Configure SQL server in a copy activity
This article outlines how to use the copy activity in data pipeline to copy data from and to SQL server.
Supported configuration
For the configuration of each tab under copy activity, go to the following sections respectively.
General
Refer to the General settings guidance to configure the General settings tab.
Source
The following properties are supported for SQL server under the Source tab of a copy activity.
The following properties are required:
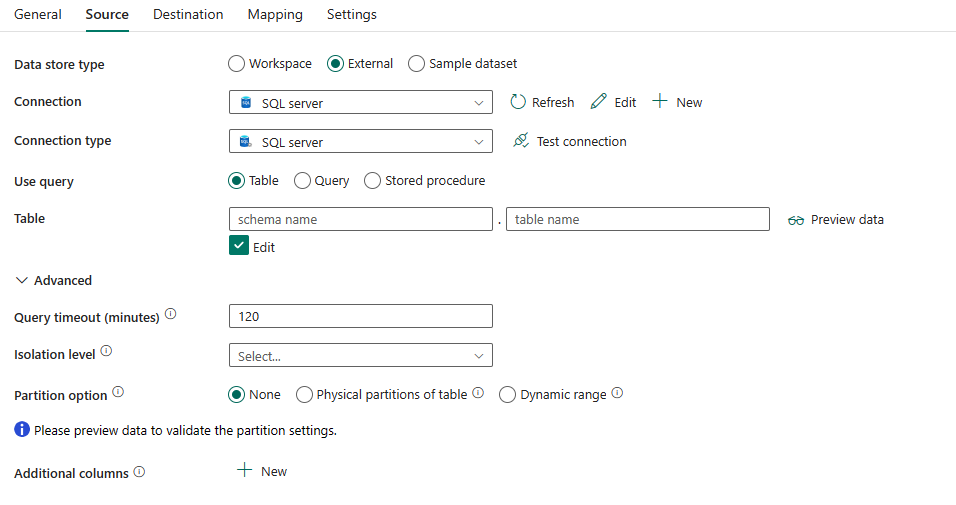
Data store type: Select External.
Connection: Select a SQL server connection from the connection list. If the connection doesn't exist, then create a new SQL server connection by selecting New.
Connection type: Select SQL server.
Use query: Specify the way to read data. You can choose Table, Query, or Stored procedure. The following list describes the configuration of each setting:
Table: Read data from the table specified. Select your source table from the drop-down list or select Edit to enter it manually.
Query: Specify the custom SQL query to read data. An example is
select * from MyTable. Or select the pencil icon to edit in code editor.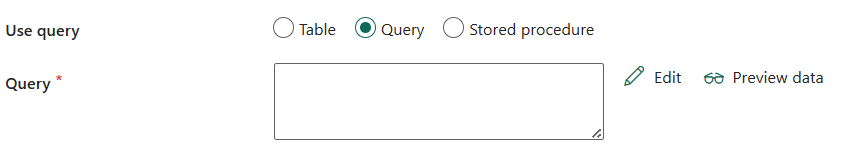
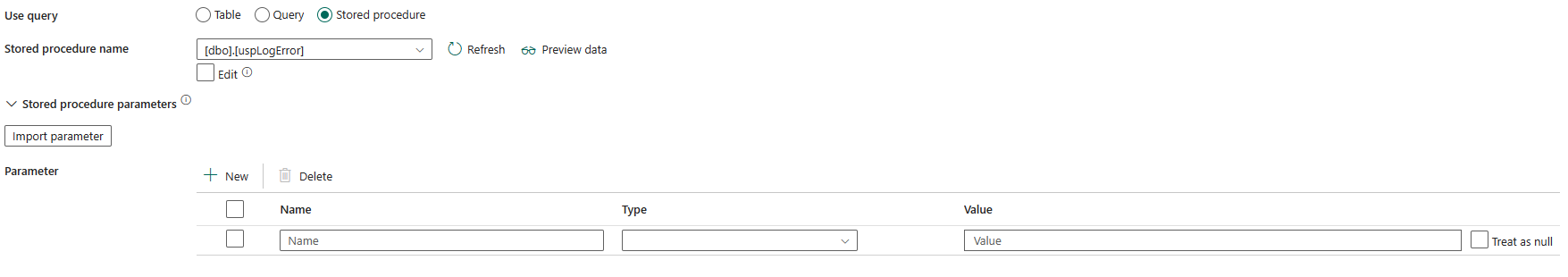
Stored procedure: Use the stored procedure that reads data from the source table. The last SQL statement must be a SELECT statement in the stored procedure.
Stored procedure name: Select the stored procedure or specify the stored procedure name manually when selecting the Edit to read data from the source table.
Stored procedure parameters: Specify values for stored procedure parameters. Allowed values are name or value pairs. The names and casing of parameters must match the names and casing of the stored procedure parameters. You can select Import parameters to get your stored procedure parameters.
Under Advanced, you can specify the following fields:
Query timeout (minutes): Specify the timeout for query command execution, default is 120 minutes. If a parameter is set for this property, allowed values are timespan, such as "02:00:00" (120 minutes).
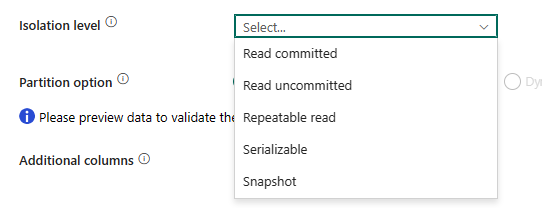
Isolation level: Specifies the transaction locking behavior for the SQL source. The allowed values are: None, Read committed, Read uncommitted, Repeatable read, Serializable, or Snapshot. If not specified, the database's default isolation level is used. Refer to IsolationLevel Enum for more details.
Partition option: Specify the data partitioning options used to load data from SQL server. Allowed values are: None (default), Physical partitions of table, and Dynamic range. When a partition option is enabled (that is, not None), the degree of parallelism to concurrently load data from an SQL server is controlled by Degree of copy parallelism in copy activity settings tab.
None: Choose this setting to not use a partition.
Physical partitions of table: When using a physical partition, the partition column and mechanism are automatically determined based on your physical table definition.
Dynamic range: When using query with parallel enabled, the range partition parameter(
?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition) is needed. Sample query:SELECT * FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition.Partition column name: Specify the name of the source column in integer or date/datetime type (
int,smallint,bigint,date,smalldatetime,datetime,datetime2, ordatetimeoffset) that's used by range partitioning for parallel copy. If not specified, the index or the primary key of the table is auto-detected and used as the partition column.If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook
?DfDynamicRangePartitionConditionin the WHERE clause. For an example, see the Parallel copy from SQL database section.Partition upper bound: Specify the maximum value of the partition column for partition range splitting. This value is used to decide the partition stride, not for filtering the rows in table. All rows in the table or query result will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detect the value. For an example, see the Parallel copy from SQL database section.
Partition lower bound: Specify the minimum value of the partition column for partition range splitting. This value is used to decide the partition stride, not for filtering the rows in table. All rows in the table or query result will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detect the value. For an example, see the Parallel copy from SQL database section.
Additional columns: Add additional data columns to store source files' relative path or static value. Expression is supported for the latter.
Note the following points:
- If Query is specified for source, the copy activity runs this query against the SQL Server source to get the data. You also can specify a stored procedure by specifying Stored procedure name and Stored procedure parameters if the stored procedure takes parameters.
- When using stored procedure in source to retrieve data, note if your stored procedure is designed as returning different schema when different parameter value is passed in, you might encounter failure or see unexpected result when importing schema from UI or when copying data to SQL database with auto table creation.
Destination
The following properties are supported for SQL server under the Destination tab of a copy activity.
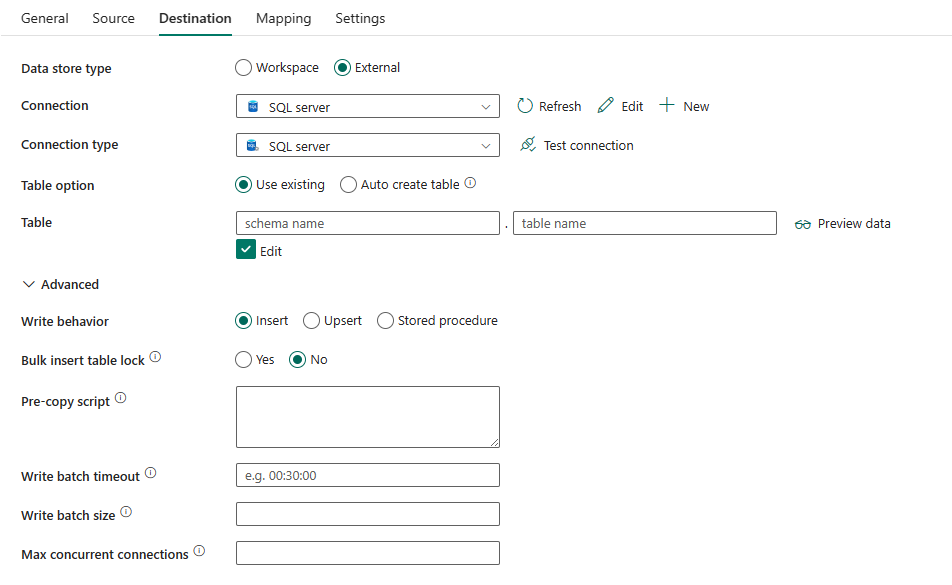
The following properties are required:
Data store type: Select External.
Connection: Select an SQL server connection from the connection list. If the connection doesn't exist, then create a new SQL server connection by selecting New.
Connection type: Select SQL server.
Table option: You can choose Use existing to use the table specified. Or choose Auto create table to automatically create a destination table if the table doesn't exist in the source schema, and note that this selection is not supported when stored procedure is used as the write behavior.
If you select Use existing:
- Table: Select the table in your destination database from the drop-down list. Or check Edit to enter your table name manually.
If you select: Auto create table:
- Table: Specify the name for your auto-created destination table.
Under Advanced, you can specify the following fields:
Write behavior: Defines the write behavior when the source is files from a file-based data store. You can choose Insert, Upsert or Stored procedure.
Insert: Choose this option use insert write behavior to load data into SQL server.
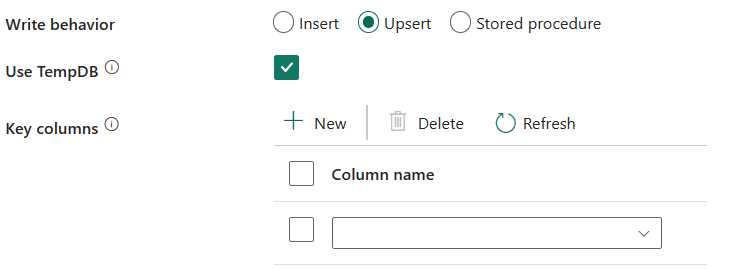
Upsert: Choose this option use upsert write behavior to load data into SQL server.
Use TempDB: Specify whether to use a global temporary table or physical table as the interim table for upsert. By default, the service uses global temporary table as the interim table and this property is selected.
Select user DB schema: When the Use TempDB isn't selected, specify the interim schema for creating an interim table if a physical table is used.
Note
You must have the permission for creating and deleting tables. By default, an interim table will share the same schema as a destination table.
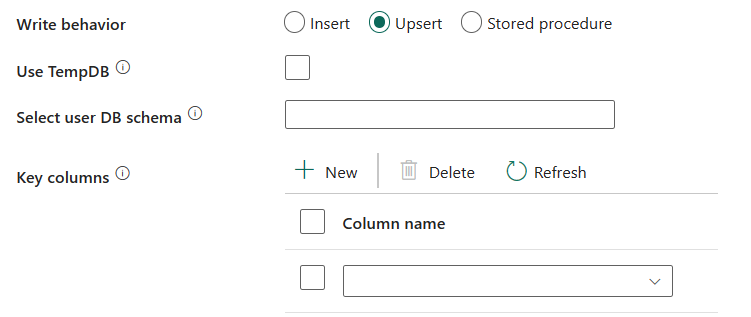
Key columns: Specify the column names for unique row identification. Either a single key or a series of keys can be used. If not specified, the primary key is used.
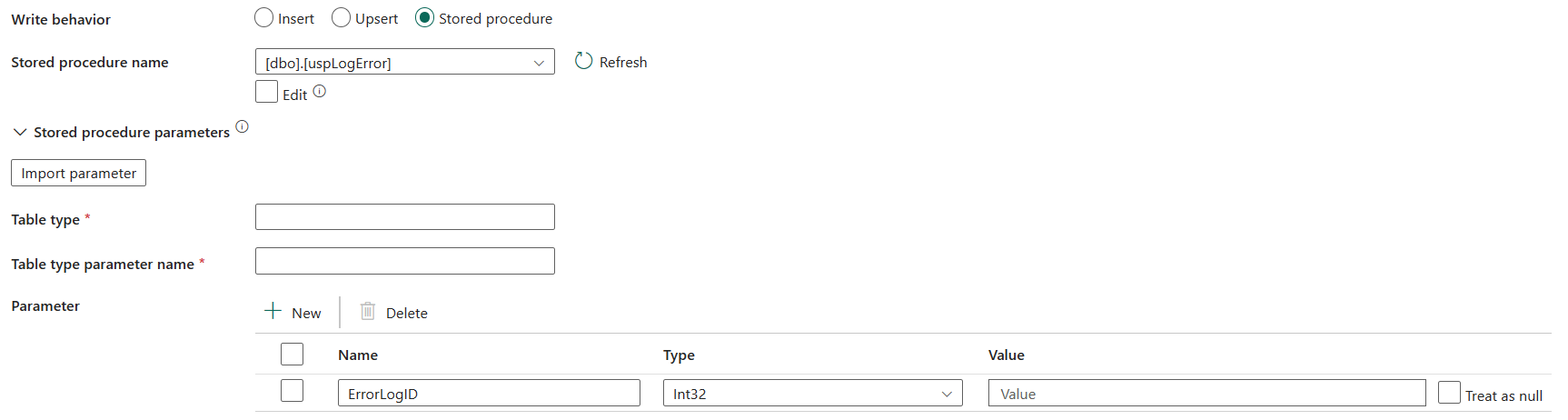
Stored procedure: Use the stored procedure that defines how to apply source data into a target table. This stored procedure is invoked per batch. For operations that run only once and have nothing to do with source data, for example, delete or truncate, use Pre-copy script property.
Stored procedure name: Select the stored procedure or specify the stored procedure name manually when checking the Edit to read data from the source table.
Stored procedure parameters:
- Table type: Specify the table type name to be used in the stored procedure. The copy activity makes the data being moved available in a temporary table with this table type. Stored procedure code can then merge the data that's being copied with existing data.
- Table type parameter name: Specify the parameter name of the table type specified in the stored procedure.
- Parameters: Specify values for stored procedure parameters. Allowed values are name or value pairs. The names and casing of parameters must match the names and casing of the stored procedure parameters. You can select Import parameters to get your stored procedure parameters.
Bulk insert table lock: Choose Yes or No (default). Use this setting to improve copy performance during a bulk insert operation on a table with no index from multiple clients. You can specify this property when you select Insert or Upsert as your write behavior. For more information, go to BULK INSERT (Transact-SQL)
Pre-copy script: Specify a script for copy activity to execute before writing data into a destination table in each run. You can use this property to clean up the pre-loaded data.
Write batch timeout: Specify the wait time for the batch insert operation to finish before it times out. The allowed value is timespan. If no value is specified, the timeout defaults to "02:00:00".
Write batch size: Specify the number of rows to insert into the SQL table per batch. The allowed value is integer (number of rows). By default, the service dynamically determines the appropriate batch size based on the row size.
Max concurrent connections: The upper limit of concurrent connections established to the data store during the activity run. Specify a value only when you want to limit concurrent connections.
Mapping
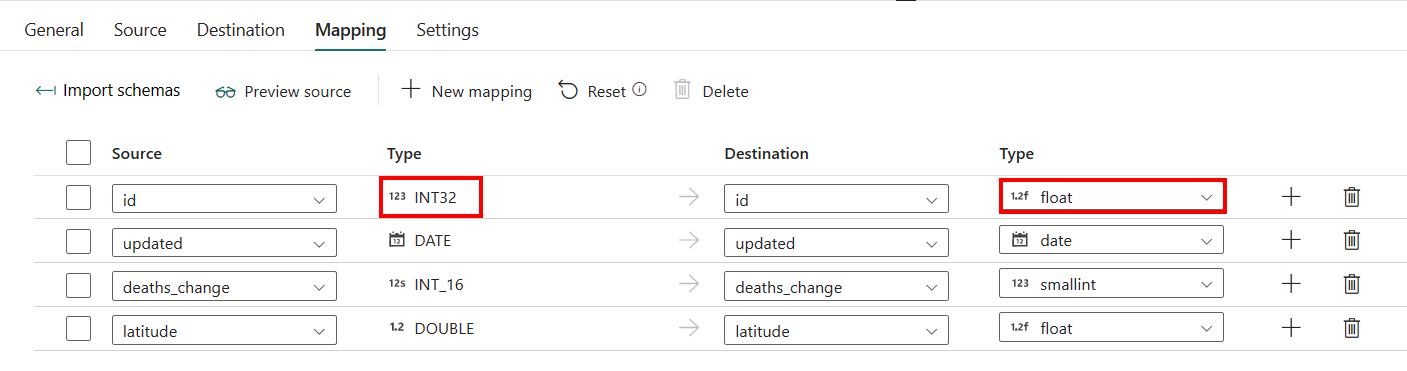
For the Mapping tab configuration, if you don't apply SQL server with auto create table as your destination, go to Mapping.
If you apply SQL Server with auto create table as your destination, except the configuration in Mapping, you can edit the type for your destination columns. After selecting Import schemas, you can specify the column type in your destination.
For example, the type for ID column in source is int, and you can change it to float type when mapping to the destination column.
Settings
For Settings tab configuration, go to Configure your other settings under settings tab.
Parallel copy from SQL database
The SQL Server connector in copy activity provides built-in data partitioning to copy data in parallel. You can find data partitioning options on the Source tab of the copy activity.
When you enable partitioned copy, copy activity runs parallel queries against your SQL Server source to load data by partitions. The parallel degree is controlled by the Degree of copy parallelism in the copy activity settings tab. For example, if you set Degree of copy parallelism to four, the service concurrently generates and runs four queries based on your specified partition option and settings, and each query retrieves a portion of data from your SQL Server.
You are suggested to enable parallel copy with data partitioning especially when you load large amount of data from your SQL Server. The following are suggested configurations for different scenarios. When copying data into file-based data store, it's recommended to write to a folder as multiple files (only specify folder name), in which case the performance is better than writing to a single file.
| Scenario | Suggested settings |
|---|---|
| Full load from large table, with physical partitions. | Partition option: Physical partitions of table. During execution, the service automatically detects the physical partitions, and copies data by partitions. To check if your table has physical partition or not, you can refer to this query. |
| Full load from large table, without physical partitions, while with an integer or datetime column for data partitioning. | Partition options: Dynamic range partition. Partition column (optional): Specify the column used to partition data. If not specified, the primary key column is used. Partition upper bound and partition lower bound (optional): Specify if you want to determine the partition stride. This is not for filtering the rows in table, all rows in the table will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detects the values and it can take long time depending on MIN and MAX values. It is recommended to provide upper bound and lower bound. For example, if your partition column "ID" has values range from 1 to 100, and you set the lower bound as 20 and the upper bound as 80, with parallel copy as 4, the service retrieves data by 4 partitions - IDs in range <=20, [21, 50], [51, 80], and >=81, respectively. |
| Load a large amount of data by using a custom query, without physical partitions, while with an integer or date/datetime column for data partitioning. | Partition options: Dynamic range partition. Query: SELECT * FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition AND <your_additional_where_clause>.Partition column: Specify the column used to partition data. Partition upper bound and partition lower bound (optional): Specify if you want to determine the partition stride. This is not for filtering the rows in table, all rows in the query result will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detect the value. For example, if your partition column "ID" has values range from 1 to 100, and you set the lower bound as 20 and the upper bound as 80, with parallel copy as 4, the service retrieves data by 4 partitions- IDs in range <=20, [21, 50], [51, 80], and >=81, respectively. Here are more sample queries for different scenarios: • Query the whole table: SELECT * FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition• Query from a table with column selection and additional where-clause filters: SELECT <column_list> FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition AND <your_additional_where_clause>• Query with subqueries: SELECT <column_list> FROM (<your_sub_query>) AS T WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition AND <your_additional_where_clause>• Query with partition in subquery: SELECT <column_list> FROM (SELECT <your_sub_query_column_list> FROM <TableName> WHERE ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition) AS T |
Best practices to load data with partition option:
- Choose distinctive column as partition column (like primary key or unique key) to avoid data skew.
- If the table has built-in partition, use partition option Physical partitions of table to get better performance.
Sample query to check physical partition
SELECT DISTINCT s.name AS SchemaName, t.name AS TableName, pf.name AS PartitionFunctionName, c.name AS ColumnName, iif(pf.name is null, 'no', 'yes') AS HasPartition
FROM sys.tables AS t
LEFT JOIN sys.objects AS o ON t.object_id = o.object_id
LEFT JOIN sys.schemas AS s ON o.schema_id = s.schema_id
LEFT JOIN sys.indexes AS i ON t.object_id = i.object_id
LEFT JOIN sys.index_columns AS ic ON ic.partition_ordinal > 0 AND ic.index_id = i.index_id AND ic.object_id = t.object_id
LEFT JOIN sys.columns AS c ON c.object_id = ic.object_id AND c.column_id = ic.column_id
LEFT JOIN sys.partition_schemes ps ON i.data_space_id = ps.data_space_id
LEFT JOIN sys.partition_functions pf ON pf.function_id = ps.function_id
WHERE s.name='[your schema]' AND t.name = '[your table name]'
If the table has physical partition, you would see "HasPartition" as "yes" like the following.
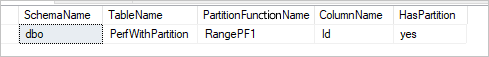
Table summary
See the following table for the summary and more information for the SQL server copy activity.
Source information
| Name | Description | Value | Required | JSON script property |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data store type | Your data store type. | External | Yes | / |
| Connection | Your connection to the source data store. | < your connection > | Yes | connection |
| Connection type | Your connection type. Select SQL server. | SQL server | Yes | / |
| Use query | The custom SQL query to read data. | • Table • Query • Stored procedure |
No | / |
| Table | Your source data table. | < name of your table> | No | schema table |
| Query | The custom SQL query to read data. | < your query > | No | sqlReaderQuery |
| Stored procedure name | This property is the name of the stored procedure that reads data from the source table. The last SQL statement must be a SELECT statement in the stored procedure. | < stored procedure name > | No | sqlReaderStoredProcedureName |
| Stored procedure parameter | These parameters are for the stored procedure. Allowed values are name or value pairs. The names and casing of parameters must match the names and casing of the stored procedure parameters. | < name or value pairs > | No | storedProcedureParameters |
| Query timeout | The timeout for query command execution. | timespan (the default is 120 minutes) |
No | queryTimeout |
| Isolation level | Specifies the transaction locking behavior for the SQL source. | • Read committed • Read uncommitted • Repeatable read • Serializable • Snapshot |
No | isolationLevel: • ReadCommitted • ReadUncommitted • RepeatableRead • Serializable • Snapshot |
| Partition option | The data partitioning options used to load data from SQL server. | • None (default) • Physical partitions of table • Dynamic range |
No | partitionOption: • None (default) • PhysicalPartitionsOfTable • DynamicRange |
| Partition column name | The name of the source column in integer or date/datetime type (int, smallint, bigint, date, smalldatetime, datetime, datetime2, or datetimeoffset) that's used by range partitioning for parallel copy. If not specified, the index or the primary key of the table is auto-detected and used as the partition column. If you use a query to retrieve the source data, hook ?DfDynamicRangePartitionCondition in the WHERE clause. |
< your partition column names > | No | partitionColumnName |
| Partition upper bound | The maximum value of the partition column for partition range splitting. This value is used to decide the partition stride, not for filtering the rows in table. All rows in the table or query result will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detect the value. | < your partition upper bound > | No | partitionUpperBound |
| Partition lower bound | The minimum value of the partition column for partition range splitting. This value is used to decide the partition stride, not for filtering the rows in table. All rows in the table or query result will be partitioned and copied. If not specified, copy activity auto detect the value. | < your partition lower bound > | No | partitionLowerBound |
| Additional columns | Add additional data columns to store source files' relative path or static value. Expression is supported for the latter. | • Name • Value |
No | additionalColumns: • name • value |
Destination information
| Name | Description | Value | Required | JSON script property |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Data store type | Your data store type. | External | Yes | / |
| Connection | Your connection to the destination data store. | < your connection > | Yes | connection |
| Connection type | Your connection type. Select SQL server. | SQL server | Yes | / |
| Table option | Specifies whether to automatically create the destination table if it doesn't exist based on the source schema. | • Use existing • Auto create table |
No | tableOption: • autoCreate |
| Table | Your destination data table. | <name of your table> | Yes | schema table |
| Write behavior | The write behavior for copy activity to load data into SQL server database.. | • Insert • Upsert • Stored procedure |
No | writeBehavior: • insert • upsert sqlWriterStoredProcedureName, sqlWriterTableType, storedProcedureTableTypeParameterName, storedProcedureParameters |
| Use TempDB | Whether to use a global temporary table or physical table as the interim table for upsert. | selected (default) or unselected | No | useTempDB: true (default) or false |
| Select user DB schema | The interim schema for creating interim table if physical table is used. Note: user need to have the permission for creating and deleting table. By default, interim table will share the same schema as destination table. Apply when you don't select Use TempDB. | selected (default) or unselected | No | interimSchemaName |
| Key columns | The column names for unique row identification. Either a single key or a series of keys can be used. If not specified, the primary key is used. | < your key column> | No | keys |
| Stored procedure name | The name of the stored procedure that defines how to apply source data into a target table. This stored procedure is invoked per batch. For operations that run only once and have nothing to do with source data, for example, delete or truncate, use the Pre-copy script property. | < your stored procedure name > | No | sqlWriterStoredProcedureName |
| Table type | The table type name to be used in the stored procedure. The copy activity makes the data being moved available in a temporary table with this table type. Stored procedure code can then merge the data that's being copied with existing data. | < your table type name > | No | sqlWriterTableType |
| Table type parameter name | The parameter name of the table type specified in the stored procedure. | < your parameter name of the table type > | No | storedProcedureTableTypeParameterName |
| Parameters | Parameters for the stored procedure. Allowed values are name and value pairs. Names and casing of parameters must match the names and casing of the stored procedure parameters. | < name and value pairs > | No | storedProcedureParameters |
| Bulk insert table lock | Use this setting to improve copy performance during a bulk insert operation on a table with no index from multiple clients. | Yes or No (default) | No | sqlWriterUseTableLock: true or false (default) |
| Pre-copy script | A script for copy activity to execute before writing data into a destination table in each run. You can use this property to clean up the pre-loaded data. | < pre-copy script > (string) |
No | preCopyScript |
| Write batch timeout | The wait time for the batch insert operation to finish before it times out. | timespan (the default is "02:00:00") |
No | writeBatchTimeout |
| Write batch size | The number of rows to insert into the SQL table per batch. By default, the service dynamically determines the appropriate batch size based on the row size. | < number of rows > (integer) |
No | writeBatchSize |
| Max concurrent connections | The upper limit of concurrent connections established to the data store during the activity run. Specify a value only when you want to limit concurrent connections. | < upper limit of concurrent connections > (integer) |
No | maxConcurrentConnections |