id)
return credentials
def get_purview_client():
credentials = get_credentials()
client = PurviewScanningClient(endpoint=purview_scan_endpoint, credential=credentials, logging_enable=True)
return client
def get_admin_client():
credentials = get_credentials()
client = PurviewAccountClient(endpoint=purview_endpoint, credential=credentials, logging_enable=True)
return client
try:
admin_client = get_admin_client()
except ValueError as e:
print(e)
collection_list = admin_client.collections.list_collections()
for collection in collection_list:
if collection["friendlyName"].lower() == collection_name.lower():
collection_name = collection["name"]
body_input = {
"kind": "AzureStorage",
"properties": {
"endpoint": f"https://{storage_name}.blob.core.windows.net/",
"resourceGroup": rg_name,
"location": rg_location,
"resourceName": storage_name,
"resourceId": storage_id,
"collection": {
"type": "CollectionReference",
"referenceName": collection_name
},
"dataUseGovernance": "Disabled"
}
}
try:
client = get_purview_client()
except ValueError as e:
print(e)
try:
response = client.data_sources.create_or_update(ds_name, body=body_input)
print(response)
print(f"Data source {ds_name} successfully created or updated")
except HttpResponseError as e:
print(e)
Scan the data source
Scanning a data source can be done in two steps:
- Create a scan definition
- Trigger a scan run
In this tutorial, you'll use the default scan rules for Blob Storage containers. However, you can also create custom scan rules programmatically with the Microsoft Purview Scanning Client.
Now let's scan the data source you registered above.
Add an import statement to generate unique identifier, call the Microsoft Purview scanning client, the Microsoft Purview administration client, the Azure error response package to be able to troubleshoot, and the client secret credential to gather your Azure credentials.
import uuid from azure.purview.scanning import PurviewScanningClient from azure.purview.administration.account import PurviewAccountClient from azure.core.exceptions import HttpResponseError from azure.identity import ClientSecretCredentialCreate a scanning client using your credentials:
client_id = "<your client id>" client_secret = "<your client secret>" tenant_id = "<your tenant id>" def get_credentials(): credentials = ClientSecretCredential(client_id=client_id, client_secret=client_secret, tenant_id=tenant_id) return credentials def get_purview_client(): credentials = get_credentials() client = PurviewScanningClient(endpoint=f"https://{reference_name_purview}.scan.purview.azure.com", credential=credentials, logging_enable=True) return client try: client = get_purview_client() except ValueError as e: print(e)Add the code to gather the internal name of your collection. (For more information, see the previous section):
collection_name = "<name of the collection where you will be creating the scan>" def get_admin_client(): credentials = get_credentials() client = PurviewAccountClient(endpoint=purview_endpoint, credential=credentials, logging_enable=True) return client try: admin_client = get_admin_client() except ValueError as e: print(e) collection_list = client.collections.list_collections() for collection in collection_list: if collection["friendlyName"].lower() == collection_name.lower(): collection_name = collection["name"]Then, create a scan definition:
ds_name = "<name of your registered data source>" scan_name = "<name of the scan you want to define>" reference_name_purview = "<name of your Microsoft Purview account>" body_input = { "kind":"AzureStorageMsi", "properties": { "scanRulesetName": "AzureStorage", "scanRulesetType": "System", #We use the default scan rule set "collection": { "referenceName": collection_name, "type": "CollectionReference" } } } try: response = client.scans.create_or_update(data_source_name=ds_name, scan_name=scan_name, body=body_input) print(response) print(f"Scan {scan_name} successfully created or updated") except HttpResponseError as e: print(e)Now that the scan is defined you can trigger a scan run with a unique ID:
run_id = uuid.uuid4() #unique id of the new scan try: response = client.scan_result.run_scan(data_source_name=ds_name, scan_name=scan_name, run_id=run_id) print(response) print(f"Scan {scan_name} successfully started") except HttpResponseError as e: print(e)
Full code
import uuid
from azure.purview.scanning import PurviewScanningClient
from azure.purview.administration.account import PurviewAccountClient
from azure.identity import ClientSecretCredential
ds_name = "<name of your registered data source>"
scan_name = "<name of the scan you want to define>"
reference_name_purview = "<name of your Microsoft Purview account>"
client_id = "<your client id>"
client_secret = "<your client secret>"
tenant_id = "<your tenant id>"
collection_name = "<name of the collection where you will be creating the scan>"
def get_credentials():
credentials = ClientSecretCredential(client_id=client_id, client_secret=client_secret, tenant_id=tenant_id)
return credentials
def get_purview_client():
credentials = get_credentials()
client = PurviewScanningClient(endpoint=purview_scan_endpoint, credential=credentials, logging_enable=True)
return client
def get_admin_client():
credentials = get_credentials()
client = PurviewAccountClient(endpoint=purview_endpoint, credential=credentials, logging_enable=True)
return client
try:
admin_client = get_admin_client()
except ValueError as e:
print(e)
collection_list = admin_client.collections.list_collections()
for collection in collection_list:
if collection["friendlyName"].lower() == collection_name.lower():
collection_name = collection["name"]
try:
client = get_purview_client()
except AzureError as e:
print(e)
body_input = {
"kind":"AzureStorageMsi",
"properties": {
"scanRulesetName": "AzureStorage",
"scanRulesetType": "System",
"collection": {
"type": "CollectionReference",
"referenceName": collection_name
}
}
}
try:
response = client.scans.create_or_update(data_source_name=ds_name, scan_name=scan_name, body=body_input)
print(response)
print(f"Scan {scan_name} successfully created or updated")
except HttpResponseError as e:
print(e)
run_id = uuid.uuid4() #unique id of the new scan
try:
response = client.scan_result.run_scan(data_source_name=ds_name, scan_name=scan_name, run_id=run_id)
print(response)
print(f"Scan {scan_name} successfully started")
except HttpResponseError as e:
print(e)
Search catalog
Once a scan is complete, it's likely that assets have been discovered and even classified. This process can take some time to complete after a scan, so you may need to wait before running this next portion of code. Wait for your scan to show completed, and the assets to appear in Microsoft Purview Unified Catalog.
Once the assets are ready, you can use the Microsoft Purview Catalog client to search the whole catalog.
This time you need to import the catalog client instead of the scanning one. Also include the HTTPResponse error and ClientSecretCredential.
from azure.purview.catalog import PurviewCatalogClient from azure.identity import ClientSecretCredential from azure.core.exceptions import HttpResponseErrorCreate a function to get the credentials to access your Microsoft Purview account, and instantiate the catalog client.
client_id = "<your client id>" client_secret = "<your client secret>" tenant_id = "<your tenant id>" reference_name_purview = "<name of your Microsoft Purview account>" def get_credentials(): credentials = ClientSecretCredential(client_id=client_id, client_secret=client_secret, tenant_id=tenant_id) return credentials def get_catalog_client(): credentials = get_credentials() client = PurviewCatalogClient(endpoint=f"https://{reference_name_purview}.scan.purview.azure.com", credential=credentials, logging_enable=True) return client try: client_catalog = get_catalog_client() except ValueError as e: print(e)Configure your search criteria and keywords in the input body:
keywords = "keywords you want to search" body_input={ "keywords": keywords }Here you only specify keywords, but keep in mind you can add many other fields to further specify your query.
Search the catalog:
try: response = client_catalog.discovery.query(search_request=body_input) print(response) except HttpResponseError as e: print(e)
Full code
from azure.purview.catalog import PurviewCatalogClient
from azure.identity import ClientSecretCredential
from azure.core.exceptions import HttpResponseError
client_id = "<your client id>"
client_secret = "<your client secret>"
tenant_id = "<your tenant id>"
reference_name_purview = "<name of your Microsoft Purview account>"
keywords = "<keywords you want to search for>"
def get_credentials():
credentials = ClientSecretCredential(client_id=client_id, client_secret=client_secret, tenant_id=tenant_id)
return credentials
def get_catalog_client():
credentials = get_credentials()
client = PurviewCatalogClient(endpoint=purview_endpoint, credential=credentials, logging_enable=True)
return client
body_input={
"keywords": keywords
}
try:
catalog_client = get_catalog_client()
except ValueError as e:
print(e)
try:
response = catalog_client.discovery.query(search_request=body_input)
print(response)
except HttpResponseError as e:
print(e)
Delete a data source
In this section, you'll learn how to delete the data source you registered earlier. This operation is fairly simple, and is done with the scanning client.
Import the scanning client. Also include the HTTPResponse error and ClientSecretCredential.
from azure.purview.scanning import PurviewScanningClient from azure.identity import ClientSecretCredential from azure.core.exceptions import HttpResponseErrorCreate a function to get the credentials to access your Microsoft Purview account, and instantiate the scanning client.
client_id = "<your client id>" client_secret = "<your client secret>" tenant_id = "<your tenant id>" reference_name_purview = "<name of your Microsoft Purview account>" def get_credentials(): credentials = ClientSecretCredential(client_id=client_id, client_secret=client_secret, tenant_id=tenant_id) return credentials def get_scanning_client(): credentials = get_credentials() PurviewScanningClient(endpoint=f"https://{reference_name_purview}.scan.purview.azure.com", credential=credentials, logging_enable=True) return client try: client_scanning = get_scanning_client() except ValueError as e: print(e)Delete the data source:
ds_name = "<name of the registered data source you want to delete>" try: response = client_scanning.data_sources.delete(ds_name) print(response) print(f"Data source {ds_name} successfully deleted") except HttpResponseError as e: print(e)
Full code
from azure.purview.scanning import PurviewScanningClient
from azure.identity import ClientSecretCredential
from azure.core.exceptions import HttpResponseError
client_id = "<your client id>"
client_secret = "<your client secret>"
tenant_id = "<your tenant id>"
reference_name_purview = "<name of your Microsoft Purview account>"
ds_name = "<name of the registered data source you want to delete>"
def get_credentials():
credentials = ClientSecretCredential(client_id=client_id, client_secret=client_secret, tenant_id=tenant_id)
return credentials
def get_scanning_client():
credentials = get_credentials()
client = PurviewScanningClient(endpoint=f"https://{reference_name_purview}.scan.purview.azure.com", credential=credentials, logging_enable=True)
return client
try:
client_scanning = get_scanning_client()
except ValueError as e:
print(e)
try:
response = client_scanning.data_sources.delete(ds_name)
print(response)
print(f"Data source {ds_name} successfully deleted")
except HttpResponseError as e:
print(e)