Parameters for Data Factory in Microsoft Fabric
This document describes how to use parameters in your pipelines for Data Factory in Fabric.
How to use parameters, expressions and functions in pipelines for Data Factory in Fabric
In this document, we focus on learning fundamental concepts with various examples to explore the ability to create parameterized data pipelines within Data Factory in Fabric. Parameterization and dynamic expressions can save a tremendous amount of time and allow for a much more flexible Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) or Extract, Load, Transform (ELT) solution, which dramatically reduces the cost of solution maintenance and speed up the implementation of new features into existing pipelines. These gains are because parameterization minimizes the amount of hard coding and increases the number of reusable objects and processes in a solution.
Parameter and expression concepts
You can use parameters to pass external values into pipelines. Once the parameter is passed into the resource, it can't be changed. By parameterizing resources, you can reuse them with different values each time. Parameters can be used individually or as a part of expressions. Parameter values in the definition can be literal or expressions that are evaluated at runtime.
Expressions can appear anywhere in a string value and always generate another string value. Here, password is a pipeline parameter in the expression. If a parameter value is an expression, the body of the expression is extracted by removing the at-sign (@). If a literal string is needed that starts with @, it must be escaped by using @@. The following examples show how expressions are evaluated.
| Parameter value | Result |
|---|---|
| "parameters" | The characters 'parameters' are returned. |
| "parameters[1]" | The characters 'parameters[1]' are returned. |
| "@@" | A 1 character string that contains '@' is returned. |
| " @" | A 2 character string that contains ' @' is returned. |
Expressions can also appear inside strings, using a feature called string interpolation where expressions are wrapped in @{ ... }. For example, the following string includes parameter values and literal string values:
"First Name: @{pipeline().parameters.firstName} Last Name: @{pipeline().parameters.lastName}"
Using string interpolation, the result is always a string. For example, if you defined myNumber as 42 and myString as foo:
| Parameter value | Result |
|---|---|
| "@pipeline().parameters.myString" | Returns foo as a string. |
| "@{pipeline().parameters.myString}" | Returns foo as a string. |
| "@pipeline().parameters.myNumber" | Returns 42 as a number. |
| "@{pipeline().parameters.myNumber}" | Returns 42 as a string. |
| "Answer is: @{pipeline().parameters.myNumber}" | Returns the string Answer is: 42. |
| "@concat('Answer is: ', string(pipeline().parameters.myNumber))" | Returns the string Answer is: 42 |
| "Answer is: @@{pipeline().parameters.myNumber}" | Returns the string Answer is: @{pipeline().parameters.myNumber}. |
Examples of using parameters in expressions
Creating and using parameters
To create parameters, select the background of the pipeline editor canvas, and then the Parameters tab of the properties window at the bottom. Select the + New button to add a new parameter to the pipeline, give it a name, a data type, and a default value:
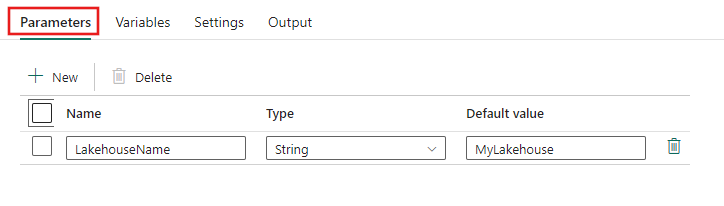
You can then use the parameter anywhere in your pipeline where dynamic content is supported. In this example, the parameter is used to dynamically provide the name of a Lakehouse data store on the Source tab of a copy activity's property pages.
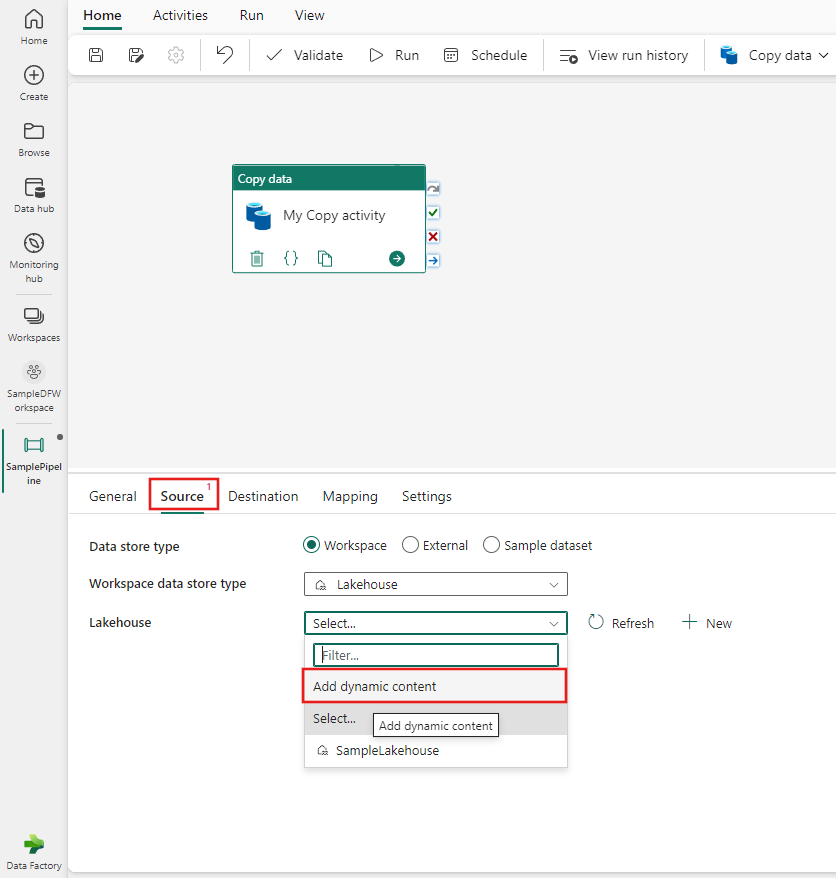
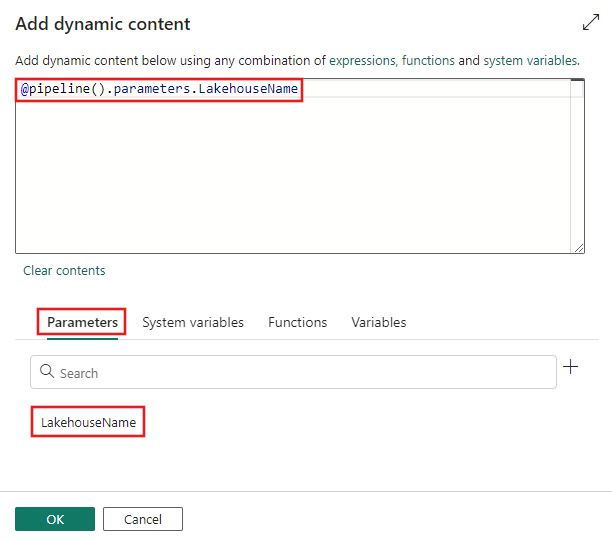
The Add dynamic content window is displayed, allowing you to specify any kind of dynamic content, including parameters, system variables, functions, or pipeline variables. In this example, the previously defined parameter is selected, and the dynamic content window is automatically populated with the correct expression to reference the parameter.
Complex expression example
The following example shows a complex example that references a deep subfield of activity output. To reference a pipeline parameter that evaluates to a subfield, use [] syntax instead of dot(.) operator (as with subfield1 and subfield2)
@activity('*activityName*').output.*subfield1*.*subfield2*[pipeline().parameters.*subfield3*].*subfield4*
Dynamic content editor
The dynamic content editor automatically escapes characters in your content when you finish editing. For example, the following content in the content editor is a string interpolation with an expression function:
@{toUpper('myData')}
The dynamic content editor converts the previous content to the following expression:
MYDATA
Using functions and variables in expressions
You can call functions and use variables within expressions. The following sections provide information about the functions that can be used in an expression.
Pipeline scope variables
These system variables can be referenced anywhere in the pipeline JSON.
| Variable Name | Description |
|---|---|
| @pipeline().DataFactory | Name of the data or Synapse workspace the pipeline run is running in |
| @pipeline().Pipeline | Name of the pipeline |
| @pipeline().RunId | ID of the specific pipeline run |
| @pipeline().TriggerId | ID of the trigger that invoked the pipeline |
| @pipeline().TriggerName | Name of the trigger that invoked the pipeline |
| @pipeline().TriggerTime | Time of the trigger run that invoked the pipeline. This is the time at which the trigger actually fired to invoke the pipeline run, and it may differ slightly from the trigger's scheduled time. |
| @pipeline().GroupId | ID of the group to which pipeline run belongs. In Microsoft Fabric, a 'group' refers to a collection of related resources that can be managed together. Groups are used to organize and control access to resources, making it easier to manage permissions and monitor activities across multiple pipelines. |
| @pipeline()?.TriggeredByPipelineName | Name of the pipeline that triggers the pipeline run. Applicable when the pipeline run is triggered by an ExecutePipeline activity. Evaluate to Null when used in other circumstances. Note the question mark after @pipeline() |
| @pipeline()?.TriggeredByPipelineRunId | Run ID of the pipeline that triggers the pipeline run. Applicable when the pipeline run is triggered by an ExecutePipeline activity. Evaluate to Null when used in other circumstances. Note the question mark after @pipeline() |
Note
Trigger-related date/time system variables (in both pipeline and trigger scopes) return UTC dates in ISO 8601 format, for example, 2017-06-01T22:20:00.4061448Z.
String functions
To work with strings, you can use these string functions and also some collection functions. String functions work only on strings.
| String function | Task |
|---|---|
| concat | Combine two or more strings, and return the combined string. |
| endsWith | Check whether a string ends with the specified substring. |
| guid | Generate a globally unique identifier (GUID) as a string. |
| indexOf | Return the starting position for a substring. |
| lastIndexOf | Return the starting position for the last occurrence of a substring. |
| replace | Replace a substring with the specified string, and return the updated string. |
| split | Return an array that contains substrings, separated by commas, from a larger string based on a specified delimiter character in the original string. |
| startsWith | Check whether a string starts with a specific substring. |
| substring | Return characters from a string, starting from the specified position. |
| toLower | Return a string in lowercase format. |
| toUpper | Return a string in uppercase format. |
| trim | Remove leading and trailing whitespace from a string, and return the updated string. |
Collection functions
To work with collections, generally arrays, strings, and sometimes, dictionaries, you can use these collection functions.
| Collection function | Task |
|---|---|
| contains | Check whether a collection has a specific item. |
| empty | Check whether a collection is empty. |
| first | Return the first item from a collection. |
| intersection | Return a collection that has only the common items across the specified collections. |
| join | Return a string that has all the items from an array, separated by the specified character. |
| last | Return the last item from a collection. |
| length | Return the number of items in a string or array. |
| skip | Remove items from the front of a collection, and return all the other items. |
| take | Return items from the front of a collection. |
| union | Return a collection that has all the items from the specified collections. |
Logical functions
These functions are useful inside conditions, they can be used to evaluate any type of logic.
| Logical comparison function | Task |
|---|---|
| and | Check whether all expressions are true. |
| equals | Check whether both values are equivalent. |
| greater | Check whether the first value is greater than the second value. |
| greaterOrEquals | Check whether the first value is greater than or equal to the second value. |
| if | Check whether an expression is true or false. Based on the result, return a specified value. |
| less | Check whether the first value is less than the second value. |
| lessOrEquals | Check whether the first value is less than or equal to the second value. |
| not | Check whether an expression is false. |
| or | Check whether at least one expression is true. |
Conversion functions
These functions are used to convert between each of the native types in the language:
- string
- integer
- float
- boolean
- arrays
- dictionaries
| Conversion function | Task |
|---|---|
| array | Return an array from a single specified input. For multiple inputs, see createArray. |
| base64 | Return the base64-encoded version for a string. |
| base64ToBinary | Return the binary version for a base64-encoded string. |
| base64ToString | Return the string version for a base64-encoded string. |
| binary | Return the binary version for an input value. |
| bool | Return the Boolean version for an input value. |
| coalesce | Return the first non-null value from one or more parameters. |
| createArray | Return an array from multiple inputs. |
| dataUri | Return the data URI for an input value. |
| dataUriToBinary | Return the binary version for a data URI. |
| dataUriToString | Return the string version for a data URI. |
| decodeBase64 | Return the string version for a base64-encoded string. |
| decodeDataUri | Return the binary version for a data URI. |
| decodeUriComponent | Return a string that replaces escape characters with decoded versions. |
| encodeUriComponent | Return a string that replaces URL-unsafe characters with escape characters. |
| float | Return a floating point number for an input value. |
| int | Return the integer version for a string. |
| json | Return the JavaScript Object Notation (JSON) type value or object for a string or XML. |
| string | Return the string version for an input value. |
| uriComponent | Return the URI-encoded version for an input value by replacing URL-unsafe characters with escape characters. |
| uriComponentToBinary | Return the binary version for a URI-encoded string. |
| uriComponentToString | Return the string version for a URI-encoded string. |
| xml | Return the XML version for a string. |
| xpath | Check XML for nodes or values that match an XPath (XML Path Language) expression, and return the matching nodes or values. |
Math functions
These functions can be used for either types of numbers: integers and floats.
| Math function | Task |
|---|---|
| add | Return the result from adding two numbers. |
| div | Return the result from dividing two numbers. |
| max | Return the highest value from a set of numbers or an array. |
| min | Return the lowest value from a set of numbers or an array. |
| mod | Return the remainder from dividing two numbers. |
| mul | Return the product from multiplying two numbers. |
| rand | Return a random integer from a specified range. |
| range | Return an integer array that starts from a specified integer. |
| sub | Return the result from subtracting the second number from the first number. |
Date functions
| Date or time function | Task |
|---|---|
| addDays | Add a number of days to a timestamp. |
| addHours | Add a number of hours to a timestamp. |
| addMinutes | Add a number of minutes to a timestamp. |
| addSeconds | Add a number of seconds to a timestamp. |
| addToTime | Add a number of time units to a timestamp. See also getFutureTime. |
| convertFromUtc | Convert a timestamp from Universal Time Coordinated (UTC) to the target time zone. |
| convertTimeZone | Convert a timestamp from the source time zone to the target time zone. |
| convertToUtc | Convert a timestamp from the source time zone to Universal Time Coordinated (UTC). |
| dayOfMonth | Return the day of the month component from a timestamp. |
| dayOfWeek | Return the day of the week component from a timestamp. |
| dayOfYear | Return the day of the year component from a timestamp. |
| formatDateTime | Return the timestamp as a string in optional format. |
| getFutureTime | Return the current timestamp plus the specified time units. See also addToTime. |
| getPastTime | Return the current timestamp minus the specified time units. See also subtractFromTime. |
| startOfDay | Return the start of the day for a timestamp. |
| startOfHour | Return the start of the hour for a timestamp. |
| startOfMonth | Return the start of the month for a timestamp. |
| subtractFromTime | Subtract a number of time units from a timestamp. See also getPastTime. |
| ticks | Return the ticks property value for a specified timestamp. |
| utcNow | Return the current timestamp as a string. |